* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lecture Notes
Remote ischemic conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Baker Heart and Diabetes Institute wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
History of invasive and interventional cardiology wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Saturated fat and cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
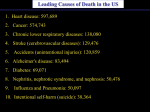
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
Lecture Notes A PowerPoint Presentation Classroom Activity to Accompany Medical Terminology Systems, Seventh Edition Barbara A. Gylys ∙ Mary Ellen Wedding 8 Cardiovascular System 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Structure and Function •Heart •Layers of the heart •Endocardium — inner lining of the heart •Myocardium — heart muscle •Epicardium — top layer of the heart •Pericardium — sac holding the heart 2 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Structure and Function (continued) •Heart (continued) •Circulates blood and delivers oxygen (O2) and nutrients to cells •Right side for circulating blood to lungs for oxygenation (pulmonary circulation) •Left side for circulating blood to all body systems (systemic circulation (see illustration) •Disposes of waste products •Aids lymphatic system in circulating substances 3 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Structure and Function (continued) •Heart (continued) •Heart chambers •Atria — receives blood •Right atria — deoxygenated blood from venae cavae •Left atria — oxygenated blood from lungs •Ventricles — pump blood to the body •Right ventricle — to lungs for oxygenation (pulmonary circulation) •Left ventricle — through the aorta to the body systems (systemic circulation) 4 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Structure and Function (continued) •Heart (continued) •Valves—prevent backflow (regurgitation) of blood •Tricuspid valve — from right ventricle into right atrium •Bicuspid (mitral) valve — from left ventricle into left atrium •Pulmonic (pulmonary semilunar) valve —from pulmonary artery into right ventricle •Aortic (aortic semilunar) valve — from aorta into left ventricle 5 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Structure and Function (continued) •Blood vessels •Arteries •Carry blood away from the heart •Carry oxygenated blood (except pulmonary artery) •Have strong muscular walls to withstand the surge of blood at each heartbeat 6 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Structure and Function (continued) •Blood vessels (continued) •Capillaries •Microscopic vessels composed of endothelial cells •Joining arterial system with venous system •Have thin walls to allow exchange of susbstances between blood and body tissues 7 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Structure and Function (continued) •Blood vessels (continued) •Veins •Carry blood to the heart •Carry deoxygenated blood (except for pulmonary vein) •Contain valves to help the return of blood to the heart 8 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Structure and Function Exercise 1. What is the main function of the heart? 2. What structures prevent backflow of blood into the heart? 9 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Structure and Function Exercise 1.What is the main function of the heart? To pump blood through blood vessels to all cells of the body 2.What structures prevent backflow of blood into the heart? Heart valves 10 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Structure and Function Exercise 3. List two major functions of the cardiovascular (CV) system. 4. What function does the CV system perform for the lymphatic system? 11 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Structure and Function Exercise 3. List two major functions of the cardiovascular (CV) system. Delivery of oxygen, nutrients, and other essential substances to body cells and removal of waste products of cellular metabolism 4. What function does the CV system perform for the lymphatic system? Aids in transporting excess fluid from interstitial spaces and returns it to blood as plasma 12 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Structure and Function Exercise 5. List the four chambers of the heart. 6. What are the four heart valves and their locations? 13 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Structure and Function Exercise 5. List the four chambers of the heart. Right atrium, right ventricle, left atrium, left ventricle 6. What are the four heart valves and their locations? Tricuspid, between the right atrium and right ventricle; bicuspid (mitral) between the left atrium and left ventricle; pulmonic (pulmonary semilunar) at the entrace of the pulmonary artery; aortic (aortic semilunar) at the entrance of the aorta 14 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Combining Forms Exercise List the CFs for: 1. heart: 2. atrium: 3. ventricle: 4. septum: 15 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Combining Forms Exercise 1. heart: cardi/o, coron/o 2. atrium: atri/o 3. ventricle: ventricul/o 4. septum: sept/o 16 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Combining Forms Exercise 5. vein: 6. artery: 7. valve: 8. electricity: 17 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Combining Forms Exercise 5. vein: phleb/o 6. artery: arteri/o 7. valve: valv/o, valvul/o 8. electricity: electr/o 18 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Combining Forms Exercise 9. fatty plaque: 10. embolus: 11. pulse: 12. muscle: 19 