* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What-you-should-know-Unit
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
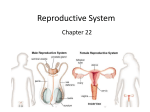
Unit 2a: What you should know 1. The _______________ of the human male produce sperm from germline cells in seminiferous tubules and make testosterone in ________________________ cells. 2. The mobility and viability of sperm are maintained by fluids secreted by the ____________ gland and _________________ vesicles. 3. The _____________ of the human female contain __________________ cells that produce ova (eggs) each surrounded by a protective ______________. Hormones made by the ovary are oestrogen and __________________. 4. The pituitary gland releases ______________________________________ hormone (FSH) and interstitial-cell-stimulating hormone (ICSH)/_____________________ hormone (LH). 5. In men, FSH stimulates sperm production and ICSH promotes ______________________ production. The concentration of testosterone is maintained at a steady level by ________________ feedback control. 6. In women, FSH stimulates the development of a follicle containing an ovum (egg) and the secretion of ___________________. LH triggers ________________ and brings about the development of the corpus ___________________ which secretes progesterone. 7. Oestrogen stimulates the proliferation of the _______________________ and progesterone promotes its further development and _________________________________. 8. The ___________________ cycle lasts for 28 days and involves a follicular ________ and a luteal phase. 9. Fertility in men is _____________________; fertility in women is __________, being restricted to the 3-4 days following ovulation in each monthly cycle. 10. Infertility may be caused by failure to ovulate, blockage of _________________ or failure of ____________________ in women, and low ____________ count in men. 11. Methods of treatment of infertility include the use of drugs that _________________ ovulation, artificial _____________________, in___________ fertilisation (IVF) and intracytoplasmic sperm ____________________ (ICSI). Pre-implantation ____________________________ diagnosis may be used during IVF to check an embryo for chromosomal defects before implantation. 12. Some methods of contraception are based on ______________________ knowledge of the menstrual cycle and the ____________________ of fertile periods. Other physical methods depend on ______________________, intrauterine devices or IUDs. Some __________________ methods prevent follicles from being stimulated and eggs from being released. Others cause thickening of cervical ___________. 13. During antenatal care, a _____________ scan is made by ultrasound imaging to determine the stage the pregnancy has reached. An _______________ scan is used to detect physical problems in the fetus. 14. Signs of medical conditions suffered by pregnant women can be detected using screening tests for ______________ chemicals. These allow risk of genetic disorders in the fetus to be assessed and may be followed up by _______________ tests. 15. A ________________ is a display of a complement of chromosomes arranged in pairs to show their form, size and number. 16. During _________________________, a sample of amniotic fluid is taken to obtain cells for karyotyping to check for __________________ abnormalities. During _______________ villus sampling, cells for the same purpose are obtained from the placenta. This procedure carries a higher risk of ____________________ than amniocentesis. 17. A Rhesus-negative mother is given ____________________________ antibodies after the birth of a Rhesus-positive baby to destroy any Rhesus ________________ before her immune system has time to respond to them. 18. ______________________ screening is carried out on newborn babies to check for metabolic disorders such as PKU. Information about a particular characteristic can be collected from the members of a family and be used to construct a _________________ chart. Single gene disorders show different patterns of inheritance, such as autosomal recessive. o o o o o amniocentesis anomaly antigens anti-rhesus avoidance o o o o o o barriers o biological dating diagnostic endometrium follicle follicle stimulating o genetic o germline o o o o o o o o o o o o chemical chorionic chromosomal continuous o cyclical o o o o o implantation injection insemination interstitial o karyotype luteinising luteum marker menstrual miscarriage o mucus o negative oestrogen ovaries oviducts ovulation o pedigree o o o o o phase postnatal progesterone prostate seminal o sperm o sterilisatio n o stimulate o testes o testosterone o vascularisat ion o vitro