* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Capital Account Liberalisation and China`s Effect on Global Capital
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
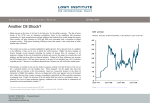
Capital Account Liberalisation and China’s Effect on Global Capital Flows Alfred Schipke* 1.Introduction In 1993, China announced a plan to fully liberalise its capital account by 2000. That plan was, however, disrupted by the Asian financial crisis. China’s capital account liberalisation process has resumed over the past few years, raising the question about the sequencing of capital account liberalisation. The debate gained prominence following the renminbi depreciation in August 2015 and subsequent capital outflow pressures (Figures 1 and 2). This paper provides a brief overview of China’s capital account liberalisation, evaluates the effect of a full liberalisation of the Chinese capital account and describes how China’s liberalisation process compares with the International Monetary Fund’s (IMF) institutional view. Figure 1: Chinese Renminbi index yuan Fixing rate(a) (RHS, inverted scale) 106 6.1 104 6.2 CFETS index(b) (LHS) 102 6.3 100 6.4 98 6.5 96 94 6.6 Spot rate(a) (RHS, inverted scale) M J 2015 S D M 2016 J 6.7 Notes: (a) Yuan per US$ (b) 31 December 2014 = 100 Sources: Bloomberg; CEIC Data; China Foreign Exchange Trade System; RBA * The author is from the IMF. The views expressed here are those of the author and do not necessarily represent the views of the IMF or those of its Executive Board. This paper is based on Bayoumi and Ohnsorge (2013) and Habermeier et al (forthcoming). C O N F E R E N C E VO L U M E | 2 016 163 ALFR ED SCH IPKE Figure 2: Foreign Currency Reserves US$b US$b Stock 4 000 4 000 3 000 3 000 2 000 2 000 US$b US$b Monthly change 75 75 0 0 -75 -150 -75 2010 2012 2014 2016 -150 Sources: CEIC Data; RBA 2. Capital Account Liberalisation in China China has gradually opened its capital account, but considerable restrictions on capital flows remain in place. According to the IMF Annual Report on Exchange Arrangements and Exchange Restrictions, 52 out of the 58 items still have some degree of control (IMF 2015).1 The different types of private capital flows – direct, portfolio investment and other – have been liberalised at different rates and restrictions on inflows have generally been eased before those on outflows. Despite formal restrictions, leakages have increased. Foreign direct investment (FDI) has dominated capital inflows to China, in part because they have been less restricted than other forms of capital flows (Figure 3). The size of other flows, which are mainly banking related, have increased in recent years and have been a particularly important component of capital outflows. By comparison, portfolio investments remain limited, reflecting greater restrictions on these flows. While portfolio investors have generally been restricted by various schemes, the allowable quotas for these schemes have been gradually relaxed (Table 1). 1 China’s State Administration of Foreign Exchange (SAFE) measures suggest that, of the 40 items in the capital account, 5 are unconvertible and 18 are partly convertible. 164 R E S E RV E B A N K O F AU S T R A L I A C A PI TA L AC C OU N T L I B E R A L I SAT ION A N D C H I N A’ S E F F E C T ON G L OB A L C A PI TA L F L OW S Figure 3: Capital Inflows and Outflows Per cent of GDP % % Gross capital inflows 6 6 3 3 0 0 -3 -3 % % Gross capital outflows 6 6 4 4 2 2 0 0 -2 1990 1995 Direct investment 2000 2005 Portfolio investment 2010 -2 2015 Other investment Notes:Gross inflows are defined as the sum of inward foreign direct investment, portfolio liabilities and other investment liabilities in the balance of payments statistics; gross outflows are defined as the sum of outward foreign direct investment, portfolio assets and other investment assets Source: Thomson Reuters C O N F E R E N C E VO L U M E | 2 016 165 166 Portfolio inflow RQFII R E S E RV E B A N K O F AU S T R A L I A Equity inflow Northbound 2014 2014 2011 2002 2006 Start year No na No No na No US$1b No (b) CNY412b US$79b US$90b Cap on individual quota No(b) Yes Yes Yes Total quotas allotted CNY300b(b) CNY250b(b) No US$150b No Cap on total quotas No CNY0.5m No US$2m No Minimum investment required CNY CNY CNY Any Any Currency Notes: QDII denotes Qualified Domestic Institutional Investor, QFII denotes Qualified Foreign Institutional Investor and RQFII denotes renminbi QFII (a) Southbound refers to investment flows from Shanghai (mainland) to Hong Kong SAR, northbound refers to investment flows from Hong Kong SAR to Shanghai (mainland) (b) Though Shanghai–Hong Kong Stock Connect (SHKSC) investors are not subject to individual quota limits, they are subject to a daily limit and an aggregate quota on total flows; net southbound flows are capped at CNY10.5 billion per day and net northbound flows are capped at CNY15 billion per day Source:IMF Equity outflow Southbound SHKSC(a) Portfolio inflow QFII Target flows Portfolio outflow QDII Scheme Quota limit Table 1: Summary of China’s Schemes to Ease Controls on Portfolio Investments ALFR ED SCH IPKE C A PI TA L AC C OU N T L I B E R A L I SAT ION A N D C H I N A’ S E F F E C T ON G L OB A L C A PI TA L F L OW S To gauge the direction of future reforms, it is useful to consider where China stands relative to other economies. Internationally, higher income per capita tends to be associated with a more open capital account (Figure 4). China appears to be an outlier, with a more closed capital account than other countries that have a similar income per capita. Similarly, China has a low level of integration with the global financial system (as measured by the sum of its external assets and liabilities as a share of GDP) given its per capita income. This could suggest that China is likely to become more open and financially integrated with the global economy in the coming years. Figure 4: De Jure Financial Account Restrictiveness and Income Level 1.0 China de jure index 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 5 6 7 8 9 10 log of GDP per capita 11 12 Notes:185 IMF member countries, including their territories where data are available; data as at 2014 or latest available Sources: IMF; World Bank, World Development Indicators 3. Recent Developments The volatility in foreign exchange markets, capital outflows and the associated decline in foreign currency reserves in late 2015/early 2016 prompted the Chinese authorities to better enforce existing capital account controls and impose some additional measures (such as the 20 per cent unremunerated reserve requirement (URR)). Nevertheless, the authorities remain committed to capital account liberalisation and the process has continued to move forward. In February 2016, the quota for individual institutions to invest under the QFII program was relaxed and the minimum investment period was reduced from one year to three months (SAFE 2016). Also in early 2016, access to the interbank bond market was expanded for international investors (PBC 2016). C O N F E R E N C E VO L U M E | 2 016 167 ALFR ED SCH IPKE 4. Implications of Full Liberalisation Given that parts of the capital account remain closed, the question arises of what would be the impact of fully opening the capital account in one go. The size and direction of those capital flows could have important implications domestically and internationally. In the past, countries that liberalised their capital account generally experienced a significant increase in both inward and outward capital flows (Figure 5). However, with a few exceptions, outflows were larger than inflows as domestic investors sought to diversify their savings. Figure 5: Change in Gross International Assets Five years following capital account liberalisation, per cent of GDP -10 Venezuela (1996:Q4) 0 Norway (1988:Q4) 0 Canada (1975:Q4) 10 Thailand (1998:Q4) 10 Peru (1991:Q4) 20 Finland (1989:Q4) 20 Colombia (1998:Q4) 30 Japan (1980:Q4) 30 Venezuela (1989:Q4) 40 Germany (1981:Q4) 40 Sweden (1989:Q4) 50 Spain (1992:Q4) 50 Italy (1992:Q4) 60 France (1990:Q4) 60 Chile (1998:Q4) % UK (1979:Q4) % -10 Source: Thomson Reuters For China, for example, Bayoumi and Ohnsorge (2013) use a portfolio allocation model and data from countries that liberalised their capital account over the past 30 years to estimate the size of capital flows following liberalisation. The authors use a partial equilibrium model that does not take into account other changes in the macroeconomic environment that would occur if the capital account were to be fully opened in one step. Nevertheless, the model’s estimates provide a useful starting point to think about what to expect following capital account liberalisation in China. Based on this exercise, capital account liberalisation may be followed by a one-time stock adjustment of Chinese assets of 15–25 per cent of GDP and a smaller adjustment for foreign assets in China (2–10 per cent of GDP; Figure 6). This would imply a net capital outflow of around 168 R E S E RV E B A N K O F AU S T R A L I A C A PI TA L AC C OU N T L I B E R A L I SAT ION A N D C H I N A’ S E F F E C T ON G L OB A L C A PI TA L F L OW S 11–18 per cent of GDP. He et al (2012) and Saadi Sedik and Sun (2012) come to similar results, estimating that net capital outflows would occur following capital account liberalisation in China. Figure 6: Predicted Impact of Capital Account Liberalisation on China’s International Portfolio Assets and Liabilities Per cent of GDP % % 25 25 20 20 15 15 10 10 5 5 0 Assets Actual (2010) Liabilities Net assets 0 Range of predicted change Note: Portfolio assets and liabilities exclude official reserve assets Source: Bayoumi and Ohnsorge (2013) 5. A Roadmap for Further Capital Account Liberalisation To date, the sequencing of China’s capital account liberalisation has been broadly in line with the IMF’s institutional view (IMF 2012) (Figure 7). The liberalisation process has proceeded gradually. China initially implemented quotas focused on specific investor groups with experiments in certain parts of the country and over time these experiments have been expanded. Going forward it would be good to move from quantity-based to price-based restrictions (e.g. Nishizawa 2016). The process of capital account liberalisation should occur alongside supporting reforms, including reforms to the domestic financial sector. For China, this would involve the ongoing modernisation of the monetary policy framework, imposing hard budget constraints and state-owned enterprise (SOE) reform. Because none of these goals are easily defined, it is difficult to determine the optimal timing of further capital account liberalisation. As a result, further opening up of the capital account is likely