* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 5 - Perry Local Schools
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
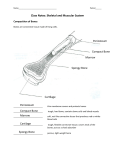
Unit 5 The Skeletal System Bone Function Support Protection Assist in movements Mineral homeostasis Blood cell production Hemopoiesis - red bone marrow Triglyceride storage Types of Bones Long bones: longer than wide Short bones: almost cube shaped Most wrist and ankle bones Flat bones: thin and extensive surface Such as thigh, leg, arm, forearm, fingers and toes Such as cranial bones sternum, ribs and scapulas Irregular bones: Such as vertebrae and some facial bones • Sesamoid Bones • develop within a tendon Macroscopic Structure Parts of a long bone Diaphysis: shaft of long bone; made up mostly of compact bone Epiphysis: broad end of long bone; mostly spongy bone Metaphysis: growth area between diaphysis and epiphysis Epiphyseal line = remnant of epiphyseal disk/plate Cartilage at the junction of the diaphysis and epiphyses (growth plate) Parts of a Long Bone • • • • • Periosteum: fibrous covering over most of bone Endosteum: membrane lining medullary cavity Contains layer of osteoblasts (bone-forming cells) & osteoclasts (bone-destroying cells) Medullary cavity: (yellow marrow) with fat and blood cells Nutrient Foramen = perforating canal allowing blood vessels to enter and leave bone Articular cartilage = pad of hyaline cartilage on the epiphyses where long bones articulate or join Microscopic Structure of Bone Matrix 25% water, 25% collagen fibers, 50% mineral salts Osteogenic cells in periosteum Develop into Osteoblasts (mature bone cell) Secrete collagen fibers Build matrix and become trapped in lacunae Osteoclasts are formed from monocytes Digest bone matrix for normal bone turnover Compact Bone Structure Arranged in osteons (haversian systems) Central canal through center of osteon Cylinders running parallel to long axis of bone Contains blood vessels, nerves, lymphatics Concentric lamellae: layers of matrix Lacunae: Contain osteocytes (bone cells) Compact Bone Structure Canaliculi (“little canals”) Contain extensions of osteocytes Permit flow of ECF between central canal and lacunae Compact bone is covered by periosteum Perforating (Volkmann’s) canals Carry blood and lymphatic vessels and nerves from periosteum They supply central (Haversian) canals and also bone marrow Spongy Bone Structure Not arranged in osteons Irregular latticework of trabeculae These contain lacunae with osteocytes and canaliculi Spaces between trabeculae may contain red bone marrow Spongy bone is lighter than compact bone, so reduces weight of skeleton Bone Formation Known as ossification Timeline Initial bone development in embryo and fetus initial “skeleton” replaced by bone tissue beginning at 6 weeks of embryonic life Growth of bone into adulthood Remodeling: replacement of old bone Repair if fractures occur Bone Formation Two different methods of ossification Intramembranous: bone forms in sheets 1. Few bones: flat bones of the skull, lower jawbone (mandible), and part of clavicle Endochondrial: forms hyaline cartilage then develops into bone 2. All other bones form by this process Intramembranous Ossification Four steps 1. Development of ossification center Mesenchyme cells osteogenic osteoblasts Osteoblasts secrete organic matrix 2.Calcification: cells become osteocytes In lacunae they extend cytoplasmic processes to each other Deposit calcium & other mineral salts 3.Formation of trabeculae (spongy bone) Blood vessels grow in and red marrow is formed 4.Periosteum covering the bone forms from mesenchyme Endochondrial Ossification Six Steps 1. Formation of cartilage model of the “bone” As mesenchyme cells develop into chondroblasts 2. Growth of cartilage model Cartilage “bone” grows as chondroblasts secrete cartilage matrix Chondrocytes increase in size, matrix around them calcifies Chondrocytes die as they are cut off from nutrients, leaving small spaces (lacunae) Endochondrial Ossification 3. Primary ossification center Perichondrium sends nutrient artery inwards into disintegrating cartilage Osteogenic cells in perichondrium become osteoblasts deposit bony matrix over remnants of calcified cartilage spongy bone forms in center of the model As perichondrium starts to form bone, the membrane is called periosteum Endochondrial Ossification 4. Medullary (marrow) cavity Spongy bone in center of the model grows towards ends of model Octeoclasts break down some of new spongy bone forming a cavity (marrow) through most of diaphysis Most of the wall of the diaphysis is replaced by a collar of compact bone Endochondrial Ossification 5. Secondary ossification center Similar to step 3 of Intramembranous Ossification; except that nutrient arteries enter ends (epiphyses) of bones and osteoblasts deposit bony matrix spongy bone forms in epiphyses from center outwards Occurs about time of birth 6. Articular cartilage and epiphyseal cartilage Ends of epiphyses becomes articular cartilage Epiphyseal (growth) plate of cartilage remains between epiphysis and diaphysis until bone