* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download file
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of beta-blockers wikipedia , lookup
Neuropharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of ACE inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Blood doping wikipedia , lookup
Intravenous therapy wikipedia , lookup
Theralizumab wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of angiotensin receptor blockers wikipedia , lookup
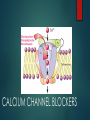
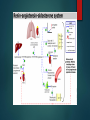
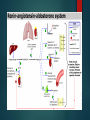
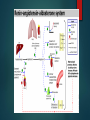
TREATMENT OF HYPERTENSION PRESENTED BY: DIONEL VENIGAS KEN DELA CRUZ JOAN KHO LORENZO NARCISO SEVA MARCIAL AHNA VANESSA IRENE DACUNO Vasodilator medication esp. Hydralazine contains CYCLIC GUANOSINE MONOPHOSPHATE a primary content which causes vasodilation in the arterioles and veinules FACT CCB are the mainstay treatment for angina pectoris, MI, CHF and Hypertension BLUFF Side effects of ACE inhibitors are Hacking dry cough and Edema FACT Angiotensin II blockers acts in increasing sodium and retention of water in the distal segment of nephron BLUFF ARBS prevent Angiotensinogen II from binding to the Angiotensinogen II receptor on blood vessels and other tissue BLUFF The only direct Renin Inhibitor available in the market is Aliskiren (Tektura) FACT PERIPHERAL VASODILATORS ARE AGENTS WHICH ACT ON THE MOST DISTAL PARTS OF THE VASCULAR SYSTEM I.E. THE ARTERIOLES AND VENULES. THEY DILATE THESE DISTAL BLOOD VESSELS AND LOWER THE BLOOD PRESSURE, THEREFORE MAKES IT EASIER FOR THE HEART TO PUMP BLOOD THROUGH THESE PERIPHERAL BLOOD VESSELS (AND THEREFORE THE WHOLE BODY). MECHANISM OF ACTION are an effective medications that reduces elevated systolic and diastolic blood pressure by decreasing peripheral vascular resistance. blood flow increases while renal blood flow and glomerular filtration rate are preserved. Reduction of peripheral arteriolar resistance and the associated fall in blood pressure trigger sympathetic, vagal inhibitory, and renal homeostatic mechanisms that lead to increased cardiac rate and output and salt and water retention. HYDRALAZINE (APRESOLINE) hye-DRAL-a-zeen Severe essential hypertension when the drug cannot be given orally or when there is an urgent need to lower blood pressure is used with or without other medications to treat high blood pressure. MECHANISM OF ACTION Relaxes vascular smooth muscles(arteries, arterioles and veins) causing peripheral vasodilation and decreasing peripheral vascular resistance. These actions decrease blood pressure and increase heart rate, stroke volume and cardiac output Dosage ADULT DOSING Max: 300mg/day Start with 10mg PO QID x 2-4 days, titrate the dose in 25mg QID x remainder of the first week. Titrate the dose upto 50mg QID for the second and subsequent weeks. Patients with low response to hydration use a lower dosafe of hydralazine combination with a thiazide and/or reserpine or a betablocker PEDIATRIC DOSING Initial dos: 0.75mg/kg/day in four divided doses gradually increase over the next 3-5 weeks to max 7.5mg/kg or 200mg daily SIDE EFFECTS AND ADVERSE REACTION fast or pounding heartbeats; nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite; swelling in your face, stomach, hands, or feet; constipation; headache; dizziness; anxiety; muscle or joint pain; runny or stuffy nose; or mild itching or skin rash. numbness, burning, pain, or tingly feeling; feeling like you might pass out; confusion, unusual thoughts or behavior; pale skin, easy bruising; painful or difficult urination; dark-colored urine; urinating less than usual or not at all; or joint pain or swelling with fever, chest pain, weakness or tired feeling. NURSING CARE: Prior taking this medication, ask for allergy