* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Population Interactions
Pleistocene Park wikipedia , lookup
Storage effect wikipedia , lookup
Molecular ecology wikipedia , lookup
Ecological fitting wikipedia , lookup
Overexploitation wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Renewable resource wikipedia , lookup
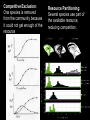
Do Now, 4.4 Food Web Labs, Please OBJECTIVE: 1. Describe interspecific interactions, including: predation, herbivores, competition, symbiosis, parasitism, mutualism, commensalism, and mimicry. TASK: 1. Using the food web shown, describe what might happen if the squid population were to decrease greatly. Which populations would benefit, and which would be harmed? Population Interactions Predators and their Prey • Predator survival depends on capturing food. • Prey survival depends on hiding, escape, or other defenses. • Since only successful organisms survive and reproduce, the genetic material of the best (or luckiest) organisms gets passed onto the next generation. This is called natural selection. Plants and Herbivores • Animals that eat plants = herbivores. Some plants produce poisonous or bad-tasting secondary compounds as a defense against herbivores… but not the grass this cow is munching! Competition • Resources (like food / energy) are limited. When two populations share the same niche, they will compete for use of that resource. • Do human populations compete for resources? • What resources? Competitive Exclusion: One species is removed from the community because it could not get enough of the resource Resource Partitioning: Several species use part of the available resource, reducing competition. Symbiosis • Symbiosis is the close association between two or more different species or organisms. • Three main types – Parasitism – Mutualism – Commensalism Parasites and Parasitism • A parasite feeds on its host. • Similar to predator / prey, but the prey isn’t usually killed. • Endoparasites are internal, Ectoparasites aren’t. Ectoparasite: Deer tick Endoparasite: Trichonella Mutualism • A cooperative relationship where both organisms benefit Commensalism One organism benefits, the other is unaffected Mimicry • Batesian mimicry: A harmless organism resembles a poisonous or distasteful one. Or… More Mimicry • Müllerian mimicry: Several poisonous or distasteful species look similar