* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Vision Lab Handout
Blast-related ocular trauma wikipedia , lookup
Idiopathic intracranial hypertension wikipedia , lookup
Visual impairment wikipedia , lookup
Photoreceptor cell wikipedia , lookup
Corrective lens wikipedia , lookup
Vision therapy wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrial optic neuropathies wikipedia , lookup
Diabetic retinopathy wikipedia , lookup
Visual impairment due to intracranial pressure wikipedia , lookup
Contact lens wikipedia , lookup
Keratoconus wikipedia , lookup
Corneal transplantation wikipedia , lookup
Dry eye syndrome wikipedia , lookup
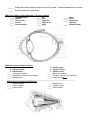
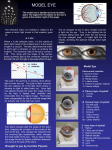
Name: _________________________________ Date:_____________ Lab Handout – The Eye Match the name to its description/function A. B. C. D. E. F. G. H. I. aqueous humor cataract chalazion choroid ciliary gland cones conjunctiva cornea fovea centralis J. K. L. M. N. iris lacrimal fluid lacrimal gland lens meibomian or tarsal gland O. nasolacrimal duct P. optic disk Q. optic nerve R. palpebra S. pupil T. retina U. rods V. sclera W. sty X. suspensory ligaments Y. vitreous humor _____ "white" of eye - tough outer coat that extends all around eye _____ “blind spot” – where optic nerve leaves the eyeball _____ blood rich middle layer that is darkly pigmented to prevent light scattering _____ carries sight impulses to brain _____ contains ciliary body muscles that adjust shape of lens as necessary to focus _____ contains only cones – site of greatest visual acuity _____ dilute salt solution that contains antibodies & lysozyme _____ eyelids _____ focuses light on retina for visual clarity _____ Gel like substance that holds shape of eyeball – located between lens & retina _____ Clouding & hardening of the lens – can be treated surgically _____ inflammation of the ciliary gland _____ inflammation of the tarsal gland _____ innermost layer that contains photoreceptors - "screen" of eye _____ produces oil to lubricate eye _____ opening through which light passes to enter the inner part of eye _____ Pigmented muscle fibers that regulates light entering eye _____ produces sweat (watery fluid) _____ produces tears to wash surface of eye _____ responsible for color vision _____ responsible for gray tone vision _____ thin moist membrane that lines eyelids & connects to surface of eye _____ transparent layer in front of lens - lets light in- often transplanted _____ Watery fluid that provides nutrients for lens & cornea – located between lens & cornea _____ Empties tears into nasal cavity Match the letters on the diagrams to the parts below _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ aqueous humor choroid ciliary body cornea fovea centralis _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ iris lens optic disc optic nerve pupil _____ retina _____ sclera _____ suspensory ligament _____ vitreous humor Match the muscles to their function a. superior oblique d. medial rectus b. inferior oblique e. superior rectus c. lateral rectus f. inferior rectus _____ moves eye laterally _____ Moves eye medially _____ Depresses eye and turns it laterally _____ Elevates eye and turns it laterally _____ Elevates eye _____ Depresses eye ___________________________________________________________________________ Match the eye muscles to the diagram _____ Superior oblique _____ Medial rectus _____ Inferior oblique _____ Superior rectus _____ Lateral rectus _____ Inferior rectus Follow-up Questions: 1. ___________________________ is the sharpness of the perceived visual image and is often evaluated in clinical situations with the _____________________ eye test. 2. A person with 20-100 vision can see an object at ____________________feet where a normal person can see that object at _______________________feet. 3. When accommodating, the pupil and the ______________________ may change shape. 4. Cones are involved in __________________________vision. (bright-light/dim-light) 5. Rods are involved in ____________________________vision. (bright-light/dim-light) 6. Color blindness usually results from: 7. Explain why there is a blind spot in your vision. 8. Colorblindness is a recessive sex-linked disorder present on the X chromosome. Explain why more men suffer from colorblindness than women. 9. How was your reaction time different from your dominant and non-dominant hand? Hypothesize why this happened. 10. Name one voluntary muscle of the eye and name one involuntary muscle of the eye. What does each do? a. Voluntary:_____________________________________________ i. Function: ___________________________________________________ b. Involuntary: ____________________________________________ i. Function: __________________________________________________ . Eye. 1. List the refractory structures of the eye. 2. Which is the only structure that can change its refractory power? ________________ Vision 1. Presbyopia a. Define: b. Cause: 2. Define Emmetropia 3. Astigmatism a. Define: b. Cause: 4. Complete the chart Myopia One word definition Explain Eyeball is too: Hyperopia Lens is too: Cornea is too: Corrective lens 5. Why do you get a headache when you’ve been reading for a long time? 6. Know these disorders for quiz. o Chalazion o Conjunctivitis o Sty o Colorblindness 7. Complete the chart Structure relaxed Distance Vision Near Vision o Cataract o glaucoma Structure tightened Light refraction (Increase or decrease)