* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Renewable energy for who?
Restoration ecology wikipedia , lookup
Ecological resilience wikipedia , lookup
Overexploitation wikipedia , lookup
Conservation biology wikipedia , lookup
Ecosystem services wikipedia , lookup
Human impact on the nitrogen cycle wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical ecology wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity wikipedia , lookup
Habitat conservation wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Reconciliation ecology wikipedia , lookup
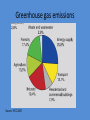
Renewable Energy Rasmus Vincentz Habitats Youth Forum - Vilnius April 2012 Habitats www.habitats.dk Habitats • Habitats provides learning, campaigns and consultancy services that promotes biodiversity sustainable development for private companies, NGOs and public institutions. • We design and plan landscapes and green urban spaces in order to increase their biological, experiential and functional value. • The vision is to create synergy between human development and evolution of life. Renewable energy for who? Renewable energy for industry Renewable energy for transport Renewable energy for housholds Renewable energy for human beings Global greenhouse gas emissions Greenhouse gas emissions Source: IPCC 2007 We are eating OIL Challenges when oil = food Economic: when oil price rises Security: less and harder to get Practically: tackling of climate changes ‘Human energy’ today Emissions Toxic chemicals Water consumption Monocultural destruction of habitats (biodiversity loss) Intensive use of fossil fuels + Unhealthy and unsustainable The way forward? • • • • • • • • Grow with less fossils Manage ressources Protect and establish eco-systems Change of cultures and habits Prepare for hard desicions Re-localisation Establish food Co-ops Seasonel based local food Leading by lust Rene Redzepi – Restaurant NOMA Re-enter the flow of ressources Cycles: Carbon Nutrient Water Energy Genetic WWF Living Planet report 2010 Can you imaging nature thrive where we live? The Economics of Ecosystems & Biodiversity (TEEB) • G8+5 in 2007 “initiate the process of analysing the global economic benefit of biological diversity, the costs of the loss of biodiversity and the failure to take protective measures versus the costs of effective conservation. = TEEB reports http://www.teebweb.org/ Published 2010 Definition Biodiversity “the variability among living organisms from all sources…and the ecological complexes of which they are part; this includes diversity within species, between species and of ecosystems” (Convention on Biological Diversity) Ecosystem services (ES) Supporting Provisioning Regulating Cultural Millennium Ecosystem Assessment 2005 TEEB • Understanding, research and tool for decision making at all levels “The invisibility of biodiversity values has often encouraged inefficient use or even destruction of natural capital that is the foundation of our economies” (TEEB Synthesis p.3) Examples of Ecosystem Services Status of biodiversity and ecosystem services • Over the past few hundred years, it is estimated that humans have increased the extinction rate of species by as much as a 1000-fold over the natural rate. Between 12% and 52% of species within well-studied groups such as birds or mammals are threatened with extinction (IUCN Redlist) • “Overall, efforts to stem biodiversity loss have clearly been inadequate, with a growing mismatch between increasing pressures and slowing responses.” (Butchardt et al: Science 2010)