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Combining Forms Exercise 9. fatty plaque: ather/o 10.embolus: embol/o 11.pulse: sphygm/o 12.muscle: my/o 20 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Combining Forms Exercise 13. narrowing, stricture: 14. blood clot: 21 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Combining Forms Exercise 13. narrowing, stricture: sten/o 14. blood clot: thromb/o 22 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Complete the Medical Word Exercise 1. forming an opening (mouth) in the septum: /o/ 2. destruction of a blood clot: /o/lysis 3. pertaining to the ventricles: /ar 4. tumor of fatty plaque: /oma 23 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Complete the Medical Word Exercise 1. forming an opening (mouth) in the septum: sept/o/stomy 2. destruction of a blood clot: thromb/o/lysis 3. pertaining to the ventricles: ventricul/ar 4. tumor of fatty plaque: ather/oma 24 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Complete the Medical Word Exercise 5. pertaining to within a vessel: endo/ 6. inflammation of an arteriole: 7. condition of an embolus: /ar / /ism 8. pertaining to the muscle of the heart: /o/ /al 25 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Complete the Medical Word Exercise 5. pertaining to within a vessel: endo/vascul/ar 6. inflammation of an arteriole: arteriol/itis 7. condition of an embolus: embol/ism 8. pertaining to the muscle of the heart: my/o/cardi/al 26 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Build Medical Words Exercise 1. narrowing of the aorta: 2. rupture of the heart: 3. condition (of a heart) without rhythm: 27 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Build Medical Words Exercise 1. narrowing of the aorta: aort/o/stenosis 2. rupture of the heart: cardi/o/rrhexis 3. condition (of a heart) without rhythm: a/rrhythm/ia 28 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Build Medical Words Exercise 4. incision of the ventricles: 5. condition of a slow heart (beat): 6. process of recording the heart: 29 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Build Medical Words Exercise 4. incision of the ventricles: ventricul/o/tomy 5. condition of a slow heart (beat): brady/card/ia 6. process of recording the heart: cardi/o/graphy 30 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Build Medical Words Exercise 7. enlargement of the heart: 8. resembling a pulse: 9. tumor of a blood vessel: 10. condition of a rapid heart (beat): 31 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Build Medical Words Exercise 7. enlargement of the heart: cardi/o/megaly 8. resembling a pulse: sphygm/oid 9. tumor of a blood vessel: hemangi/oma 10.condition of a rapid heart (beat): tachy/card/ia or tachy/cardia 32 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Diseases and Conditions Arteriosclerosis •Progressive, degenerative disease of the arteries •Commonly caused by build-up of fatty plaque (atheroma) • Illustration: Arteriosclerosis of the carotid artery (Note embolization of plaque that may travel to the brain.) 33 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Diseases and Conditions (continued) Arteriosclerosis (continued) •Possibly affecting any artery but most commonly the coronary and carotid arteries •Causes wall weakness, loss of elasticity, and blood clot formation 34 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Diseases and Conditions (continued) Arteriosclerosis •Treatment (continued) • Pharmacological • Decrease blood cholesterol level • Control blood clotting • Surgical • Endarterectomy • Vascular bypass surgery • Stenting 35 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Clinically Related Exercise 1. Mr. L. has dizziness, confusion, and weakness on the left side of his body. Ultrasound of his carotid artery shows blockage by fatty plaque. The physician diagnoses this condition as (arteriosclerosis, aneurysm, arteriorrhexis). 2. Mr. L. will undergo removal of plaque build-up from his carotid artery, a surgical procedure called (arteriectomy, endarterectomy, venulectomy). 36 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Clinically Related Exercise 1. Mr. L. has dizziness, confusion, and weakness on the left side of his body. Ultrasound of his carotid artery shows blockage by fatty plaque. The physician diagnoses this condition as arteriosclerosis. 2. Mr. L. will undergo removal of plaque buildup from his carotid artery, a surgical procedure called (arteriectomy, endarterectomy, venulectomy). 37 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Clinically Related Exercise 3. Mrs. J. underwent ultrasound of her carotid arteries. This test revealed minimal plaque in her left carotid artery. Although not imminent, her physician explained that an excessive build-up of plaque may cause a(n) (myocardial infarction, stroke, aneurysm). 38 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Clinically Related Exercise 3. Mrs. J. underwent ultrasound of her carotid arteries. This test revealed minimal plaque in her left carotid artery. Although not imminent, her physician explained that an excessive buildup of plaque may cause a (myocardial infarction, stroke, aneurysm). 