* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Conversations with the Earth
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Spitzer Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Kepler (spacecraft) wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
IAU definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Space Interferometry Mission wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
H II region wikipedia , lookup
Exoplanetology wikipedia , lookup
Cosmic distance ladder wikipedia , lookup
Late Heavy Bombardment wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Future of an expanding universe wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Stellar kinematics wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Star formation wikipedia , lookup
Circumstellar habitable zone wikipedia , lookup
Planetary system wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Directed panspermia wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
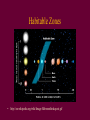
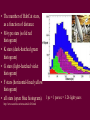
Conversations with the Earth Tom Burbine [email protected] Last Quiz on Thursday • Life in the Solar System and Galaxy Final • May 9 (Monday) – 11:30 am - (Monday, Wednesday, Thursday class) • May 11 (Wednesday) – 8 am - (Tuesday, Thursday class) • 25 short answer questions • No calculators • Besides your new sheet of paper, you can bring in the sheet of paper you used for the Midterm • Currently, there are 547 candidate extra-solar planets that have been identified, orbiting 458 stars • It is estimated that there are 50 billion planets in our galaxy The only star we know that has Earth-Like Planets is the Sun • Sun is sometimes called Sol Galactic Habitable Zone • It is the area in the galaxy whose boundaries are set by its calm and safe environment, and access to the chemical materials necessary for building terrestrial planets similar to the Earth. http://astronomy.swin.edu.au/GHZ/ green is habitable zone Habitable Zones • http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Image:Habzonethinkquest.gif HabCat • Catalog of Nearby Habitable Systems made by Jill Tarter and Margaret Turnbull • These Sun-like, habitable stars have just the right distance, constancy, and temperature to qualify in a forthcoming enlarged radio search. What do else do you need? • You need “metals” to make planets –Metals are elements heavier in mass than helium For simple life • You need a planet with an atmosphere and some water • Stars must remain nearly constant in brightness over billions of years for complex life to have time to develop. – On Earth, single cells may have developed after only 800 million years or so, but the fossil record indicates that it took another ~3 billion years before multi-cellular life flourished. • The number of HabCat stars, as a function of distance • M-type stars (solid red histogram) • K stars (dark-hatched green histogram) • G stars (light-hatched violet histogram) • F stars (horizontal-lined yellow histogram) • all stars (open blue histogram). 1 pc = 1 parsec = 3.26 light years http://www.astrobio.net/news/article436.html Drake Equation • The Drake Equation is an attempt to estimate the number of extraterrestrial civilizations in our galaxy with which we might come in contact. • http://www.activemind.com/Mysterious/Topics/SETI/drake_equation.html Number of habitable planets • 100 billion? Fraction of Planets that have life in the Galaxy • ? Fraction of the Life-Bearing Planets in the Galaxy upon which a Civilization capable of interstellar communication has at some time arisen • ? Intelligent Life • Intelligent life that we can detect is usually defined as life that can build a radio telescope Radio • Transmitting information over radio waves is very cheap • uses equipment that is easy to build • has the information-carrying capacity necessary for the task • The information also travels at the speed of light. Fraction of all civilizations that have existed in the galaxy that exist now • ? Fermi’s Paradox • Where are they? Fermi’s Paradox • Why have we not observed alien civilizations even though simple arguments would suggest that some of these civilizations ought to have spread throughout the galaxy by now? Reason for question • Straightforward calculations show that a technological race capable of interstellar travel at (a modest) one tenth the speed of light ought to be able to colonize the entire Galaxy within a period of one to 10 million years. Explanation • Interested in us but do not want us (yet) to be aware of their presence (sentinel hypothesis or zoo hypothesis) Explanation • Not interested in us because they are by nature xenophobic or not curious Explanation • Not interested in us because they are so much further ahead of us Explanation • Prone to annihilation before they achieve a significant level of interstellar colonization, because: (a) they self-destruct (b) are destroyed by external effects, such as: (i) the collision of an asteroid or comet with their home world (ii) a galaxy-wide sterilization phenomenon (e.g. a gamma-ray burster (iii) cultural or technological stagnation Explanation • Capable of only interplanetary or limited interstellar travel because of fundamental physical, biological, or economic restraints Fermi’s paradox • The Fermi paradox is the apparent contradiction between high estimates of the probability of the existence of extraterrestrial civilizations and the lack of evidence for, or contact with, such civilizations. • http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fermi_paradox Any Questions?