* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Eaton Presentation from May 2014
Fuse (electrical) wikipedia , lookup
War of the currents wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Earthing system wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Single-wire earth return wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic core wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
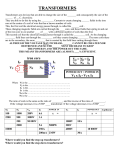
Article 450 - Transformers Thomas A. Domitrovich, P.E. National Application Engineer LEED® Accredited Professional Eaton Corporation Electrical Group 1000 Cherrington Parkway Moon Township, PA 15108 Cell: 412-716-1475 email: [email protected] Tim McBride, P.E. Application Engineer © 2008 Eaton Corporation. All rights reserved. The Transformer An electrical device that transfers energy by magnetic induction from one circuit to another. Usually the voltage and current are transformed from one level to another. 2 2 The Transformer – Basic Components Dry-Type Transformer Example • Primary & Secondary Windings • Core • Frame • Enclosure • Ventilation 3 3 Transformer Types – Sampling • Step – Up • Step – Down • Autotransformer • Isolation Transformer • Single – Phase • Polyphase • Harmonic Transformers • Instrument Transformers 4 4 Transformer Locations / Applications • Utility Supply To Facilities • Commercial, Industrial, Residential and More • Power Distribution Equipment • Switchgear, Switchboards • Utilization Equipment Control Power • Motor Control Centers, Industrial Control Panels • Instrumentation Applications • Metering and Relaying 5 5 Utility G OC PD OC PD OC PD OC PD OC PD OC PD VT OC PD CT OC PD M M OC PD Industrial Control Panel OC PD OC PD OC PD OC PD M OC PD OC PD 6 6 Utility G OC PD OC PD • Main Incoming Utility Transformer OC PD OC PD OC PD OC PD VT OC PD CT OC PD M M OC PD Industrial Control Panel OC PD OC PD OC PD OC PD M OC PD OC PD 7 7 Utility G OC PD OC PD Instrumentation Transformers OC PD OC PD OC PD OC PD VT OC PD CT OC PD M M OC PD Industrial Control Panel OC PD OC PD OC PD OC PD M OC PD OC PD 8 8 Utility G OC PD OC PD Power Distribution Transformers OC PD OC PD OC PD OC PD VT OC PD CT OC PD M M OC PD Industrial Control Panel OC PD OC PD OC PD OC PD M OC PD OC PD 9 9 Utility G OC PD OC PD Control Power Transformers OC PD OC PD OC PD OC PD VT OC PD CT OC PD M M OC PD Industrial Control Panel OC PD OC PD OC PD OC PD M OC PD OC PD 10 10 Utility G OC PD OC PD Transformers Are A Very Important Part of The Power Distribution System OC PD OC PD OC PD OC PD VT OC PD CT OC PD M M OC PD Industrial Control Panel OC PD OC PD OC PD OC PD M OC PD OC PD 11 11 Transformer Basics © 2008 Eaton Corporation. All rights reserved. • 3-Phase Transformers • Incorporate three sets of windings • Can be wired Delta or Y on primary or secondary • Can be grounded or ungrounded • 1-Phase Transformers 13 13 Three Phase Delta-Wye Vll = VΦ 14 Vll - √ 3*VΦ 14 VΦ 14 Basic Transformer Principle ● A voltage and current in the primary coil magnetize the iron core. ● The magnetic field in the core induces a voltage and current in the secondary coil. CORE Enclosure Primary Secondary windings windings 15 15 Transformer Example Primary Core Secondary V1 N1 = V1 = 480 volts V2 = 120 volts V2 N2 A2 N1 = N2 = 100 N1 = 400 A1 N2 V1 A2 = A1 = 52 amps N1 - # turns (primary) A2 = V2 208 amps V1-primary voltage N2 - # turns (secondary) V2-secondary voltage A1 A1-primary current A2-secondary current 16 16 KVA KVA is the transformer’s capacity or load that it can handle. Three Phase Single Phase KVA = Volts * Amps 1000 KVA = 3*VoltsØ * AmpsØ 1000 -orKVA = VoltsL * AmpsL * 1.732 1000 17 17 17 KVA Example Customer’s load - three phase, 480 