* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Heart
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
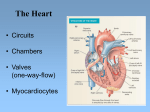
The Heart
• Circuits
• Chambers
• Valves
(one-way-flow)
• Myocardiocytes
heart –> lungs –> heart
heart –> body –> heart
Volumes?
Pressures?
The Circulatory system is a "closed
circulation"
Systemic
Circuit
Pulmonary
Circuit
Systemic
Circuit
Artery =
Vein =
Trace a RBC!
The Heart has 4 Valves
To prevent retrograde flow of blood.
2 atrioventricular valves (AV)
between the atria and ventricles.
1) Right AV (tricuspid) valve
2) Left AV (bicuspid/mitral) valve
2 semilunar valves
between a ventricle and artery.
1) Aortic semilunar valve
2) Pulmonary semilunar valve
Two heart sounds: “Lub” and “Dup”
1. Closure of AV valves = “Lub”
2. Closure of Semilunar valves = “Dup”
Disorders of Heart Valves
Stenosis Prolapse -
Can lead to abnormal Heart sounds,
e.g., heart murmurs.
Indicates: 1) turbulence
2) retrograde flow
stimulus
Myocardiocytes: Calcium induced Calcium release
Graded Contraction of Heart
Force generated by myocardiocyte contraction is:
1. Proportional to amount of Calcium ions (Ca2+)
[Ca2+] => more crossbridges, more force & speed.
Graded Contraction of Heart
Force generated by myocardiocyte contraction is:
1. Proportional to amount of Calcium ions (Ca2+)
[Ca2+] => more crossbridges, more force & speed.
2. Modulated by Autonomic N.S.
=> Sym HR and Force
=> Para HR
Sympathetic – speeds heart rate by Ca2+ influx.
Parasympathetic – slows rate by K+ efflux,
Ca2+ influx.
Graded Contraction of Heart
Force generated by myocardiocyte contraction is:
1. Proportional to amount of Calcium ions (Ca2+)
[Ca2+] => more crossbridges, more force & speed.
2. Modulated by Autonomic N.S.
=> Sym HR and Force
=> Para HR
3. Stretch-Length-Tension Relationship
stretch, => Ca2+ entering => contraction force
Factors Influencing Stroke Volume
The Cardiac Cycle
The Cardiac Cycle
Mechanical Events of the Heart
1. Late Diastole: “Heart at rest” all chambers relaxed
filling with blood (passive filling ~ 80% full).
2. Atrial Systole: atria contract, adds the last 20% of
blood to ventricles (top off ventricles)
Occurs after P-wave on EKG
End Diastolic Volume (EDV) = Maximum ventricular volume
3. Ventricular Systole (part 1):
Ventricular contraction begins - Pressure (P).
Closure of AV valves = 1st heart sound ("lub")
Sealed Compartment – all valves are closed.
Isovolumetric ventricular contraction:
=> pressure builds as volume stays the same.
4. Ventricular Systole (part 2):
Ejection phase: P pushes open semilunar valves,
blood forced out into artery leaving ventricle.
Pulmonary Semilunar => 25 mmHg (minimum pressure)
Aortic Semilunar => 80 mmHg (minimum pressure)
End Systolic Volume (ESV) = volume remaining in
heart after ejection (~½).
Stroke Volume = EDV - ESV (ml/beat)
5. Ventricular Diastole:
Relaxation of ventricles, artery back flow slams
semilunar valves shut = 2nd heart sound ("dup").
Sealed Compartment again – all valves are closed.
Isovolumetric ventricular relaxation:
=> pressure as volume stays the same.
The AV valves then open, refilling starts –
back to start of cycle.
Electrical Conduction System
Sino Atrial (SA) Node
Atrial Ventricular (AV) Node
AV Bundle (of His)
L and R Bundle Branches
Purkinje Fibers
The ECG
P wave:
PR interval:
QRS complex:
T wave: