* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Recap on the cardiovascular system and its response to exercise
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
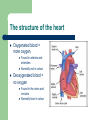
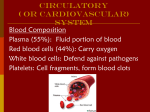
Recap on the cardiovascular system and its response to exercise The function of the circulatory system The circulatory system has three major function: Transport Body temperature control Moving things around the body in the blood stream such as oxygen and nutrients like glucose. Thermoregulation, moving blood near the skin cools down the body. That’s why you look redder when you exercise heavily. Protection Moving anti-bodies around the body fighting diseases and clotting cuts. The structure of the heart Oxygenated blood = more oxygen. Found in arteries and arterioles Normally red in colour Deoxygenated blood = no oxygen Found in the veins and venules Normally blue in colour The cardiovascular system: HEART Structure of the Heart Surrounded by sac known as the pericardium, which prevents friction as the heart beats. Heart wall is made of: – – – Epicardium (outer layer) Myocardium (strong middle layer) Endocardium (inner layer) Right separated from left by the Septum Strokes of the heart Heart rate = how many times your heart beats (normally in one minute, BPM) Stroke volume = blood pumped per beat. Cardiac output = blood pumped per minute – Cardiac output = Stroke volume x Heart rate Task Calculate a persons cardiac output when stroke volume = 10ml Heart rate = 78 BPM Cardiac output = ? Circuits of the body There are two circuits of the body you need to know: Systemic Carries blood around the body via the transport system supplying the major organs and muscles with blood. Pulmonary Consists of the heart and lungs, deoxygenated from the heart to the lungs to be oxygenated. The oxygenated blood then goes back to the heart to be pumped around the body. Blood Flow Through the Heart 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Vena Cava – Superior/Inferior Right Atrium Tricuspid Valve Right ventricle Pulmonary Artery LUNGS Blood Flow Through the Heart 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Pulmonary veins Left Atrium Bicuspid/Mitral/Atrioventricular valve Left Ventricle Aorta MAJOR ORGANS Control of the Heart Initial Stimulus originates in the Sinoatrial node (SA node) Pacemaker determines heart rate Wave of excitation across both atria causes them to contract Control of the Heart Sinoventricular node (SV node) Both atria and both ventricles contract at the same time Systole-contraction of heart Diastole-Relaxation/filling of the heart Blood vessels There are three types of blood vessels you need to know: Arteries Veins Capillaries Types of Blood Vessels Arteriole Artery Capillary Vein Venuole Arteries Carry oxygenated blood away from the heart (the pulmonary artery brings blood to the heart!!) They have thick strong elastic walls. Small arteries are called arterioles. Veins Carry deoxygenated blood back to the heart (the pulmonary vein carries blood away from the heart!!). The veins have thinner walls as the blood pressure is lower. Veins have valves that keep blood flowing in the right direction. Small veins are called venules. Capillaries Carry digested foods and oxygen directly to the tissue. Take away waste products of the body. Very small and vary in size. How it works!! Heart Arteries Arterioles Capillaries Venules Veins Heart Gas exchange Blood flow through the heart Warm-up questions How many circuits are there in the circulatory system? What type of blood is carried back to the heart? Which type of blood vessel carries blood away from the heart? Which type of blood cell carries oxygen? Which type of blood cell fights diseases? Changes in heart rate during exercise There is a anticipatory rise due to hormonal action. Then there is a sharp rise due to stimuli and hormonal response. The heart rate steadies off during constant maximal exercise (heart rate max) Changes in the respiratory Tidal volume increases. Residual volume increases. Breathing rate and the volume of oxygen consumed is increased due to the onset of lactic acid. Adaptations to the body over long periods of exercise. Increase in the number of capillaries. Increase in the efficiency of gaseous exchange. Lower resting heart rate.