volts, 60 Hz, 100 amps KVA = Volts * Amps * 1.732 1000 KVA = 480 X 100 X 1.732 1000 KVA = 83.14 18 18 18 FLA & Isc Example Full Load Amps - three phase, 480 volts, 60 Hz, 300 kVA Amps = 1000* kVA 1.732 *Volts Amps = 300 X 1000 480 X 1.732 Amps = 361 A Isc = FLA %Z 19 = 361 = 6278 A .0575 19 19 Taps • Correct for high or low input voltage conditions so the transformer will still provide its rated output voltage • Connection off of the primary winding • Usually in 2.5% or 5.0% increments • FCAN - Full Capacity Above Nominal • FCBN - Full Capacity Below Nominal 20 20 20 Taps Correct for high or low input voltage conditions so that transformer will still provide its rated output voltage. Connection off the primary winding, usually in 2.5% or 5.0% increments. FCAN - Full Capacity Above Nominal FCBN - Full Capacity Below Nominal 21 21 21 Taps Example + 2 @ 2-1/2% FCAN - 4 @ 2-1/2% FCBN 480V 120V 22 22 22 Tap Example – Low Primary V Change The Turns Ratio 4 1 480 120 Primary Secondary 480V 120V 432 108 4 1 432 3.6 1 120 23 23 23 Insulation Systems and Temperature Rise Temperature Rise 55 80 115 150 Hot Spot 10 30 30 30 Ambient 40 40 40 40 105 150 185 220 A B F H Insulation Class/ Limiting Temperature Former Designation Temperatures in degrees centigrade 24 24 24 Auxiliary Cooling • Liquid filled transformers Fan cooling - 15% 750 kVA to 2000 kVA Fan cooling - 25% 2500 kVA and above • Dry type transformers Fan cooling - 33% 25 All ratings 25 25 Ratings - Liquid Filled `Fluid Filled 65°C Rise 26 OA (Base Rating) FA (OA x 1.15 <2500 kVA, OA x 1.25 2500kVA & >) 300 500 750 1000 1500 2000 2500 ----862 1150 1725 2300 3125 55/65°C Rise OA 55°C OA 65°C OA x 1.12 (Base Rating) 300 500 750 1000 1500 2000 2500 336 560 840 1120 1580 2240 2800 FA 55°C (OA x 1.15 FA 65°C <2500 kVA, OA x 1.25 2500kVA & >) OA 65C x 1.15 <2500 kVA, OA 65C x 1.25 2500kVA & > ----862 1150 1725 2300 3125 ----966 1288 1932 2576 3500 26 26 Ratings - Cast Coil 100°C Rise 27 80/100°C Rise AA 100 (Base) FA (AA100 x 1.33) AA 80 (Base) AA 100 (AA80 x 1.125) FA 100 (AA100 X 1.33) 300 500 750 1000 1500 2000 2500 --667 1000 1333 2000 2667 3333 300 500 750 1000 1500 2000 2500 338 563 844 1125 1688 2250 2813 --750 1125 1500 2250 3000 3750 27 27 Ratings - Dry Type 150°C Rise 115/150°C Rise AA 150C (Base) FA (AA150 x 1.33) AA 115°C (Base) AA 150°C (AA115 x 1.15) FA 150°C (AA150 x 1.33) 300 500 750 1000 1500 2000 2500 400 667 1000 1333 2000 2667 3333 300 500 750 1000 1500 2000 2500 345 575 863 1150 1725 2300 2875 460 767 1151 1533 2300 3067 3833 80/115°C Rise 28 AA 80° (Base) AA 115° (AA80 x 1.18) 300 500 750 1000 1500 2000 2500 354 590 885 1180 1770 2360 2950 80/150°C Rise FA 115° (AA115 x 1.33) AA 80°C (Base) AA 150°C (AA80 x 1.35) FA 150°C (AA150 x 1.33) 472 787 1180 1573 2360 3147 3933 300 500 750 1000 1500 2000 2500 405 675 1013 1350 2025 2700 3375 540 900 1351 1800 2700 3600 4500 28 28 Insulation Levels Kv BIL High Voltage Rating 2400 4160 4800 6900 7200 12000 12470 13200 13800 22,900 34,400 29 Liquid Filled Transf. HV 45 60 60 75 75 95 95 95 95 125 150 Liquid Filled Transf. LV (600 Max). Vent. Dry Transf. HV Vent. Dry Transf. LV (600 Max.) Cast Coil Transf. HV Cast Coil Transf. LV (600 Max.) 30 30 30 30 30 30 30 30 30 30 30 30 30 30 40 40 60 60 60 60 110 150 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 45 60 60 75 75 95 95 95 95 110 150 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 29 29 Sound Levels Table 6 - NEMA TR-1 Maximum Sound Level Comparison USTs Liquid-Types Dry-Types kVA (All Fluids) VPI,VPE,CAST OA OA/FA AA AA/FA 301 to 500 56 67 60 67 501 to 700 57 67 62 67 701 to 1000 58 67 64 67 1001 to 1500 60 67 65 68 1501 to 2000 61 67 66 69 2001 to 2500 62 67 68 71 2501 to 3000 63 67 68 71 30 30 30 Transformer Standards © 2008 Eaton Corporation. All rights reserved. Transformer Standards UL 506 “Specialty Transformers” UL 1561 “Dry-Type General Purpose and Power Transformers” UL 1562 ‘‘Transformers, Distribution, Dry-Type – Over 600 Volts,’’ UL 2161 “Neon Transformers and Power Supplies” 32 32 Transformer Standards UL 506 “Specialty Transformers” 1.1 These requirements cover ignition transformers for use with gas burners and oil burners and specialty step-up transformers used in applications such as insect electrocuting. Transformers incorporating overcurrent or over-temperature protective devices, transient voltage surge protectors, or power factor correction capacitors are also covered by these requirements. These transformers are intended to be used in accordance with the National Electrical Code, NFPA 70. 33 33 Transformer Standards UL 1561 “Dry-Type General Purpose and Power Transformers” These requirements cover: a) General purpose and power transformers of the air-cooled, dry, ventilated, and non-ventilated types to be used in accordance with the National Electrical Code, ANSI/NFPA 70. Constructions include step up, step down, insulating, and autotransformer type transformers as well as aircooled and dry-type reactors or b) General purpose and power transformers of the exposed core, aircooled, dry, and compound-filled types rated more than 10 kVA to be used in accordance with the National Electrical Code, ANSI/NFPA 70. Constructions include step up, step down, insulating, and autotransformer type transformers as well as air-cooled, dry, and compound-filled type reactors. 34 34 Transformer Standards UL 1562 ‘‘Transformers, Distribution, Dry-Type – Over 600 Volts,’’ 1.1 These requirements cover single-phase or three-phase, dry-type, distribution transformers, including solid cast and resin encapsulated transformers. The transformers are provided with either ventilated or nonventilated enclosures and are rated for a primary or secondary voltage from 601 to 35000 V. 35 35 Transformer Standards UL 2161 “Neon Transformers and Power Supplies” 1.1 This standard applies to transformers and power supplies, including those intended to be connected to a Class 2 source of supply, that provide the voltage and ballasting for neon and cold-cathode tubing (electric-discharge tubing) consisting of electrodes and gas such as neon, mercury, helium, argon, and similar gases, enclosed in glass. Neon transformers and power supplies for use in signs and outline lighting are intended to be used in accordance with Article 600 of the National Electrical Code, NFPA 70. Cold-cathode supplies identified for use only in cold-cathode lighting systems are intended to be used in accordance with Article 410 of the National Electrical Code. 1.2 Neon transformers and power supplies covered by this standard are designated by their construction and intended use as specified in Table 1.1. 36 36 Transformer Standards UL 2161 “Neon Transformers and Power Supplies” 37 37 Transformers and The NEC © 2008 Eaton Corporation. All rights reserved. Transformers and The NEC • Article 450 “Transformers and Transformer Vaults (Including Secondary Ties)” • 450.1 Scope. This article covers the installation of all transformers. The NEC Has An Entire Article, Article 450, Dedicated To Transformers 39 39 Transformers and The NEC 450.1 Scope. This article covers the installation of all transformers. Exceptions 1. Current transformers. 2. Dry-type transformers that constitute a component part of other apparatus and comply with the requirements for such apparatus. 3. Transformers that are an integral part of an X-ray, highfrequency, or electrostatic-coating apparatus. 