to occur gradually and in parallel with other reforms. C O N F E R E N C E VO L U M E | 2 016 169 ALFR ED SCH IPKE Figure 7: Capital Account Opening Gradual increase of quotas; relaxing qualification requirements (inflow and outflow FDI and portfolio) • Modernising monetary policy framework • Implementing hard budget constraints • Reforming SOEs, addressing high corporate debt • • • • Deepening of financial markets Strengthening regulation and supervision Building up capital and liquidity buffers Adequate investment regulations (institutional) • Contingency plans Replacing quotas and qualification requirements with price-based controls (URR or tax) • Further strengthening monetary and exchange rate framework • Continued reform of SOEs and corporate sector • Enhancing monitoring of capital flows • Continued deepening of financial markets • Introducing net stable funding ratio/liquidity charges on non-core funding • Higher risk weights on foreign exchange loans • Eliminating direct lending • Expanding regulatory perimeter to shadow banking/corporate sector Gradual move from pre-approval to registration and notification requirement followed by reporting requirement • Continued improvement of monetary and exchange rate framework • Adequate capital flow monitoring framework in place • Continued deepening of financial markets • Further strengthening of supervisory and regulatory framework Removal of most controls • Track record of well-defined credible monetary policy and full exchange rate flexibility • Adequate supervisory, micro and macro prudential framework in place Source:IMF 6.Conclusion China has made considerable progress in opening the capital account in recent years; however, it continues to formally maintain significant capital controls and remains more closed than other economies at a similar level of development. In the future, one would expect China to integrate further into the global financial system. If China’s capital account were to be fully opened, there would be both sizable inflows and outflows. Previous studies suggest that on net there would initially be a capital outflow. In recent years, China has continued to open its capital account and has indicated that its goal is to move toward ‘managed convertibility’ (Zhou 2015). 170 R E S E RV E B A N K O F AU S T R A L I A C A PI TA L AC C OU N T L I B E R A L I SAT ION A N D C H I N A’ S E F F E C T ON G L OB A L C A PI TA L F L OW S So far, China has opened up its capital account in a way that is broadly in line with the IMF institutional view. As this process moves forward, China should move from quantity- to price-based restrictions, and then also from administrative controls to currency-based regulation and supervision. One of the challenges going forward is the increasing difficulty of enforcing the remaining restrictions as the capital account becomes more open and there are more opportunities to circumvent the rules. C O N F E R E N C E VO L U M E | 2 016 171 ALFR ED SCH IPKE References Bayoumi T and F Ohnsorge (2013), ‘Do Inflows or Outflows Dominate? Global Implications of Capital Account Liberalization in China’, IMF Working Paper No WP/13/189. Habermeier K, A Kokenyne Ivanics, SM Darbar, B Chikako and L Zhu (forthcoming), ‘Capital Account Opening and Capital Account Management’, in WR Lam, M Rodlauer and A Schipke (eds), Modernizing China– Investing in Soft Infrastructure, International Monetary Fund, Washington DC. He D, L Cheung, W Zhang and T Wu (2012), ‘How Would Capital Account Liberalization Affect China’s Capital Flows and the Renminbi Real Exchange Rates?’, China & the World Economy, 20(6), pp 29–54. IMF (International Monetary Fund) (2012), ‘The Liberalisation and Management of Capital Flows: An Institutional View’, Policy Paper, 14 November. IMF (2015), Annual Report on Exchange Arrangements and Exchange Restrictions 2015, International Monetary Fund, Washington DC. Nishizawa K (2016), ‘China May Adopt Tobin Tax on Short-Term Capital Flows, SAFE Says’, Bloomberg online, 22 March. Available at <http://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2016-03-22/china-may-adopt-tobin-taxon-short-term-capital-flows-safe-says>. PBC (The People’s Bank of China) (2016), ‘中国人民银行进一步放开境外机构投资者投资银行 间债券市场’ (The People’s Bank of China Further Opens the Interbank Bond Market to Investment by Cross-Border Institutional Investors), 25 February. Available at <http://www.pbc.gov.cn/goutongjiaol iu/113456/113469/3021206/index.html>. Saadi Sedik T and T Sun (2012), ‘Effects of Capital Flow Liberalization—What is the Evidence from Recent Experiences of Emerging Market Economies?’, IMF Working Paper No WP/12/275. SAFE (State Administration of Foreign Exchange) (2016), ‘改革合格境外机构投资者外汇管理制度 进 一步扩大境内资本市场开放’ (Reform of QFII Foreign Exchange Management System to Further Expand Domestic Capital Market Liberalisation), 4 February. Available at <http://www.safe.gov.cn/resources/ wcmpages/wps/wcm/connect/safe_web_store/safe_web/whxw/zcfgjd/node_news_zcfgjd_store/a500ca0 04b8ef02781dee5196274af30/>. Zhou X (2015), ‘Statement by the Honorable Zhou Xiaochuan Governor of the IMF for China to the ThirtyFirst Meeting of the International Monetary and Financial Committee Washington, D.C., April 18, 2015’, IMFC Statement by Zhou Xiaochuan Governor, People’s Bank of China: On Behalf of the People’s Republic of China, 18 April. 172 R E S E RV E B A N K O F AU S T R A L I A