growth ceases Growth in Length Chondrocytes divide and grow more cartilage on epiphyseal side of the epiphyseal plate Chondrocytes on the diaphyseal side die and are replaced by bone Bone grows from diaphyseal side towards epiphyseal side Growth in length stops between 18-25 years Cartilage in epiphyseal plate is completely replaced by bone (epiphyseal line) Growth in Thickness As bones grow in length, they must also grow in thickness (width) Perichondrial osteoblasts lay down additional lamellae of compact bone Simultaneously, osteoclasts in the endosteum destroy interior bone to increase width of the marrow Remodeling and Repair Remodeling in response to use Resorption by osteoclasts and Deposition by osteoblasts Repair after a fracture Dead tissue removed Chondroblasts fibrocartilage spongy bone deposited by osteoblasts remodeled to compact bone Types of Fractures Partial: incomplete break (crack) Complete: bone broken into two or more pieces Closed (simple): not through skin Open (compound): broken ends break skin Green stick • Fissured • Comminuted • Transverse • Oblique • Spiral • Types of Fractures 7-62 Copyright 2010, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Factors Affecting Growth Adequate minerals (Ca, P, Mg) Vitamins A, C, D Hormones Before puberty: hGH + insulin-like growth factors Thyroid hormone and insulin also required Sex hormones contribute to adolescent growth spurt Weight-bearing activity • Deficiency of Vitamin A – retards bone development • Deficiency of Vitamin C – results in fragile bones, scurvy • Deficiency of Vitamin D – rickets (children), osteomalacia (adults) • Insufficient Growth Hormone – dwarfism • Excessive Growth Hormone – gigantism, acromegaly • Insufficient Thyroid Hormone – delays bone growth • Physical Stress – stimulates bone growth 7-11 Calcium Homeostasis Blood levels of Ca2+ controlled Negative feedback loops Parathyroid hormone (PTH) increases osteoclast activity + decreases loss of Ca2+ in urine Calcitonin decreases osteoclast activity Negative Feedback Exercise & Bone Tissue Bone strengthened in response to use Bone reabsorbed during disuse; examples: During prolonged bed rest Fracture with cast/immobilizer Astronauts without gravity Divisions of Skeletal System Two divisions: axial and appendicular Axial: bones around body axis Examples: skull bones, hyoid, ribs, sternum, vertebrae Appendicular: bones of upper and lower limbs plus shoulder and hip bones that connect them Examples: clavicle, humerus, radius and ulna, femur Skull Eight Cranial bones Frontal, 2 parietal, 2 temporal, occipital, sphenoid, and ethmoid Fourteen Facial bones 2 nasal, 2 maxilla, 2 zygomatic, 2 lacrimal 2 palatine, 2 inferior nasal conchae, 1 mandible, 1 vomer Skull Frontal (1) • Forehead • Frontal sinuses • Supraorbital foramen • Coronal suture 7-17 Skull Parietal (2) • Side walls of cranium • Roof of cranium • Sagittal suture 7-18 Skull Temporal (2) • Squamosal suture • External acoustic meatus • Mandibular fossa • Mastoid process • Styloid process • Zygomatic process 7-19 Skull Occipital (1) • Back of skull • Foramen magnum • Occipital condyles • Lambdoidal suture 7-20 Skull Sphenoid (1) • Sella turcica • Sphenoidal sinuses 7-21 Skull Ethmoid (1) • Cribiform plates • Perpendicular plate • Superior and middle nasal conchae • Ethmoidal sinuses • Crista gallis 7-22 Facial Skeleton Maxillary (2) • Upper jaw • Alveolar processes • Maxillary sinuses • Palatine process 7-23 Facial Skeleton Palatine (2) • Posterior roof of mouth 7-24 Copyright 2010, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Facial Skeleton Zygomatic (2) • Prominences of cheeks • Temporal process 7-25 Facial Skeleton Lacrimal (2) • Medial walls of orbits Nasal (2) • Bridge of nose 7-26 Facial Skeleton Vomer (1) • Inferior portion of nasal septum 7-27 Facial Skeleton Inferior Nasal Conchae (2) • Extend from lateral walls of nasal cavity 7-28 Facial Skeleton Mandible (1) • Lower jaw • Body • Ramus • Mandibular condyle • Coronoid process • Alveolar process • Mandibular foramen • Mental foramen 7-29 Unique Features of Skull Sutures: immovable joint between skull bones Paranasal sinuses: cavities Coronal, sagittal, lambdoidal, squamous Located in bones near nasal cavity Fontanels: soft spot in fetal skull Allow deformation at birth Calcify to form sutures hyoid Vertebrae Functions Encloses spinal cord Supports head Point of attachment for muscles of back, ribs and pelvic girdle Regions (from superior to inferior) 7 cervical 12 thoracic 5 lumbar 1 sacrum and 1 coccyx Normal Curves in Column Four normal curves Cervical and lumbar curves are convex (bulge anteriorly) Thoracic and sacral curves are concave (bulge posteriorly) Curves increase strength, help in balance and absorb shocks Structure of Vertebra Body: disc-shaped anterior portion Vertebral arch: posteriorly back from body With the body, creates a hole called vertebral foramen Seven processes from this arch Transverse process extending laterally on each side Spinous process extending dorsally Two each of superior and inferior articular processes that form joints with vertebrae