4. Transformers used with Class 2 and Class 3 circuits that comply with Article 725. 5. Transformers for sign and outline lighting that comply with Article 600. Exceptions Illustrate Other Articles Important to Proper Application of Transformers 6. Transformers for electric-discharge lighting that comply with Article 410. 7. Transformers used for power-limited fire alarm circuits that comply with Part III of Article 760. 8. Transformers used for research, development, or testing, where effective arrangements are provided to safeguard persons from contacting energized parts. Don’t Stop At Article 450 Understand The Application 40 40 Transformers and The NEC Article 725: Class 1, Class 2, and Class 3 Remote – Control, Signaling, and Power-Limited Circuits 450.1 Scope. This article covers the installation of all Article 600: Electric Signs and Outline Lighting transformers. Article 410: Luminaires, Lampholders, and Lamps Article 760: Fire Alarm Systems Exceptions 1. Current transformers. 2. Dry-type transformers that constitute a component part of other apparatus and comply with the requirements for such apparatus. 3. Transformers that are an integral part of an X-ray, highfrequency, or electrostatic-coating apparatus. 4. Transformers used with Class 2 and Class 3 circuits that comply with Article 725. 5. Transformers for sign and outline lighting that comply with Article 600. Exceptions Illustrate Other Articles Important to Proper Application of Transformers 6. Transformers for electric-discharge lighting that comply with Article 410. 7. Transformers used for power-limited fire alarm circuits that comply with Part III of Article 760. 8. Transformers used for research, development, or testing, where effective arrangements are provided to safeguard persons from contacting energized parts. Don’t Stop At Article 450 Understand The Application 41 41 Protection – Table 450.3(A) PRIMARY OVER 1000 VOLTS Any Location IMPEDANCE Not More Than 6% PRIMARY PROTECTION 600% - Circuit Breaker 300% - Fuse Seconday > 1000Volts 300% - Circuit Breaker 250% - Fuse Seconday 1000Volts or Less 125% - Circuit Breaker 42 125% - Fuse 42 42 Protection – Table 450.3(A) PRIMARY OVER 1000 VOLTS Any Location IMPEDANCE More Than 6% & Not More Than10% PRIMARY PROTECTION 400% - Circuit Breaker 300% - Fuse Seconday > 1000Volts 250% - Circuit Breaker 225% - Fuse Seconday 1000Volts or Less 125% - Circuit Breaker 43 125% - Fuse 43 43 Protection – Table 450.3(A) PRIMARY OVER 1000 VOLTS Supervised Location IMPEDANCE Not More Than 6% PRIMARY PROTECTION 600% - Circuit Breaker 300% - Fuse Seconday > 1000Volts 300% - Circuit Breaker 250% - Fuse Seconday 1000Volts or Less 250% - Circuit Breaker 44 250% - Fuse 44 44 Protection – Table 450.3(A) PRIMARY OVER 1000 VOLTS Supervised Location IMPEDANCE More Than 6% & Not More Than10% PRIMARY PROTECTION 400% - Circuit Breaker 300% - Fuse Seconday > 1000Volts 250% - Circuit Breaker 225% - Fuse Seconday 1000Volts or Less 250% - Circuit Breaker 45 250% - Fuse 45 45 Protection – Table 450.3(A) PRIMARY OVER 1000 VOLTS Supervised Location IMPEDANCE Any PRIMARY PROTECTION 300% - Circuit Breaker 250% - Fuse Seconday > 1000Volts N/A - Circuit Breaker N/A - Fuse Seconday 1000Volts or Less N/A - Circuit Breaker 46 N/A - Fuse 46 46 Protection – Table 450.3(A) Next Standard Rating 6 Disconnect Rule – Single Location Total Rating Not to Exceed Allowed Value of Single Over Current Device 47 47 47 Protection – Table 450.3(B) PRIMARY 1000 VOLTS & LESS PRIMARY PROTECTION ONLY 48 Currents of 9 Amps or More 125% Currents Less Than 9 Amps 167% Currents Less Than 2 Amps 300% 48 48 Protection – Table 450.3(B) PRIMARY 1000 VOLTS & LESS PRIMARY PROTECTION SECONDARY PROTECTION Currents of 9 Amps