* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Boundaries
Gene regulatory network wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
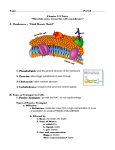
Cell Boundaries HONORS BIOLOGY Cell Membranes 1. One of the most important functions of a cell membrane is: to regulate the movement of molecules into and out of a cell 2. A cell membrane is said to be Selectively Permeable __________________________ • Which means only specific kinds of molecules can get through the membrane • Another word for it is Semipermeable ______________________ 3. Selectively Permeable Cell membranes let some molecules enter a cell, but prevents other molecules from getting in. Can Enter - Water - Small Molecules (O2 & CO2) - Non-polar lipids Can Not Enter - Macromolecules - Ions (Na+,Cl-) - Hydrophilic molecules (glucose) 5. Concentration The concentration of a solution is: The mass of the SOLUTE divided by the volume of the SOLUTION For example: 10g/1L The more solute per volume equals a greater concentration. 6. Diffusion The movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration Example of Diffusion: Beaker of water. Add salt to the water. Will all of the water be salty or just the side of the beaker that you dumped the salt into? When you add salt the salt will diffuse to all of the water. Example of Diffusion: The smell of popcorn after it’s been popped. Does the smell of popcorn stay where the popcorn was popped? Why or why not? Diffusion http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0072495855/student_vi ew0/chapter2/animation__how_diffus ion_works.html Osmosis The diffusion of water. The movement of water from a high water concentration to a low water concentration. Osmosis http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0072495855/student_vi ew0/chapter2/animation__how_osmo sis_works.html Hypotonic Solution has a lower solute concentration than the cell Water enters the cell, animal cells can expand and possibly burst. Isotonic The concentration of the solutes is the same inside and outside the cell Hypertonic Solution has a higher solute concentration than the cell Water leaves the cell, animal cells can shrink. Facilitated Diffusion The movement of specific molecules across cell membranes through protein channels. Facilitated Diffusion http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0072495855/student_vi ew0/chapter2/animation__how_facilit ated_diffusion_works.html Active Transport Energy requiring process that moves material across a cell membrane against a concentration difference. Active Transport http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0072495855/student_vi ew0/chapter2/animation__how_the_s odium_potassium_pump_works.html Overview Endocytosis: Taking material in to the cell through cell membrane pockets Phagocytosis: Solids or large molecules moved Pinocytosis: Liquids moved Exocytosis: Releasing material from the cell