* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Top 5- Vectors
Quantum vacuum thruster wikipedia , lookup
Coriolis force wikipedia , lookup
Hooke's law wikipedia , lookup
Hunting oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Derivations of the Lorentz transformations wikipedia , lookup
Laplace–Runge–Lenz vector wikipedia , lookup
Faster-than-light wikipedia , lookup
Four-vector wikipedia , lookup
Specific impulse wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Photon polarization wikipedia , lookup
Faraday paradox wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic angular momentum wikipedia , lookup
Seismometer wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Matter wave wikipedia , lookup
Velocity-addition formula wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Newton's laws of motion wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
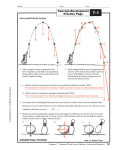
The Top 5- Linear Motion 1. d vs. t graphs SLOPE = AVERAGE VELOCITY (v = d/t) 2. v vs. t graphs SLOPE = AVERAGE ACCELERATION (a = v / t) AREA UNDER GRAPH = DISPLACEMENT (d) 3. Objects dropped from rest or free falling means vi = 0 and a = 9.8 m/s2 4. Objects thrown up in the air means vi ≠ 0, vtop = 0, a = -9.8 m/s2 5. Speed = distance / time (distance is sum of all paths taken) AND Velocity = displacement / time (displacement is straight length from start to finish) The Top 5 – Projectiles 1. “X-T-Y” chart for Horizontally Fired Projectiles: 2. “X-T-Y” chart for Angled Projectiles: ax = 0; ay = 9.8 m/s2; viy = 0 ax = 0; ay = -9.8 m/s2; vy,top = 0 3. Only formula that “works” in horizontal direction is: x = vix t 4. Time to hit the ground is the same for a dropped ball and a horizontally thrown ball if they start from the same height above ground. 5. Special angles: 45 maximum range (dx); 90 maximum height (dy) and time in air (t) The Top 5- Vectors 1. Use this sentence to remember the 8 vector quantities – first letter of each word represents a vector quantity I Fall For Vectors With Magnitude And (impulse) (force) (field) (velocity) (weight) (momentum) (acceleration) 2. Vectors are added tip to tail; Direction (displacement) Resultant is drawn lonely tail to lonely tip 3. Largest (max) resultant occurs when vectors point in the same direction (0 angle); Smallest (min) resultant occurs when vectors point in opposite directions (180 angle); Perpendicular vectors (90 angle) are in between the max and min. 4. When drawing vectors to scale: you need arrows, label each vector, arrow on the Resultant. 5. E = -R this means the magnitude of equilibrant is the same as the resultant but they point in opposite directions The Top 6 – FORCES AND CIRCULAR MOTION 1. Greatest mass determines the greatest inertia 2. Constant velocity means Fnet = 0 ; a=0 ; forces are balanced ; equilibrium 3. When in doubt draw a force diagram the 5 usual forces are Fg, FN, Ff, FA, T (FANGT!) 4. If object P pulls on object Q with force, F……then object Q pulls on object P with force F. This is known as Newton’s 3rd law. 5. Important vectors in UCM: velocity is directed tangent to circle, centripetal acceleration and centripetal force are directed to the center of the circle. 6. Play the one game with these equations from UCM : Fg = Gm1m2/ r2 ac = v2 / r Fc = mv2 / r The Top 5 – Work and Energy 1. Work is done when the force (all of it or just a component) acts parallel to the motion. W = F// d 2. Doing work changes an object’s energy KE if it accelerates; PEg if it is lifted; PEs if a spring is stretched or squeezed; Q if friction acts. 3. The rate at which work is done is POWER. 4. Spring constant, k, is constant for a particular spring. 5. Know your common energy transformations sliding down a ramp, rollercoasters, swinging pendulums, bow and arrow (ex. PEs KE for bow and arrow) The Top 5 – Momentum and Impulse 1. Impulse, J, means change in momentum, p (they are the same thing). 2. Use (Ft = mv)….in addition to other formulas on the Reference Table . 3. Draw before and after diagrams for collisions and: pbefore = pafter 4. Momentum and impulse are vectors (+p is to the right; -p is to the left). 5. “Happy ball” (bouncing backwards) has greater impulse then “sad ball” (stopping). The Top 5 – ELECTROSTATICS 1. Charge only comes in whole multiples of the elementary charge (ex. +53e, -1000e ) OR charge only comes in multiples of 1.6 x 10-19 Coulombs (ex. 4.8 x 10-18 C) 2. Positives DON’T move in solids. Negative charges move from the more negative to the less negative object 3. Direction of Electrostatic Force use opposites attract and likes repel 4. Direction of Electric Field use What Would A Positive Do? (WWPD) 5. UNIFORMLY spaced Electric Field lines indicate a UNIFORMLY strong electric field The Top 5 – Circuits 1. Know the Junction Rule (charge is conserved in circuits) and Loop Rule (energy is conserved in circuits) 2. Know your units so you can list givens and solve problems: charge (Coulombs), potential difference (Volts), current (Amps), resistance (ohms), power (Watts), and energy (Joules) 3. V.A.C.T. – Voltage Across, Current Through (voltmeter in parallel, ammeter in series) 4. The only way to change the resistance in a circuit is to change the physical characteristics of the device. Remember R = L / A 5. When in doubt use a “VIRP Chart”: put givens in, circle unknown box, if you have 2 in any row you can find everything else in that row The Top 5 – Magnetism 1. Magnetic field lines are drawn from NORTH to SOUTH. 