and history of certain heart condition Take with or without food Seek PCP for dose adjustment (if s/sx occurs) Get up slowly when rising from sitting of lying position Do not drive, use machinery or do any activity that requires alertness Limit alcohol intake Lifestyle changes: stress reduction, exercise and dietary changes Periodic lab/medical test shall be made; regular monitroring of blood pressure Store at room temperature; keep away from children. MINOXIDIL (LOMITEN) mə-ˈnäk-sə-ˌdil used with other medications to treat high blood pressure (hypertension). Lowering high blood pressure helps prevent strokes, heart attacks, and kidney problems. Minoxidil works by relaxing blood vessels so blood can flow more easily. It is also used for hair regrowth. DOSING Severe or Refractory Hypertension (HTN) Initial: 5mg PO qDay, increase every 3 days PRN Maintenance: 2.5-80 mg/day qDay or q12hr; not to exceed 100 mg/day < 12 years Initial: 0.1-0.2 mg/kg; not to exceed 5 mg/day PO; titrate to response every 3 days 0.25-1 mg/kg/day PO qDay or q12hr; not to exceed 50 mg/day > 12 years Initial: 5mg PO qDay, increase every 3 days PRN Maintenance: 2.5-80 mg/day qDay or q12hr; not to exceed 100 mg/day SIDE EFFECTS/ADVERSE EFFECTS Tachycardia Hirsutism Fluid and sodium retention Hypotension Pericarditis Angina Cardiac tamponade Stevens-Johnson syndrome (rare ) Leukopenia (rare) Thrombocytopenia (rare) NURSING CONSIDERATION If excessive hairs is undesired, immediately seek doctor for replacement. Inform doctor if chest pain occurs or call 911 Slowly rise from lying or sitting position Avoid driving or use of machineries which requires alertness . CALCIUM CHANNEL BLOCKERS MECHANISM OF ACTION NIFEDIPINE (Adalat) 10mg, 20 mg/capsule, 30 mg, 60 mg, 90 mg sustained release tablet NIFEDIPINE (Adalat) USES Vasospastic “ variant” or Prinzmetal’s angina Chronic stable angina without vasospasm Essential hypertension: (extended release tablet) MECHANISM OF ACTION Selectively blocks calcium ion influx across cell membranes of cardiac muscle and vascular smooth muscle without changing serum calcium concentration NIFEDIPINE (Adalat) Adverse effect Hypotension, Dizziness, Facial flushing, Palpitations May precipitate CHF, MI in patient with cardiac disease Overdose: nausea, confusion and slurred speech Nsg care Blood pressure Diabetogenic properties Gingival Hyperplasia Withdrawal symptoms Smoking decreases efficacy Amlodipine 2.5 mg, 5 mg and 10 mg Amlodipine Uses Treatment of mild to moderate hypertension and angina Mechanism of Action Blocks calcium ion reflux across cell membranes cardiac and vascular smooth muscle Decrease peripheral resistance Amlodipine Adverse effect Nsg care Postural hypotension BP (6- 9 hours) therapeutic effect. Palpitations, flushing tachycardia, peripheral or facial edema. Edema not accompanied by weight gain urogenital: sexual dysfunction, nocturia Postural hypotension Report: SOB, palpitation and constipation Support on mobility Diltiazem 30, 60,90, 120 mg tablets: 120 mg, 180 mg 240 mg sustained release tablet 25 and 50 mg vials Diltiazem Uses Angina Essential hypertension Mechanism of Action Inhibit calcium ion influx through slow channels into cell of myocardial and arterial smooth muscle Diltiazem Adverse effect Nsg care Headache, fatigue, dizziness Check BP Arrhythmia Manage constipation Av block Lab Test GI: VANDA S/Sx of CHF Wt gain Supervise Ambulation Rash FF up appointments Renin-AngiotensinAldosterone System (RAAS) IT IS A HORMONE SYSTEM THAT REGULATES BLOOD PRESSURE AND WATER BALANCE. IF THE RAAS IS ABNORMALLY ACTIVE, BLOOD PRESSURE WILL BE TOO HIGH. THERE ARE MANY DRUGS THAT INTERRUPT DIFFERENT STEPS IN THIS SYSTEM TO LOWER BLOOD PRESSURE. THESE DRUGS ARE ONE OF THE MAIN WAYS TO CONTROL HIGH BLOOD PRESSURE, HEART FAILURE, KIDNEY FAILURE, AND HARMFUL