* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download HW-subtopic-1-answers
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
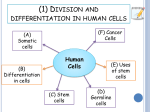
Higher Human Biology: Homework Questions Topic 1: Human Cells Sub-Topic 1: Division and differentiation in human cells Sub-Topic 2: Structure and function of DNA Sub-Topic 3: Cell Metabolism Marking Scheme – Answers in bold print Name _____________________________ Class ______________________________ Human Biology Higher Homework: Topic Human Cells Sub-topic 1: Division and differentiation in Human Cells 5. Which of the following statements regarding 1. Which of the following is not a use of stem cells? A Skin grafts B Drug testing C IVF treatment D Bone marrow transplant stem cells is TRUE? A Stem cells are specialised cells that continue to divide. B Stem cells cannot differentiate into specialised cells C Stem cells are unspecialised cells that can differentiate into specialised cells. 2. Which line in the table below describes correctly cell division in a specific cell type A B C D Cell Type Type of cell division somatic somatic germline germline meiosis meiosis mitosis mitosis None of the above 6. Cancer cells can divide excessively to Chromosome number in cells produced diploid haploid haploid diploid produce a mass of abnormal cells known as a tumour. A tumour cell can double every 40 minutes. If one tumour cell starts to divide how many tumour cells will be present after 12 hours? A 720 3. Which of the following statements about cancer cells is TRUE? A. B. C. D. D B 32768 C 131072 Cancer cells respond to regulatory signals Cancer cells cannot spread through the body Cancer cells cannot divide excessively Cancer cells can form secondary tumours D 262144 7. The cell shown below is magnified six hundred times. What is the actual size of the cell? Blood cells and muscle cells are undifferentiated germline cells B. Blood cells and muscle cells are differentiated germline cells C. Blood cells and muscle cells are undifferentiated somatic cells D. Blood cells and muscle cells are differentiated somatic cells 18 mm A 1080 μm B 108 μm C 30 μm D 3 μm 2 ---------------------- A. --------------------- 4. Which of the following statements is TRUE? 8. The diagram below shows some stages in the development of blood cells and nerve cells. (a) What are stem cells? Unspecialised cells that can develop into any / a number of / other cell types (1) (b) State the location of the tissue stem cells which develop into blood cells. (Red) bone marrow (1) (c) Describe what is meant by the term differentiation. Cells become specialised / specific types of cells are formed / Genes switch on or off to allow cell to function in a certain way. (1) 3 8. (continued) (d) Both embryonic stem cells and tissue stem cells are used in medical research. Give one reason why embryonic stem cells are potentially more useful than tissue stem cells. Embryonic stem cells can become any type of cell while tissue stem cells give rise to a more limited range of cell types. (1) (e) (i) Stem cells can be used in research and therapeutics (branch of medicine relating to the treatment of disease) because stem cells are able to develop into different types of cells. Explain why stem cells are able to develop into different types of cells. Stem cells are relatively unspecialised cells that can continue to divide and can differentiate into specialised cells. (1) (ii) List 3 therapeutic uses of stem cells. 1. Repair of damaged and / or diseased organs 2. Drug testing / treatment of cancers etc 3. Bone marrow transplants / cornea repair etc (3) (f) Tumours can be found in patients suffering from cancer. (i) Describe what a tumour is: A mass of abnormal cells formed when cancer cells divide excessively and do not respond to regulatory signals. (1) (ii) Describe how a secondary tumour develops: If cancer cells fail to attach to each other they can spread through the body to form secondary tumours. 4 (1)