2. Magnetic fields exist around: MAGNETS AND MOVING CHARGES. 3. Magnetic fields are strongest where the magnetic field lines are closest together. 4. Poles come in pairs – north and south; Poles are strongest part of magnet. 5. Magnetic force is maximum when charge moves at 90° to magnetic field. The Top 5 – Waves 1. Transverse: wave moves perpendicular to disturbance Longitudinal: wave moves parallel to the disturbance 2. Amplitude is proportional to Energy of the wave 3. Frequency = (# waves / # seconds ) unit: Hertz Period = ( # seconds / # waves) unit: second 4. Wave speed is only affected by the MEDIUM is travels through. 5. Sound is fastest in solids; Light is fastest in a vacuum (or nothing-ness ). The Top 5 – LIGHT 1. The absolute index of refraction, n, is a measure of how optically dense a transparent material is for light passing through it. 2. FIST and SIFA help to determine the direction of bending. 3. Angles of reflection, refraction, and incidence are measure from an imaginary NORMAL (a line perpendicular to the boundary). 4. All types of light on the Electromagnetic Spectrum chart travel at a speed of 3.0 x 108 m/s in a vacuum. 5. When light refracts the SPEED, DIRECTION, and WAVELENGTH all change BUT….the frequency does not change The Top 6 – MODERN PHYSICS 1. When using the Energy Level Diagrams for Hydrogen and Mercury electron transitions from low to high mean energy is absorbed; electron transitions from high to low mean energy is released. 2. Mass Energy Equivalence if mass is in kilograms, kg, use E = mc2; if mass is in universal mass units, u, use the proportion 1 u = 931 MeV. 3. Quark composition of 1 proton is uud; Quark composition of 1 neutron is udd. 4. Hadrons, (protons and neutrons) CAN feel the strong force (nuclear force). 5. Leptons (electrons) CAN NOT feel the strong force (nuclear force) 6. Antiparticles have the same mass but the opposite sign as their corresponding particle. The Top 5 – Circuits 1. There is so much information on the Reference Table. Make sure you use it!! (formulas, symbols, resistivity values, , differences between series and parallel) 2. Know the units: charge (________), potential difference (_______), current (________), resistance (_______), power (_______), energy (________) 3. Ammeters are connected ____________; Voltmeters are connected ________________ 4. The only way to change the resistance is to ______________________________________. Hint: R = L / A 5. In series the _____________________ each resistor is the same. In parallel the ____________________ each resistor is the same. The Top 5- Linear Motion 1. d vs. t graphs SLOPE = ____________________________________ 2. v vs. t graphs SLOPE = _____________________________________ AREA UNDER GRAPH = _________________________ 3. Objects dropped from rest or free falling means vi = ______ and a = _______ 4. Objects thrown up in the air means vi ≠ ______, vtop = _____, a = __________ 5. Speed = AND Velocity = The Top 5- Vectors 1. Use this sentence to remember the 8 vector quantities – first letter of each word represents a vector quantity What do you think? I Fall For Vectors With Magnitude And Direction ________________________________________________________________________________ 2. Vectors are added __________________but the Resultant is drawn ____________________ 3. E = -R What does this mean?_____________________________________________ 4. Largest (max) resultant occurs when vectors point in _____________________ (0 angle); Smallest (min) resultant occurs when vectors point in ____________________ (180 angle); Perpendicular vectors (90 angle) are in between the max and min. 5. When drawing vectors to scale: you need ____________________ and ________________. The Top 5 – Projectiles 1. Projectiles do not accelerate in the ______________ direction (on the chart ) 2. Projectiles only accelerate in the _________ direction due to gravity (on the chart 3. For a horizontal projectile the horizontal velocity, vx, does not affect __________________. 4. Time to hit the ground is the same for a dropped ball and a horizontally thrown ball if they both: 5. Special firing angles: 45:____________________ 90:__________________________ The Top 5 – FORCES AND CIRCULAR MOTION 1. Greatest ____________________________ determines the greatest inertia 2. Constant velocity means ________________________________________________ 3. When in doubt draw a force diagram the 5 usual forces are:____________________ 4. If a tow truck pulls on a SmartCar with force,F, then SmartCar pulls on tow truck with __ This is known as Newton’s __________ law. 5. Important vectors in UCM: velocity is __________________ to the circle, centripetal acceleration and centripetal force are _____________________ of the circle. 6. Play the one game for these equations from UCM: The Top 5 – ELECTROSTATICS 1. Charge only comes in whole multiples of the __________________ (ex. OR charge only comes in multiples of _________________ (look for ) ) 2. _________ DON’T move in solids. _________ charges move from the ________________ object to the ____________________object. 3. Direction of Electrostatic Force 4. Direction of Electric Field 5. UNIFORMLY spaced Electric Field lines indicate a ________________________________