EFFECTS OF DIABETES.] ANGIOTENSIN-CONVERTING ENZYME INHIBITOR CAPTOPRIL (CAPOTEN) Used to treat hypertension, congestive heart failure, kidney problems caused by diabetes, and improve survival after a heart attack. MECHANISM OF ACTION Captopril competitively inhibits the conversion of angiotensin I (ATI) to angiotensin II (ATII), thus resulting in reduced ATII levels and aldosterone secretion. It also increases plasma renin activity and bradykinin levels. Reduction of ATII leads to decreased sodium and water retention. By these mechanisms, captopril produces a hypotensive effect and a beneficial effect in congestive heart failure DOSING ACUTE HYPERTENSION 12.5-25 mg PO HYPERTENSION Initial:25 mg PO q8-12 Maintenance: 25-150 mg PO q8-12 Max: 450 mg/day CONGESTIVE HEART FAILURE Initial: 6.25-12.5mg PO q8 AVAILABILITY ADVERSE REACTION Lightheadedness Dry cough, persistent sore throat Tachycardia High potassium blood level Sign of infection Hepatotoxic (jaundice, dark urine, abdominal pain, persistent N/V) SIDE EFFECTS Gynecomastia Hyperkalemia Orthostatic hypotension Hyponatremia Anemia Increase in BUN/Crea Hyponatremia Myalgia Confusion/somnolence Elevated liver transaminases, alkaline phosphatase and serum bilirubin Rhinitis Blurred vision impotence NURSING CARE History taking: allergy to medication, angioedema, renal diseases, CHF, pregnancy and lactation Physical: Skin color, tumors, vital signs, mucous membranes, diagnostic findings Instruct member to take medication one hour before meals Educate client to monitor blood pressure regularly Inform PCP if member experiences dry cough, GI upset and the like Limit activities which requires alertness Enalapril (Vasotec) Indications: Hypertension CHF Asymptomatic left ventricular dysfunction Injection Solution: 1.25mg/ml Tablets: 2.5mg, 5mg, 10mg, 20mg Lisinopril (Zestril) Indications: Hypertension CHF Stable pt within 24hrs of acute MI Adverse Effects Reflex tachycardia Renal Insufficiency Chest pain Renal Failure CHF Proteinuria Cardiac arrhythmia Rash GI irritation Dermatitis Ulcers Photosensitivity Constipation Liver Injury Cough Nursing Considerations Lifestyle changes Monitor BP Patient health Teaching Alert: Breathing problem Lightheadedness Pregnancy Salt substitute Angiotensin II Receptor Antagonist THE ANGIOTENSIN II RECEPTOR BLOCKERS (ARBS) REPRESENT A NEWER CLASS OF ANTIHYPERTENSIVE AGENTS. THEIR MECHANISM OF ACTION DIFFERS FROM THAT OF THE ANGIOTENSIN-CONVERTING ENZYME (ACE) INHIBITORS, WHICH ALSO AFFECT THE RENIN-ANGIOTENSIN SYSTEM. Mechanism of action: Losartan (Cozaar) Losartan is the first Angiotensin II receptor blocker that was developed in 1986. Cozaar is an angiotensin II receptor antagonists. Action: Blocks vasoconstrictor, aldosterone-secreting effects of an angiotensin II, inhibiting binding of angiotensin II to A1 receptors. This keeps blood vessels from narrowing, which lowers blood pressure and improves blood flow. This is a potent vasodilator. Indication: Hypertension, stroke with heart disease Kidney damage with DM2 Appearance : Film-coated tablet form 50 mg – white color with mark 952 in teardrop shape 100 mg – white color with mark 960 in teardrop shape Hypersensitive to Losartan. Pregnante women. Losartan Losartan Losartan Potassium sparing diuretics or potassium supplements Lithium NSAIDS Hyperkalemia Lithium toxicity Decrease effect of Losartan Valsartan (Diovan) Used to treat high blood pressure in adults and children who are at least 6 years old. Used in adults to treat heart failure and to lower the risk of death after a heart attack. Used with or without other medications to treat high blood pressure. Dosages 40 mg are scored yellow ovaloid tablets with beveled edges, imprinted NVR/DO (Side 1/Side 2) 80 mg are pale red almond-shaped tablets with beveled edges, imprinted NVR/DV 