* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Passive Transport foldable
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Gene regulatory network wikipedia , lookup
Paracrine signalling wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Protein adsorption wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
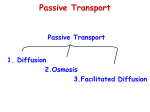
Outside Std. 2 Passive Transport -Does not require energy Diffusion Facilitated Diffusion Carrier Protein Osmosis Channel Protein Facilitated Diffusion Movement of molecules from a high concentration to a low concentration using a protein Inside of the foldable Carrier Protein Changes shape to match the particle’s shape and then carries it through the cell membrane Channel Protein Forms a channel that allows particles through Isotonic Solution The solute in the solution is EQUAL to the solute inside the cell so water moves in and out equally “ISO- means equal” Hypotonic Solution The solute in the solution is LESS THAN the solute inside the cell so water enters the cell “HYPO- means less” Isotonic Hypotonic Hypertonic Solution The solute in the solution is MORE THAN the solute inside the cell so water leaves the cell “HYPER- means more” Hypertonic Outside Std. 2 Active Transport -molecules move from low to high concentration which requires energy! Endocytosis Diffusion Movement of molecules from a high concentration to a low concentration Phagocytosis Pinocytosis Receptor-mediated Exocytosis Transport Proteins Phagocytosis Solid materials are engulfed; AKA “cell eating” Pinocytosis Liquid materials are engulfed; AKA “cell drinking” Receptor-mediated Molecules are received at receptor sites that are specific to those molecules Exocytosis Materials exit the cell; “exo-” means exit Transport Proteins Act as gatekeepers of the cell because they help molecules enter and exit the cell membrane 1