* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 16: Endocrine System
History of catecholamine research wikipedia , lookup
Xenoestrogen wikipedia , lookup
Mammary gland wikipedia , lookup
Triclocarban wikipedia , lookup
Breast development wikipedia , lookup
Neuroendocrine tumor wikipedia , lookup
Menstrual cycle wikipedia , lookup
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (female-to-male) wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
Hyperthyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Bioidentical hormone replacement therapy wikipedia , lookup
Hyperandrogenism wikipedia , lookup
Endocrine disruptor wikipedia , lookup
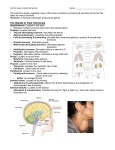
Chapter 16: Endocrine System Two types of glands: •Exocrine – secretions delivered to body surface or organ cavity via ducts – delivers materials to locations contiguous to external environment •Endocrine glands – no ducts, release hormones into extracellular fluid or “blood” – Hormones affect cell function •Mixed glands – Have both exocrine and endocrine function (pancreas) Major endocrine glands: – – – – – – Hypothalamus Pituitary Thyroid Parathyroid Thymus Adrenal cortex – – – – – Adrenal medulla Pineal Pancreas Ovaries Testis Other organs/tissues having endocrine function: – – – – Heart Stomach Duodenum Placenta – Kidneys – Adipose tissue – Liver Two Major Classes of Hormones 1) Amino acid based (mostly hydrophilic) – Catecholamines (epinephrine, norepinephrine & dopamine) – Indolamines (serotonin, melatonin & histamine) – Thyroid hormone (hydrophobic thyroxine T4 & triiodothyronine T3) – peptide and protein hormones 2) Steroids – sex and adrenocortical hormones (cholesterol-based and hydrophobic) Estrogens, progesterone, testosterone, DHEA, cortisol/corticosterone & aldosterone Hormone Action •Hormones alter target cell activity by one of two mechanisms 1) Second messengers: Receptors embedded in cell membrane Mechanism used by all hydrophilic (polar) hormones nd +2 Generate or release intracellular 2 messengers: cAMP, cGMP, Ca 2nd messengers diffuse throughout cell & “turn on the desired effect” nd 2 messengers are targeted for therapeutics (sildenafil increases cGMP and promotes vasodilation in “certain” blood vessels) 2) Direct gene activation: Receptors in the nucleus Used by hydrophobic hormones (Steroids & thyroid hormone) Activate specific regions of the genetic code that encode for proteins that are required for desired function. Hypothalamus • Regulates many endocrine functions from water balance to sex drive • Most effects are mediated via pituitary gland • Hypothalamic-pituitary-__________ axis. Pituitary Gland (Hypophysis) • “Master endocrine gland – regulates many other glands & processes” • Location and size – housed in sella turcica of sphenoid bone • Has two lobes: anterior & posterior Anterior Lobe secretes tropic hormones that regulate other endocrine glands: • Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH or thyrotropin) – regulates thyroid • Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) – regulates gonads • Luteinzing hormone (LH) – regulates gonads • Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH or corticotrophin) – regulates adrenal cortex • Prolactin (PRL) – regulates mammary glands • GH, somatotropin or growth hormone – stimulates liver to make growth factors Negative feedback & hypothalamic – pituitary – (thyroid/cortical/gonadal) axes Function of the Posterior Pituitary •Stores and releases oxytocin (OT) and anti-diuretic hormone (ADH) •Both produced in hypothalamus & transported down Posterior Lobe Hormones & Regulation •ADH – Hyperosmolarity (dehydration) causes hypothalamus to signal release – ADH Æ kidneys ↑ water retention, Æ concentrated low volume urine – Release is inhibited by alcohol – Functions also as neurotransmitter – implicated in male monogamy. •Oxytocin – labor contractions, lactation, sexual arousal & female affection. – neuroendocrine reflexes trigger release 1) Suckling infant→ stimulates nerve endings → hypothalamus → posterior lobe → oxytocin → milk ejection. 2) Uterine contraction→ stimulates nerve endings → hypothalamus → posterior lobe → oxytocin → uterine contraction. – higher brain centers •milk ejection reflex can be triggered by a baby's cry. •ADH & oxytocin are both 7 amino acid peptides and share considerable structural similarity – thus it is important for pregnant women to avoid being ____________ ! Adrenal Cortex •Corticosteroids – Mineralocorticoid: aldosterone + + •Promotes Na & H2O retention + K secretion. controls BP via renin: angiotensinogen low BP Æ kidneys Æ renin angiotensin I lungs Æ angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) angiotensin II (potent vasoconstrictor) aldosterone (Na+ & H2O retention) – Glucocorticoids: cortisol & corticosterone •Alters metabolism: stimulates release of glucose into blood •Antiinflammatory effect becomes immune suppression with long-term – sex steroids •Adrenal androgens (including DHEA which other tissues convert to testosterone) and estrogen (important after menopause) Ovary •Regulated by hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis – Chapter 27 Testes •Regulated by hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis •Interstitial cells (between seminiferous tubules) – LH Æ produce testosterone •Seminiferous tubules – FSH Æ promotes sperm production Other Organs with Endocrine Function: •Heart – atrial natriuretic peptide released with an increase in BP ↓ blood volume + ↓ BP by ↑ Na+ and H2O loss by kidneys •Stomach and small intestines (produce 10 enteric hormones) – coordinate digestive motility and secretion – Ghrelin – produced by stomach stimulates appetite – Gastrin – produced by stomach increases gastric (stomach acid secretion) – Secretin – produced by duodenum stimulates pancreas to release bicarbonate & neutralize stomach acid. – Cholecystokinin – produced by duodenum stimulates gallbladder to contract and stimulates release of digestive enzymes from the pancreas •Placenta – secretes HCG, estrogen, progesterone: regulate pregnancy (Chapt 28)