or More 250% 125% Currents Less Than 9 Amps 250% 167% Currents Less Than 2 Amps 250% -- 49 49 49 Protection – Table 450.3(B) Next Standard Rating 6 Disconnect Rule – Single Location Total Rating Not to Exceed Allowed 50 50 50 Protection – Table 450.10 (A) & (B) 450.10 Grounding (A) Dry-Type Transformer Enclosures. Where separate equipment grounding conductors and supply-side bonding jumpers are installed, a terminal bar for all grounding and bonding conductor connections shall be secured inside the transformer enclosure. The terminal bar shall be bonded to the enclosure in accordance with 250.12 and shall not be installed on or over any vented portion of the enclosure. Exception: Where a dry-type transformer is equipped with wire-type connections (leads), the grounding and bonding connections shall be permitted to be connected together using any of the methods in 250.8 and shall be bonded to the enclosure if of metal. (B) Other Metal Parts 51 51 51 Protection – Table 450.10 (A) & (B) 450.11 Markings (A) General (1) Name of Manufacturer (2) Rated Kilovolt-Amperes (3) Frequency (4) Primary and Secondary Voltage (5) Impedance of Transformers 25 kVA and Larger (6) Required Clearance for Transformers with Ventilated Openings (7) Amount and Kind of Insulating Liquid Where Used (8) For Dry-Type Transformers, Temperature Class for the Insulation System 52 52 52 Transformer Standards Using Listed Products Provides A Level of Assurance That The Product Will Perform As Expected 53 53 Transformers and The NEC • Other NEC Articles Important To Transformer Applications • Article 312 “Cabinets, Cutout Boxes, and Meter Socket Enclosures” • Article 426 “Fixed Outdoor Electric Deicing and Snow-Melting Equipment” • Article 427 “Fixed Electric Heating Equipment for Pipelines and Vessels” • Article 430 “Motors, Motor Circuits, and Controllers” • Article 501 “Class I Locations” • Article 502 “Class II Locations” • Article 503 “Class III Locations” • Article 680 “Swimming Pools, Fountains, and Similar Installations” 54 54 Questions And Comments © 2008 Eaton Corporation. All rights reserved. 56 56 The Transformer – Basic Components 57 57 • General Provisions • Overcurrent Protection • Transformers over 1000 Volts • Transformers 1000 Volts Nominal or Less • Autotransformers • Standard • Grounding Transformers • Grounding • Markings 58 58 Three- Core Construction Wound Cores Stacked Cores 59 59 Coil Construction LV Sheet Winding with Cold Welded Lead 60 60 Coil Construction LV Sheet Winding with Cold Welded Lead Finished Coil HV Winding with Diamond Epoxy Insulation Complete Core & Coil Assembly 61 61 Coil Construction LV Sheet Winding with Cold Welded Lead Finished Coil HV Winding with Diamond Epoxy Insulation Complete Core & Coil Assembly 62 62 Coil Construction LV Sheet Winding with Cold Welded Lead Finished Coil HV Winding with Diamond Epoxy Insulation Complete Core & Coil Assembly 63 63 Serving Many Locations 64 64 64 Open Type Transformer • Open Type Transformer for Utility Applications: • Investor Owned • Public Power • Municipal • REA • CO-OP 65 65 Unit Substation Transformer • Unit Substation Transformer for Industrial/Commercial Applications: • Petro/Chem • Pulp & Paper • Government/Military • Institutional • Food & Drug • Mining & Minerals • Manufacturing • Data Centers 66 66 67 67 The Transformer – Codes and Standards PJXS – Metering Transformer Cabinets PWIK – Neon Transformers and Power Supplies WDGV – Swimming Pool and Spa Transformers XNWX – Transformers XOBA, XOKV, XOYT, XPFS, XPLH, XPTQ, XPZZ, XQNX, XRBV XPAF – Transformers in Hazardous Locations XPJF, XPLP 68 68 The Transformer – Codes and Standards PJXS – Metering Transformer Cabinets Article 312 Cabinets, