* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Core Concepts of Marketing
Market penetration wikipedia , lookup
Dumping (pricing policy) wikipedia , lookup
Price discrimination wikipedia , lookup
Service parts pricing wikipedia , lookup
First-mover advantage wikipedia , lookup
Market segmentation wikipedia , lookup
Product lifecycle wikipedia , lookup
Sales process engineering wikipedia , lookup
Bayesian inference in marketing wikipedia , lookup
Affiliate marketing wikipedia , lookup
Perfect competition wikipedia , lookup
Social media marketing wikipedia , lookup
Pricing strategies wikipedia , lookup
Ambush marketing wikipedia , lookup
Consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Marketing research wikipedia , lookup
Food marketing wikipedia , lookup
Sports marketing wikipedia , lookup
Supermarket wikipedia , lookup
Segmenting-targeting-positioning wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Digital marketing wikipedia , lookup
Target audience wikipedia , lookup
Multi-level marketing wikipedia , lookup
Guerrilla marketing wikipedia , lookup
Viral marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing plan wikipedia , lookup
Youth marketing wikipedia , lookup
Product planning wikipedia , lookup
Direct marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing mix modeling wikipedia , lookup
Target market wikipedia , lookup
Integrated marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Street marketing wikipedia , lookup
Multicultural marketing wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
Marketing strategy wikipedia , lookup
Marketing channel wikipedia , lookup
Sensory branding wikipedia , lookup
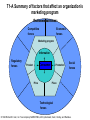
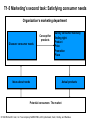
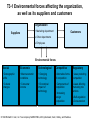
Core Concepts of Marketing Definition: Marketing is a social and managerial process by which individuals and groups obtain what they need and want through creating, offering and exchanging products of value with others. Alternative Definition: Producing and distributing the right goods: • to the right people • at the right place • at the right time • at the right price • with the right communication and promotion. Concepts: • • • • • Needs, Wants, Demand Products, Services, Ideas Exchange, Transactions, Relationships Markets, Marketer Consumers, Customers 4 Satisfaction = Σ (utilities) L=1 1. 2. 3. 4. Form Place Time Possession Exchange: The Process by which needs and wants are satisfied. Fife Necessary Conditions: 1. Two or more parties 2. Each has something of value to other 3. Each can communicate and deliver 4. Each is free to accept or reject offers 5. Each finds it desirable or appropriate to deal with the other. Transactions: Measurable Entities: 1. At least two things of value 2. Agreeable Conditions 3. Time of Agreement 4. Place of Agreement “Law of Contracts” Countertrading: 1. Barter 2. Compensation Deal 3. Product Buyback 4. Counterpurchase T1-A Summary of factors that affect an organization’s marketing program Environmental forces Competitive forces Economic forces Marketing program Information Regulatory forces Consumer Product Price Promotion Social forces Place Technological forces © 1994 Richard D. Irwin, Inc. To accompany MARKETING, 4/E by Berkowitz, Kerin, Hartley, and Rudelius. T1-5 Marketing’s second task: Satisfying consumer needs Organization’s marketing department Concept for products Discover consumer needs Satisfy consumer needs by finding right: Product Price Promotion Place Ideas about needs Actual products Potential consumers: The market © 1994 Richard D. Irwin, Inc. To accompany MARKETING, 4/E by Berkowitz, Kerin, Hartley, and Rudelius. Company orientation toward the market place 1. Production approach: • • • Large Scale Production Wide Distribution Homogeneous Product Problem: Consumer insensitive 2. Product approach: • • • Quality Performance Features Problem: Emphasis on product rather than consumer needs Examples: ELGIN WATCH CO. KEVIAR ISDN DIOLIGHT 3. Sales approach: • • Unsought goods Methods to sell whatever products are produced 4. Marketing approach: • • • Know customer needs and satisfy them more efficiently than your competitors Optimal combination of the four “P” Marketing research T1-6 Four different orientation in the history of American business Product area Sales area Marketing concept area Market orientation area 1860 1880 1900 1920 1940 1960 1980 © 1994 Richard D. Irwin, Inc. To accompany MARKETING, 4/E by Berkowitz, Kerin, Hartley, and Rudelius. 2000 T3-1 Environmental forces affecting the organization, as well as its suppliers and customers Organization • Marketing department Suppliers Customers Other departments Employees Environmental forces Social Economic Technological Competitive Regulatory • Demographic shifts • Macroeconomic conditions • Changing technology • Alternative forms of competition • Laws protecting competition • Cultural changes • Consumer income • Economical impact of technology • Components of competition Laws affecting marketing mix actions • Increasing foreign competition © 1994 Richard D. Irwin, Inc. To accompany MARKETING, 4/E by Berkowitz, Kerin, Hartley, and Rudelius. Self-regulation Consumerism