* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download WHICH PATTERN IS IT?
Sociocultural evolution wikipedia , lookup
Objections to evolution wikipedia , lookup
Creation–evolution controversy wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Jewish views on evolution wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Mormon views on evolution wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Hindu views on evolution wikipedia , lookup
Unilineal evolution wikipedia , lookup
Creation and evolution in public education in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Evolving digital ecological networks wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
Punctuated equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Acceptance of evolution by religious groups wikipedia , lookup
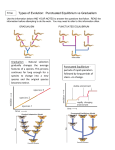
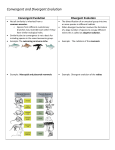
Bellwork Imagine that you are traveling in Madagascar when you find the plant to the left. You see that the plant has an unusually large spur containing nectar in its tip. You remember learning in science class that some moths feed on nectar. Draw a picture of what you think a moth may look like that feeds on this plant. How might natural selection bring about the evolution of this orchid and the moth? Today’s WHAT: I will evaluate and analyze mechanisms and patterns of evolution. Today’s HOW: I will write notes. I will read and discuss scenarios with a partner. KEY CONCEPT Evolution occurs in patterns. REMEMBER: Evolution through natural selection is not random. • Natural selection can have direction. • The effects of natural selection add up over time. The 3 patterns we’re going to discuss today are: 1. Coevolution 2. Convergent Evolution 3. Divergent Evolution – We’ll also look at how these might be seen in the fossil record Coevolution Co-evolution • • • Sometimes organisms that are closely connected to one another by ecological interactions evolve together. An evolutionary change in one organism may also be followed by a corresponding change in another organism. The process by which two species evolve in response to changes in each other over time is called coevolution. Coevolution Coevolution can occur with species that help or compete with each other The Star Orchid and the Hawk Moth Mimicry is another example of coevolution • Mimicry occurs when one organism evolves to look like the other in order to benefit itself. The mimic benefits from the situation while the organism it mimics in unaffected. Example: Orchid flowers that mimic female wasps Convergent Evolution Convergent Evolution • Convergent evolution describes evolution toward similar traits in unrelated species. • When two species are similar in a particular characteristic, it’s only convergent evolution if their ancestors were not similar Divergent Evolution • Divergent evolution describes evolution toward different traits in closely related species. • Divergent evolution can lead to speciation. kit fox red fox ancestor Changes in the frequency of a gene in a gene pool leads to Microevolution: small change over a period of time leads to Macroevolution: total of many changes that transform organisms over a long period of time. leads to Speciation: creation of 2 different species from 1 original species How does this affect the fossil record?? So what about the fossil record… Things to Consider: • Stasis - The organisms in the fossil record looks the same from when they appear to when they disappear; • Sudden appearance - When a species does not arise by gradually changing steadily from its ancestors; it appears all at once and fully formed. • Sequential nature – Based on the layers of rock, we sequence organisms in the fossil record. • What might cause stasis or sudden appearance? http://images.encarta.msn.com/xrefmedia/aencmed/targets/illus/ilt/T014608A.gif WHICH PATTERN IS IT? coevolution convergent evolution divergent evolution The Galápagos finches evolved through natural selection from a common ancestor into a wide variety of different looking species with different kinds of beaks divergent evolution WHICH PATTERN IS IT? coevolution convergent evolution divergent evolution Hummingbirds have a beak just the right length to reach the nectar in a cardinal flower and as they feed their foreheads bump into the pollen structure. Cardinal flowers are red which hummingbirds can see, but bees can’t, and their pollen structure is at just the right height for the hummingbird to pick up pollen as it feeds. coevolution WHICH PATTERN IS IT? coevolution convergent evolution divergent evolution Whales, sharks, and penguins all have streamlined bodies and fins/flipper for moving in water even though they belong in different animal groups (mammals, fish, and birds) Convergent evolution WHICH PATTERN IS IT? coevolution convergent evolution divergent evolution Beaver Beaver NORTH AMERICA Muskrat Muskrat Beaver and Muskrat Capybara SOUTH AMERICA Coypu Coypu divergent evolution BIOLOGY by Miller and Levine Pearson Publishing Beaver in North America and capybara in South America are closely related species living in very different environments that have evolved to look different over time. WHICH PATTERN IS IT? coevolution convergent evolution divergent evolution The tortoises on the Galapagos islands share a common ancestor, but over time they have become adapted for obtaining food in different habitats on different islands by having different neck lengths divergent evolution