* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Rock Cycle
Anoxic event wikipedia , lookup
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
Abyssal plain wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Future of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Supercontinent wikipedia , lookup
Mantle plume wikipedia , lookup
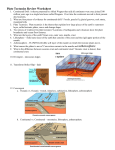
•The Earth system involves many cycles. •For example •The Hydrologic Cycle is the cycle that circulates the earths water supply. • The Rock Cycle illustrates the origin of the three basic rock types The Formation of the Solar System • A) dust and gasses (nebula) started to gravitationally collapse. • B) the nebula thinned into a rotating disk that heated up. • C) as it cooled the nebular cloud caused rocky and metallic material to reduce into solid particles. • D) repeated collisions caused the dust sized particles to combine into asteroid sized bodies. • E) in a few million years the bodies turned into planets. • The earths interior is divided into three different layers. Mantle Core Inner Core Layer Thickness (kilometers) Chemical composition Notes Continental Crust 35-40 km Consists of many rock types, but mostly granite Ranges the rocky mountains and Himalayas Oceanic Crust 7 km Composed of dark igneous rock basalt Made with continental crust also Upper Mantle 660 km Stiff lithosphere, and weaker asthenosphere, and the bottom is the transition zone Extends from crust to mantle boundary Lower Mantle 660 km Lays between rocky mantle and not liquid iron outer core The bottom few hundred layers are called the D layers Outer Core 2270 km Liquid layer metallic iron Earths magnetic field Inner Core 1216 km Solid iron Has a sphere radius Lithosphere 250 km Weak asthenosphere Lithosphere can move independently Asthenosphere 350 km Soft weak layer The lithosphere is attached to asthenosphere • The oldest crustal material that has been identified was found in Northwestern territories of Canada, about 4 billion years ago. • Continents and Ocean basins are the two principal divisions of Earth’s surface. • Lands and mountains are the two categories of features found on the continents. Near sea lands are usually flat and green, and mountains are high and rocky most of the time. • Geologists predict all of their theories about Earth’s interior because there is no way to drill a hole that would be deep enough to reach Earth’s core. Three regions of ocean floor Deep-Ocean Basins Continental Margins Oceanic Ridges Describing three portions of the continental margins. • Continental shelf-flooded extension of the continents • Continental slope 60% of Earth’s Surface is made from the Oceans. • Continental Rise-consists of a thick accumulation of sediment that moved down slope from the continental shelf to the deep ocean floor Characteristics of different features found in deep-ocean basins • The linear chains of volcanoes, deep canyons, plateaus, and large expense of monotonously flat plains are widely visible