* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download S0735109716344436_mmc1
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Cardiothoracic surgery wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Echocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
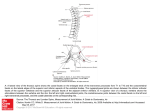
ONLINE APPENDIX INCLUSION AND EXCLUSION CRITERIA. Patients could be included in the study if they agreed to undergo thoracoscopic ablation because of persistent AF, enlarged left atria (left atrial volume index (LAVI) >33 ml/m2, previously failed catheter ablation, or patient preference, and had failed at least 1 class Ic or III AAD, were 18 to 80 years old, and had a life expectancy ≥2 years. Exclusion criteria were: unable or unwilling to take AADs; catheter ablation for AF within the preceding 4 months; myocardial infarction within the preceding 2 months; cerebrovascular accident (any sudden neurological deficit lasting ≥24 h, with or without pathological computed tomographic cerebrum) within the preceding 6 months; New York Heart Association (NYHA) III/IV heart failure, NYHA II or III/IV heart failure with recent hospitalization for decompensation (unless related to or aggravated by AF); left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) <35%; documented carotid stenosis >80%; planned cardiac surgery for other purposes than AF alone; active infection; pregnant or being of childbearing potential without adequate anticonception; requiring AADs for ventricular arrhythmias; documentation of an intracardiac mass or thrombus; being unable to undergo transesophageal echocardiography (TEE); previous thoracic radiation; comorbid conditions possessing undue risks for general anesthesia or thoracoscopic port access; or being unwilling/unable to adhere to the follow-up protocol. 1 Figure 1: Anatomical Localization of the Major Ganglion Plexi. This posterior view of the left and right atrium displays the anatomical location of each major ganglion plexus (GP) and the ligament of Marshall (LOM). ARGP = anterior right GP; ILGP = inferior left GP; IRGP = inferior right GP; IVC = inferior caval vein; LIPV = left inferior PV; LSPV = left superior PV; PA = pulmonary artery; PV = pulmonary vein; RIPV = right inferior PV; RSPV = right superior PV; SLGP = superior left GP; SVC = superior caval vein. 2