160 mg are grey-orange almond-shaped tablets with beveled edges, imprinted NVR/DX 320 mg are dark grey-violet almond-shaped tablets with beveled edges, imprinted NVR/DXL Side effect Insomnia, fatigue, heartburn, abdominal pain, dizziness, headache, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, arthralgia, edema Adverse effect/ toxic reactions Overdosage may manifest as hypotension, tachycardia. Bradycardia occurs less often. Viral infection and URTI (cough, pharyngitis, sinusitis, rhinitis) occur rarely. Contraindication Hypersensitive t o Diovan Severe hepatic impairment, biliary cirrhosis and cholestasis Second and third trimester of pregnancy Caution Concurrent use of potassium-sparing diuretics or potassium supplements Mild to severe hepatic impairment Unstented bilateral/unilateral renal artery stenosis Renal impairment Significant aortic/mitral stenosis Heart failure Therapeutic indications Hypertension - Treatment of hypertension in children and adolescents 6 to 18 years of age. Recent myocardial infarction - Treatment of clinically stable adult patients with symptomatic heart failure or asymptomatic left ventricular systolic dysfunction after a recent (12 hours-10 days) myocardial infarction In clinically stable patients, therapy may be initiated as early as 12 hours after a myocardial infarction. After an initial dose of 20 mg twice daily, valsartan should be titrated to 40 mg, 80 mg, and 160 mg twice daily over the next few weeks. The starting dose is provided by the 40 mg divisible tablet. The target maximum dose is 160 mg twice daily. Heart failure - Treatment of symptomatic heart failure in adult patients when Angiotensin Converting Enzyme (ACE) inhibitors cannot be used, or as add-on therapy to ACE inhibitors when beta blockers cannot be used Heart failure - Treatment of symptomatic heart failure in adult patients when Angiotensin Converting Enzyme (ACE) inhibitors cannot be used, or as add-on therapy to ACE inhibitors when beta blockers cannot be used The recommended starting dose of Diovan is 40 mg twice daily. Up titration to 80 mg and 160 mg twice daily should be done at intervals of at least two weeks to the highest dose, as tolerated by the patient. Consideration should be given to reducing the dose of concomitant diuretics. The maximum daily dose administered in clinical trials is 320 mg in divided doses. Elderly - No dose adjustment is required in elderly patients. Renal impairment - No dose adjustment is required for patients with a creatinine clearance > 10ml/min. Hepatic impairment - Diovan is contraindicated in patients with severe hepatic impairment, biliary cirrhosis and in patients with cholestasis. In patients with mild to moderate hepatic impairment without cholestasis, the dose of valsartan should not exceed 80 mg. Monitor BP and apical pulse at drug trough (prior to a scheduled dose), in addition to regular monitoring (be alert of fluctuations) Monitor BP regularly. Question for possibility of pregnancy. Assess medication history. Check for drug interaction and also diuretics. Question for history of hepatic/renal impairment, renal artery stenosis, history of severe CHF. Maintain hydration. Offer fluids frequently. Assess for evidence of URTI and cough. Monitor daily pattern of bowel activity and consistency. Obtain baseline chemistries and blood counts. Lab tests: Monitor CBC, electrolytes, liver & kidney function with longterm therapy. Patient & Family Education •Instruct to avoid task that requires alertness, motor skills until response to drug is established. (Dizziness is possible) •Notify physician immediately of pregnancy. Pt should avoid pregnancy. •Do not breast feed while taking this drug. •Report any signs of infection (sore throat, fever) and chest pain. •Do not take OTC cold preparations, nasal decongestant. •Do