* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Subject-Verb Agreement
Sanskrit grammar wikipedia , lookup
English clause syntax wikipedia , lookup
Old Irish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Macedonian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Udmurt grammar wikipedia , lookup
Compound (linguistics) wikipedia , lookup
Ukrainian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Navajo grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ojibwe grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old Norse morphology wikipedia , lookup
Georgian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Lithuanian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Kannada grammar wikipedia , lookup
Chinese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old English grammar wikipedia , lookup
Japanese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Portuguese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Arabic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Swedish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Malay grammar wikipedia , lookup
Modern Hebrew grammar wikipedia , lookup
Modern Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Zulu grammar wikipedia , lookup
Latin syntax wikipedia , lookup
Sotho parts of speech wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Italian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Romanian nouns wikipedia , lookup
Vietnamese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Esperanto grammar wikipedia , lookup
Yiddish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Icelandic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Scottish Gaelic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Serbo-Croatian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Turkish grammar wikipedia , lookup
French grammar wikipedia , lookup
Pipil grammar wikipedia , lookup
Spanish grammar wikipedia , lookup
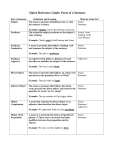
The Sentence & Parts of Speech The Sentence In English, a sentence—also known as an independent or main clause—needs a subject and verb, and it should express a complete thought. Example: I subject graduated recently from Ashford University. verb complete thought Subject A subject indicates who or what is being talked about in a given sentence as well as who or what is doing the action. It is the noun form that comes before the verb (the action), but it is not always the first word in a sentence. Verb A verb is an action word that indicates what the subject does in a given sentence. However, verbs can also indicate actions we cannot see (or “states of being”), such as think, believe, love, hope, feel, dream, exist, etc. Complete Thought The complete thought finishes what the sentence is about, adding necessary or extra information at the end. Parts of Speech Noun A noun names a person (Joe, mom, mailman), place (eg. New York, Sea World, post office), or thing (laptop, honesty, swimming, dog grooming, shoes). Pronoun A pronoun replaces a noun in a given sentence. There are various types of pronouns: subject (I, you, he, she, it, we, they), object pronouns (me, you, him, her, it, us, them), Possessive pronouns (mine, yours, his, hers, its, ours, yours, theirs), Reflexive (myself, yourself, himself, herself, itself, ourselves, yourselves, themselves), demonstrative (this, that, these, those), indefinite (someone, something, anything, anyone, nothing, everyone), and relative (who, that, which, when, where, why). Adjective Adjectives describe nouns. Examples: Turkish coffee, one-year-old bulldog, tired baby, Fran’s expensive car. Adverb Adverbs describe verbs or other adjectives. Examples: snore loudly, arrived late, very handsome, quite nice. Article There are two types: definite (the) and indefinite (a/an). As a rule thumb, “the”—used with singular and plural nouns—refers to a specific noun. “A/An”—used with only singular countable nouns—refer to a generic noun. Example: I bought a banana yesterday. (The speaker bought one banana.) Example: Sarah’s dog ended up eating the banana. (Her dog ate a specific banana: the one the speaker bought.) Preposition Prepositions link nouns, pronouns, and phrases in a sentence. Usually, they indicate direction, location, or time. Examples: to the airport, from the park, on the desk, in her car, at midnight, for their 50th anniversary.