* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Earth`s Interior
Survey
Document related concepts
Geomorphology wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotellurics wikipedia , lookup
Plate tectonics wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geodesy wikipedia , lookup
Future of Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
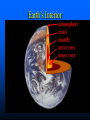
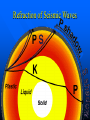
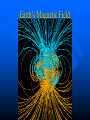
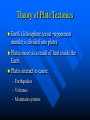
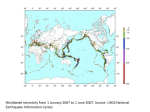
Earth: the home planet Earth’s Interior Earth’s Layered Structure Earth’s interior consists of layers Layers are arranged according to density Most dense material is at the center – core Density decreases outward Density layering includes the hydrosphere (oceans) and atmosphere Thickness and Composition of Earth’s Layers Earth’s Temperature Structure How Do We Know? Refraction of Seismic Waves Seismic Waves Refraction – change in speed and direction when passing through a material of different density. Other Evidence Refraction of seismic waves Density of the entire planet Gravity (mass) of entire planet Composition of meteorites Existence of magnetic field Earth’s Magnetic Dynamo Earth’s Magnetic Field Was it always this way? Accretion of the protoplanet Homogeneous structure Density differentiation Density Differentiation Gravitational effects vary with density of material Materials must be free to move Requires plastic flow or fluid flow Requires heat Earth: The Unfinished Planet Earth continues to lose heat Volcanism brings material to Earth’s surface Other processes (subduction) return more dense material to interior Conclusion: Earth is still under construction! Implications of an Unfinished Planet Volcanism Earthquakes Atmospheric and climate change Effects on life Theory of Plate Tectonics Earth’s lithosphere (crust +uppermost mantle) is divided into plates Plates move as a result of heat inside the Earth Plates interact to cause: – Earthquakes – Volcanos – Mountain systems What makes the plates move? Uneven distribution of heat in the upper mantle (Asthenosphere) causes heat to rise in some places Differences in density cause colder, more dense Lithosphere to sink back into the asthenosphere This Convection drives the motion of the plates Interactions between Plates cause: Earthquakes Volcanos Formation of mountains Formation of ocean basins Increase amount of continental lithosphere