Vertebral Column • Rib facets • Intervertebral discs • Intervertebral foramina 7-32 Cervical Area Cervical (C1-C7 from superior to inferior) C1: atlas Spinous process often bifid with transverse foramina on transverse processes Articulates with head, specialized to support head Lacks body and spinous process C2: axis Has body and spinous process Dens (“tooth”) that creates a pivot for head rotation Other Vertebrae Thoracic (T1-T12 ) Lumbar (L1-L5) Largest and strongest; spinous processes short and thick Sacrum (S1-S5 fused into one unit) Larger than cervical Have facets for articulations with ribs Foundation for pelvic girdle Contain sacral foramina for nerves and blood vessels Coccyx: 4 coccygeal vertebrae fused into 1 Thorax Thoracic cage: sternum, costal cartilages, ribs and bodies of T1-T12 Sternum: 3 portions fused by about age 25 Manubrium, body, xiphoid process True ribs #1-7: articulate with sternum by costal cartilages False ribs #8-12: articulate with coastal cartilage of true ribs 2 - Floating Ribs (no attachment) Rib Structure • Shaft • Head – articulates with vertebrae • Tubercle • Costal cartilage 7-40 Pectoral Girdle Function: attach bones of upper limbs to axial skeleton Clavicles and scapulas: bilateral Clavicles • Articulate with manubrium • Articulate with scapulae (acromion process) 7-43 Scapula • Spine • Supraspinous fossa • Infraspinous fossa • Acromion process • Coracoid process • Glenoid cavity 7-44 Copyright 2010, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Upper Limb Humerus: arm bone Articulates with scapula (glenoid cavity) Articulates with radius and ulna at elbow Ulna: medial bone Radius: lateral bone (thumb side) Humerus • Head • Greater tubercle • Lesser tubercle • Anatomical neck • Surgical neck • Deltoid tuberosity • Capitulum • Trochlea • Coronoid fossa • Olecranon fossa • Lateral epicondyle • Medial epicondyle 7-46 Copyright 2010, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Radius • Lateral forearm bone • Head • Radial tuberosity • Styloid process 7-47 Ulna • Medial forearm bone • Trochlear notch • Olecranon process • Coronoid process • Styloid process 7-48 Wrist and Hand Carpals (wrist): 8 bones Metacarpals: 5 bones of palm of hand Number 1-5 starting with thumb Phalanges: 14 bones of fingers Each finger except thumb has proximal, middle and distal phalanges; thumb lacks middle phalanx Wrist and Hand Carpals • Trapezium • Trapezoid • Capitate • Scaphoid • Pisiform • Triquetrum • Hamate • Lunate 7-49 Pelvic (Hip) Girdle Pelvic girdle includes two hip (coxal) bones Joined anteriorly at pubic symphysis + sacrum and coccyx False (greater) pelvis: broad region superior to pelvic brim; contains abdominal organs True (lesser) pelvis: small region inferior to pelvic brim; contains urinary bladder + internal reproductive organs Parts of Each Hip (Coxal) Bone 3 separate bones fuse by age 23 to form a hip bone Ilium: largest and most superior Ischium: lower posterior part Pubis: lower anterior part Acetabulum - socket for head of femur Lower Limb Femur: largest bone in the body Patella: kneecap in anterior of knee joint Tibia: shin bone Articulates with hip proximally and with the tibia and patella distally Large medial, weight-bearing bone of leg Fibula: longest, thinnest bone in body Lateral to tibia and smaller Does not articulate with femur Femur • Head • Fovea capitis • Neck • Greater trochanter • Lesser trochanter • Linea aspera • Condyles (medial/lateral) • Epicondyles (medial/lateral) 7-55 Patella • Flat sesamoid bone located in a tendon 7-56 Tibia • Medial to fibula • Condyles • Tibial tuberosity • Anterior crest • Medial malleolus 7-57 Copyright 2010, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Fibula • Lateral to tibia • Head • Lateral malleolus • Does not bear any body weight Insert figure 7.54 7-58 Copyright 2010, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Ankle and Foot Tarsals (ankle) - 7 bones Large talus (ankle bone) and Calcaneus (heel bone) navicular cuboid lateral cuneiform intermediate cuneiform medial cuneiform Ankle and Foot Metatarsals (foot bones) • Numbered 1 to 5 from medial to lateral Phalanges (toe bones) • Big toe has proximal and distal phalanges while others have proximal, middle and distal phalanges. 7-59 Copyright 2010, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Male and Female Differences Males usually have heavier bones Related to muscle size and strength Female pelvis is wider and shallower than male pelvis: allows for birth Aging and Skeletal System Birth through adolescence: more bone formed than lost Young adults: gain and loss about equal As levels of sex steroids decline with age: bone reabsorption > bone formation Bones become brittle and lose calcium Life-Span Changes • Decrease in height at about age 30 • Osteoclasts outnumber osteoblasts • Spongy bone weakens before compact bone • Hip fractures common • Bone loss rapid in menopausal women • After age 70 bone loss between sexes is similar • Vertebral compression fractures common 7-61 Homeostatic Disorders Sickle Cell Disease Osteoporosis Cleft Palate Polydactyly