39 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Diseases and Conditions (continued) Coronary artery disease (CAD) •Any disorder of the coronary arteries that affects their ability to deliver blood to the myocardium • Illustration: (A) Partial coronary artery occlusion. (B) Almost total occlusion 40 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Diseases and Conditions (continued) CAD (continued) •Most commonly caused by arteriosclerosis •Partial or total occlusion • Partial occlusion — distal tissues become ischemic, compromising heart function • Total occlusion — distal tissues undergo infarction, possibly causing death •Possible blood clot formation or rupture caused by plaque 41 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Diseases and Conditions (continued) CAD (continued) •Signs and symptoms • Classic signs and symptoms • Anginal pain (See illustration for typical sites of anginal pain.) • Shortness of breath (SOB) • Diaphoresis • Pallor 42 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Diseases and Conditions (continued) CAD (continued) •Signs and symptoms • Risk factors (continued) • Smoking • Stress • Physical inactivity • Family history • Diabetes • Obesity • High cholesterol 43 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Diseases and Conditions (continued) CAD (continued) •Treatment • Lifestyle changes • Quit smoking • Low-fat diet • Regular exercise • Weight and stress management • Pharmacological • Control of angina, hypertension, and triglyceride levels • Anticoagulant therapy, if needed 44 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Diseases and Conditions (continued) CAD (continued) •Treatment (continued) • Surgical intervention • Percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty (PTCA) • Coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) 45 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Clinically Related Exercise 1. Mr. T. has chest pain that radiates to his left arm. He is pale and perspiring profusely. An ECG reveals necrosed heart tissue. His diagnosis is (fibrillations, MI, palpitations). 2. Mr. X. is diagnosed with CAD. The physician tells him that lifestyle changes could reduce the risk of further heart complications. These changes include exercising regularly, losing weight, reducing stress, and maintaining a diet low in saturated . 46 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Clinically Related Exercise 1. Mr. T. has chest pain that radiates to his left arm. He is pale and perspiring profusely. An ECG reveals necrosed heart tissue. His diagnosis is (fibrillations, MI, palpitations). 2. Mr. X. is diagnosed with CAD. The physician tells him that lifestyle changes could reduce the risk of further heart complications. These changes include exercising regularly, losing weight, reducing stress, and maintaining a diet low in saturated fat. 47 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Clinically Related Exercise 3. A 50-year-old male arrives at the clinic complaining of pressure and pain in his chest. After a brief examination, the physician concludes that his symptoms are due to lack of oxygen to the heart muscle, a condition called (infarction, ischemia, necrosis). 48 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Clinically Related Exercise 3. A 50-year-old male arrives at the clinic complaining of pressure and pain in his chest. After a brief examination, the physician concludes that his symptoms are due to lack of oxygen to the heart muscle, a condition called (infarction, ischemia, necrosis). 49 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Diseases and Conditions (continued) Aneurysm •Local dilation of an artery or chamber of the heart due to weakening of its walls •May cause thrombus formation, hemorrhage from rupture, or ischemia •Commonly located in the abdomen, chest, or peripheral arteries 50 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Diseases and Conditions (continued) Aneurysm (continued) •Three main types (see illustration below) • Fusiform (spindle-shaped) • Saccular (sac-shaped) • Dissecting (separated layers of the vessel wall) 51 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Diseases and Conditions (continued) Aneurysm (continued) •Signs and symptoms • Possibly asymptomatic • In a slender patient, a pulsating middle and upper abdominal mass • Mild to severe weakness • Sweating • Tachycardia • Hypotension 52 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Diseases and Conditions (continued) Aneurysm (continued) •Treatment • Depends on the size of the aneurysm and likelihood that it will rupture as well as the general physical status of the patient • Surgical treatment for a large unruptured aneurysm •Interventional minimally invasive repair using imaging to guide the catheter and graft inside the artery • Catheter is passed into the femoral artery and directed to the aneurysm •Open surgical treatment, in which a Dacryon graft (synthetic material) replaces the damaged blood vessel 53 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Clinically Related Exercise 1. An aneurysm may cause weakness, sweating, tachycardia, and low blood pressure, also known as (hypotension, hypertension, hypothymia). 2. During a physical examination, the physician palpates a pulsating mass in the patient's abdomen. This sign is characteristic of a(n) (aneurysm, carcinoma, tumor). 54 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Clinically Related Exercise 1. An aneurysm may cause weakness, sweating, tachycardia, and low blood pressure, also known as (hypotension, hypertension, hypothymia). 2. During a physical examination, the physician palpates a pulsating mass in the patient's abdomen. This sign is characteristic of an (aneurysm, carcinoma, tumor). 55 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Clinically Related Exercise 3. Mr. B.'s physician advises him that he has an abdominal aneurysm. The physician explains that the aneurysm is likely the cause of his episodes of a very rapid heartbeat, called . 4. During surgery, the surgeon discoveres a spindle-shaped aneurysm in a patient's artery. This type of aneurysm is known as a (dissecting, fusiform, saccular) aneurysm. 56 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Clinically Related Exercise 3. Mr. B.'s physician advises him that he has an abdominal aneurysm. The physician explains that the aneurysm is likely the cause of his episodes of a very rapid heartbeat, called tachycardia. 4. During surgery, the surgeon discoveres a spindle-shaped aneurysm in a patient's artery. This type of aneurysm is known as a (dissecting, fusiform, saccular) aneurysm. 57 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Diseases and Conditions (continued) Varicose veins •Twisted, enlarged veins caused by blood pooling from incompetent valves (See illustration.) •Common locations • Lower legs • Esophagus (called esophageal varices) • Rectum (called hemorrhoids) 58 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Diseases and Conditions (continued) Varicose veins (continued) •Signs and symptoms • Engorged, twisted veins of the legs • Pain • Edema • Skin ulcers • Burning sensation • Itching 59 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Diseases and Conditions (continued) Varicose veins •Treatment (continued) • Lifestyle changes • Avoiding long periods of standing • Elevating legs as much as possible • Wearing compression stockings • Surgery • Sclerotherapy • Laser ablation • Radiofrequency ablation • Ligation and stripping (in heavily damaged or diseased veins) 60 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Clinically Related Exercise 1. With each of her four pregnancies, Mrs. M. noticed an increase in her varicose veins. She now complains of pain that is not relieved when she elevates her legs or uses compression stockings. She will have an injection of an agent that hardens and eventually destroys the varicose veins. This procedures is known as (sclerotherapy, ligation and stripping, laser ablation). 61 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Clinically Related Exercise 1. With each of her four pregnancies, Mrs. M. noticed an increase in her varicose veins. She now complains of pain that is not relieved when she elevates her legs or uses compression stockings. She will have an injection of an agent that hardens and eventually destroys the varicose veins. This procedures is known as (sclerotherapy, ligation and stripping, laser ablation). 62 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Clinically Related Exercise 1. Mr. G. is an 87-year-old nursing home resident who has a history of vascular problems and dependent edema. Recently, he developed skin ulcers on his lower legs. His daughter asked what caused the ulcers. The nurse explains that skin ulcers are a complication associated with (varicose veins, advanced age, skin allergies). 63 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Clinically Related Exercise 1. Mr. G. is an 87-year-old nursing home resident who has a history of vascular problems and dependent edema. Recently, he developed skin ulcers on his lower legs. His daughter asked what caused the ulcers. The nurse explains that skin ulcers are a complication associated with (varicose veins, advanced age, skin allergies). 64 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Vocabulary Challenge Exercise 1. arrhythmia: 2. embolus: 3. hypertension: 65 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Vocabulary Challenge Exercise 1. arrhythmia: inability of the heart to maintain a normal sinus rhythm; also called dysrhythmia 2. embolus: mass of undissolved matter (foreign object, gas, tissue, thrombus) circulating in the blood until it becomes lodged in a vessel 3. hypertension: in adults, a persistently elevated blood pressure that exceeds a systolic pressure of 140 mm Hg or a diastolic pressure of 90 mm Hg 66 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Vocabulary Challenge Exercise 4. infarct: 5. ischemia: 6. stent: 67 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Vocabulary Challenge Exercise 4. infarct: area of tissue that undergoes necrosis following cessation of blood supply 5. ischemia: local and temporary deficiency of blood supply due to circulatory obstruction 6. stent: slender, thread-like device used to hold open vessles, tubes, or obstructed arteries 68 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Medical and Surgical Procedures •Automatic implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (AICD) • Device implanted in patients at risk for developing arrhythmias (See illustration.) • Monitoring heart rate and correcting tachycardia or bradycardia • Delivery of a jolt of electricity to restart the heart if it stops 69 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Medical and Surgical Procedures (continued) •Coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) • Surgical treatment for coronary artery disease • Grafted vessel anastomosed around a blocked segment of the coronary artery (see illustration) 70 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Medical and Surgical Procedures (continued) •Percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty (PTCA) • Balloon catheter insertion through a small incision • Balloon inflation, pressing fatty plaque to the vessel's sides, widening the opening • Illustration: (A) Catheter insertion. (B) Balloon inflation and widening of opening. (C) Balloon deflation. (D) Catheter withdrawal. 71 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Medical and Surgical Procedures (continued) •Stent insertion • Scaffolding device used to hold a vessel open • Illustration: (A) Balloon catheter delivering stent. (B) Balloon inflation, compressing plaque and expanding stent. (C) Balloon catheter withdrawal, leaving stent in vessel. 72 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Medical and Surgical Procedures (continued) •Endarterectomy • Procedure to remove atheromatous plaque from the inner lining of an artery • Illustration: (A) Incision of carotid artery. (B) Removal of plaque. (C) Suture of carotid artery. 73 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Clinically Related Exercise 1. The surgeon removed a vessel from Mr. C.'s leg. The surgeon used it to bypass a blocked segment in Mr. C.'s coronary artery. The surgeon anastomosed one end of this vessel to the aorta and the other end to the coronary artery distal to the occlusion. The abbreviation for this bypass surgery is . 74 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Clinically Related Exercise 1. The surgeon removed a vessel from Mr. C.'s leg. The surgeon used it to bypass a blocked segment in Mr. C.'s coronary artery. The surgeon anastomosed one end of this vessel to the aorta and the other end to the coronary artery distal to the occlusion. The abbreviation for this bypass surgery is CABG. 75 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Clinically Related Exercise 2. Mr. D. is diagnosed with CAD. To treat Mr. D., the surgeon proposes an endovascular procedure using a balloon catheter. This procedure will reopen narrowed blood vessels and restore blood flow and is known as an (anastomosis, angioplasty, endarterectomy). 76 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Clinically Related Exercise 2. Mr. D. is diagnosed with CAD. To treat Mr. D., the surgeon proposes an endovascular procedure using a balloon catheter. This procedure will reopen narrowed blood vessels and restore blood flow and is known as an (anastomosis, angioplasty, endarterectomy). 77 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Clinically Related Exercise 3. Ms. L. presents with complaints associated with stroke. After a complete workup, the physician diagnoses her with hardening of the corotid artery and proposes implantation of a device to hold this vessel open. This device is known as a(n) . 78 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Clinically Related Exercise 3. Ms. L. presents with complaints associated with stroke. After a complete workup, the physician diagnoses her with hardening of the corotid artery and proposes implantation of a device to hold this vessel open. This device is known as a stent. 79 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Clinically Related Exercise 4. Mrs. B. is diagnosed with ventricular fibrillation. To treat her condition, the cardiac surgeon will implant an automatic battery-powered defibrillator. This device automatically corrects arrhythmias by sending electrical impulses to the heart. The abbreviation for this defibrillator is . 80 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Clinically Related Exercise 4. Mrs. B. is diagnosed with ventricular fibrillation. To treat her condition, the cardiac surgeon will implant an automatic battery-powered defibrillator. This device automatically corrects arrhythmias by sending electrical impulses to the heart. The abbreviation for this defibrillator is AICD. 81 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Clinically Related Exercise 5. Mr. W. is scheduled to undergo balloon angioplasty to crush fatty deposits in the coronary vessel and improve blood flow. The nurse explains that this procedure is known as PTCA, which stands for . 82 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Clinically Related Exercise 5. Mr. W. is scheduled to undergo balloon angioplasty to crush fatty deposits in the coronary vessel and improve blood flow. The nurse explains that this procedure is known as PTCA, which stands for percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty. 83 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Clinically Related Exercise 6. Mr. S. has suffered with cardiomyopathy for several years and is now experiencing heart failure. He is wheelchair-bound and suffers from shortness of breath and a very slow heart rate. The nurse charts his abnormally slow heart rate as . 84 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Clinically Related Exercise 6. Mr. S. has suffered with cardiomyopathy for several years and is now experiencing heart failure. He is wheelchair-bound and suffers from shortness of breath and a very slow heart rate. The nurse charts his abnormally slow heart rate as bradycardia. 85 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Diagnostic Procedures •Cardiac catheterization • Catheter guided into the heart via a vein or an artery (see illustration) for diagnostic purposes, including: • Measuring blood flow through coronary vessels • Measuring intracardiac or intravascular pressure • Obtaining blood samples • Conducting radiological studies 86 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Diagnostic Procedures (continued) •Electrocardiography (ECG, EKG) • Painless, noninvasive test that records electrical impulses of the heart using electrodes placed strategically on the body • Impulses displayed as a line tracing on a paper strip with spikes and dips called waves • Wave interpretation used to identify various cardiac irregularities 87 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Diagnostic Procedures (continued) •ECG (continued) • Holter monitor • ECG that records electrical activity for 24 to 48 hours (See illustration.) • Identifies irregularities that would be missed with a regular ECG 88 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Diagnostic Procedures (continued) •ECG (continued) •ECG stress test •ECG that evaluates heart function under stressful conditions •Performed in a controlled environment •Drug-induced stress •Exercise-induced stress, also called treadmill test (See illustration.) 89 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Diagnostic Procedures (continued) •Carotid artery ultrasound • Painless screening test that uses an ultrasound probe passed over the carotid arteries • Display of blockage in the carotid artery that places one at risk for a stroke 90 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Diagnostic Procedures (continued) •Transesophageal echocardiography (TEE) • Insertion of an esophagoscope fitted with an ultrasound transducer that is guided down the throat • Images of the heart shown without interference from the ribs or other structures • Provides information on the heart chambers and valves 91 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Diagnostic Procedures (continued) •Coronary angiography • Radiological procedure that visualizes the coronary arteries • Use of a cardiac catheter to administer contrast medium to the coronary arteries • Images used to identify areas of blockage • Illustration: Coronary angiography with fluoroscopy (real-time images to guide catheterization) 92 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Build a Medical Word Exercise 1. record of electrical (activity) of the heart: 2. process of recording electrical (activity) of the heart: 93 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Build a Medical Word Exercise 1. record of electrical (activity) of the heart: electr/o/cardi/o/gram 2. process of recording electrical (activity) of the heart: electr/o/cardi/o/graphy 94 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Build a Medical Word Exercise 3. process of recording (radiography) a vein: 4. process of recording (radiography) the aorta: 95 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Build a Medical Word Exercise 3. process of recording (radiography) a vein: ven/o/graphy 4. process of recording (radiography) the aorta: aort/o/graphy 96 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Build a Medical Word Exercise 5. process of recording (radiography) (heart and blood) vessels (after injection of a contrast dye): 6. pertaining to across the esophagus: 97 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Build a Medical Word Exercise 5. process of recording (radiography) (heart and blood) vessels (after injection of a contrast dye): angi/o/graphy 6. pertaining to across the esophagus: trans/esophag/eal 98 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Pharmacology •Statins • Drugs used to lower cholesterol in the blood and reduce its production in the liver by blocking enzymes that produce it •Nitrates • Drugs used to dilate blood vessels, increasing oxygen flow to the heart 99 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Pharmacology •Thrombolytics • Drugs that break up clots and limit damage that may result from vessels blocked by a clot • Also called clot busters •Beta-blockers • Drugs that cause a decrease in heart rate • Commonly prescribed for hypertension 100 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Clinically Related Exercise 1. Mrs. T. is diagnosed with deep vein thrombosis in her lower leg. Her physician prescribes a drug that dissolves a blood clot, known as a (beta blocker, nitrate, thrombolytic). 2. Mr. B.'s doctor diagnoses him with hypercholesterolemia. The doctor advises him to follow a low-fat diet and prescribes a drug that reduces cholesterol levels, known as a (beta blocker, nitrate, statin). 101 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Clinically Related Exercise 1. Mrs. T. is diagnosed with deep vein thrombosis in her lower leg. Her physician prescribes a drug that dissolves a blood clot, known as a (beta blocker, nitrate, thrombolytic). 2. Mr. B.'s doctor diagnoses him with hypercholesterolemia. The doctor advises him to follow a low-fat diet and prescribes a drug that reduces cholesterol levels, known as a (beta blocker, nitrate, statin). 102 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Clinically Related Exercise 3. Three years ago Mrs. S. underwent angioplasty. She is now diagnosed with reccurring CAD. To relieve her “tightening chest pain” the physician prescribes a drug called a (beta blocker, nitrate, statin). 4. Mr. K.’s BP is persistently over 150/95. To address this problem, the doctor prescribes a (beta blocker, nitrate, statin). 103 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Clinically Related Exercise 3. Three years ago Mrs. S. underwent angioplasty. She is now diagnosed with reccurring CAD. To relieve her “tightening chest pain” the physician prescribes a drug called a (beta blocker, nitrate, statin). 4. Mr. K.’s BP is persistently over 150/95. To address this problem, the doctor prescribes a (beta blocker, nitrate, statin). 104 Copyright © 2013 by F.A. Davis Company. All rights reserved. This product is protected by copyright. No part of it may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any means— electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or otherwise—without written permission from the publisher. 105