* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CNS Worksheet - Moore Public Schools
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
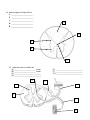
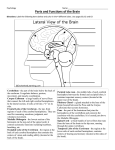
Anatomy & Physiology Central Nervous System Worksheet 1. What are the two parts of the CNS? a) b) 2. What are the four functions of the CNS a) b) c) d) 3. What are three functions of the meninges? a) b) c) 4. Starting with the most superficial, what are the three meninges? a) b) c) 5. Which of the following is NOT a function of the cerebrospinal fluid? a) nourish the CNS tissue b) protect the CNS from blows and trauma c) reduce brain weight by 97% and thus prevent the brain from crushing itself d) aids in the diagnosis of various diseases e) aid in the conduction of impulses in and around the brain 6. An inflammation of the meninges is called ___________________________. 7. The layer of the meninges that clings closely to the brain and is composed of several tiny blood vessels is the __________________________ mater. 8. The spinal cord ends around L- _____. 9. The gray matter of the spinal cord is in the shape of the letter ________. 10. A crossbar of gray matter called the _________________________________ connects the lateral gray masses. 11. The inferior end of the spinal cord terminates in a mass of branching nerves called the __________________________________. 12. The posterior white column of the spinal cord mainly contains tracts of nerve fibers that are a) ascending b) descending c) transverse 13. The posterior or dorsal gray horns contain afferent / efferent tracts of sensory / motor neurons. 1 14. Descending tracts of the white mater of the spinal cord deliver afferent / efferent impulses that connect to receptors / effectors neurons. 15. How many pairs of spinal nerves branch off the spinal cord? 16. The five parts of a reflex arc are the _____________________, _____________________ neuron, _______________________ neuron, ________________________ neuron, & __________________. 17. The part of the reflex that is only located in the spinal cord is the ______________________ neuron. 18. A muscle or gland that responds to a reflex is called the _____________________. 19. Reflexes that people are born with are called _________________________ reflexes. 20. Reflexes that are learned over time (such as catching a ball) are called __________________ reflexes. 21. The three general parts of the brain are a) b) c) 22. The third & fourth ventricles are connected via the _____________________________________. 23. The first & second ventricles are also referred to as the _______________________ ventricles. 24. The ventricles are filled with _____________________ ______________________. 25. The ridges on the surface of the brain are called __________________, while the shallow groves are called ___________________. 26. The four lobes of the cerebrum are a) b) c) d) 27. The ________________________________ fissure separates the left and right hemispheres, while the ______________________________ fissure separates the cerebral hemispheres from the cerebellum. 28. The _______________________ sulcus separates the temporal lobe from the parietal & frontal lobes. 29. The primary motor cortex is located on the _______________________ gyrus of the frontal lobe. 30. What is Broca’s Area? 31. All motor areas are confined to the ____________________ lobe. 32. The primary visual cortex is located on the _______________________ lobe. 2 33. Judgment, reasoning, & problem solving skills are found on the _______________________ lobe. 34. The primary auditory cortex is located on the _____________________ lobe. 35. The senses of touch, temperature, & pain are located on the ______________________ gyrus of the ____________________lobe. 36. The thin layer of gray matter that covers the cerebrum is called the ___________________________. 37. The gyri & sulci function to increase the surface area of the cerebral cortex. Why is this important? 38. The ______________________________________ connect the two hemispheres of the cerebrum. 39. The cerebellum is divided into two hemispheres by the __________________________________. 40. The gray & white matter of the cerebellum form a plant-like shape called the ___________ of _____________ in English or the ___________________ ___________________ in Latin. 41. What is the function of the Cerebellum? 42. What are the four main parts of the Brainstem? a) b) c) d) 43. In what portion of the brain does “crossing over” occur? _______________________________ 44. What two parts of the Brainstem control respiration? a) b) 45. What two parts of the Central Nervous System contain white matter surrounding an H-shaped grey matter? a) b) 46. Which of the following is NOT controlled by the Medulla Oblongata? a) The cardiac center of heart rate. b) The respiratory center of breathing. c) The emetic center for vomiting. d) The vasomotor center of blood pressure. e) The endocrine center of hormonal control. 47. The mesencephalon is AKA the _____________________________. 48. The interbrain is AKA the ____________________________. 49. What sense is not relayed through the Thalamus? __________________________ 50. What are Circadian Rhythms? 3 51. The Hypothalamus serves as a link between what two systems of the body? a) b) 52. The __________________________ NS controls the body under ordinary conditions, while times of stress is controlled by the _____________________________ NS. 53. The hypothalamus is basically located __________ the Thalamus. a) above b) below c) lateral d) inside 54. Death of brain tissue due to a blood clot or hemorrhage is called a ____________________________. 55. What neurotransmitter is lacking in a person with Parkinson’s disease? 56. A severe, 3-4 minute seizure is called a __________________ mal. 57. EEG stands for : _______________________________________________________________ 58. When taking a test (in here), what brain waves are probably most common? _______________ 59. What brain wave do we see in kids? _______________________ 60. Color the parts of the brain a) Frontal Lobe – Red b) Precentral Gyrus – Dark Red c) Parietal Lobe – Blue d) Postcentral Gyrus - Dark Blue e) Temporal Lobe – Green f) Occipital Lobe - Orange g) Cerebellum – Purple h) Pons – Brown i) Medulla Oblongata – Gray 4 61. Below is a diagram of a sagittal view of the human brain. Match the letters on the diagram with the following list of terms and insert the appropriate letters in the answer blanks. 1) _____ Cerebellum 6) _____ Hypothalamus 11) _____ Pons 2) _____ Cerebral Aqueduct 7) _____ Medulla Oblongata 12) _____ Thalamus 3) _____ Cerebrum 8) _____ Optic Chiasm 13) _____ Third Ventricle 4) _____ Corpus Collosum 9) _____ Pineal body 5) _____ Fourth Ventricle 10) _____ Pituitary gland M A B C L D K E J I F G 5 H 62. Label the parts of a Spinal Cord A. ________________________ B. ________________________ C. ________________________ A D. ________________________ E. ________________________ B E D C 63. Label the parts of a Reflex Arc (A) ________________________ matter (B) ________________________ matter (C) ______________________________ (D) ______________________________ C (E) ______________________________ (F) ______________________________ (G) ______________________________ D A E B F 6 G