not stop taking medication abruptly. •Limit salt intake. •Report swelling of extremities, chest pain and palpitations. Antihypertensive Combinations Valsartan/ Hydrochlorothiazide (Diovan Hct) A combination tablet of valsartan (Diovan), an angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB) and hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ), a diuretic. For treatment of hypertension Lowering blood pressure reduces the risk of fatal and nonfatal cardiovascular events, primarily strokes and myocardial infarctions. Mechanism of Action Blocks the binding of angiotensin II to receptor sites in vascular smooth muscle and the adrenal gland, which inhibits the pressor effects of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system Increases sodium and water excretion by inhibiting sodium and chloride reabsorption in distal segment of the nephron Dosages Side Effects stomach pain, diarrhea headache, dizziness Photosensitivity Orthostatic hypotension Dry cough Warnings and Precautions Impaired Renal Function Fetal Toxicity Hypersensitivity Reaction Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Acute Myopia and Secondary Angle-Closure Glaucoma Metabolic Disturbances Adverse Effects severe hypotension hyponatremia (headache, slurred speech, hallucinations, vomiting, severe weakness, muscle cramps, loss of coordination, feeling unsteady, seizure, fainting, shallow breathing) low or high potassium (confusion, slow or uneven heart rate, weak pulse, tingly feeling, extreme thirst, increased urination, leg discomfort, muscle weakness or limp feeling) Adverse Effects blurred vision, tunnel vision, eye pain, or seeing halos around lights joint pain or swelling with fever, headaches, chest pain, shortness of breath skin sores, butterfly-shaped skin rash on your cheeks and nose (worsens in sunlight) numbness, cold feeling, or pale appearance of your fingers or toes Nursing Considerations Avoid sudden posture changes to avoid dizziness upon standing quickly Encourage member to use a sunblock to prevent photosensitivity reactions Watch out for hypotension. Take drug in the morning Nursing Considerations Instruct member to take drug with food to minimize GI upset Monitor blood pressure and obtain weight daily In women, avoid pregnancy and breastfeeding while taking the drug Maintain hydration by increasing oral fluid intake and adequate sodium intake of 2gms/day DIRECT RENIN INHIBITOR Aliskiren (Tekturna) 150 mg light pink biconvex round tablet, imprinted NVR/IL 300 mg light red biconvex ovaloid round tablet, imprinted NVR/IU Mechanism of Action Direct renin inhibitor. Decreases plasma renin activity (PRA), inhibiting the conversion of angiotensinogen to angiotensinogen I, blocking the effects of increased renin levels. Therapeutic effect: Reduces B/P. Contraindications Tekturna is contraindicated in patients with diabetes who are receiving ARBs or ACEIs because of the increased risk of renal impairment, hyperkalemia, and hypotension. Warning and Precautions Fetal toxicity Anaphylactic Reactions and Head and Neck Angioedema Hypotension Impaired Renal Function Hyperkalemia Cyclosporine or Itraconazole Adverse Reactions Injury or death to unborn baby Severe allergic reactions and angioedema Renal impairment or failure Hypotension Side effects Diarrhea Cough Dizziness Headache Flu-like symptoms Back pain Tiredness Hyperkalemia Nursing Considerations Pregnancy Anaphylactic Reactions and Angioedema Symptomatic hypotension Potassium Supplements Relationship to meals Dosage and Administration The usual recommended starting dose of Tekturna is 150 mg once daily. In patients whose blood pressure is not adequately controlled, the daily dose may be increased to 300 mg. The antihypertensive effect of a given dose is substantially attained (85-90%) by 2 weeks.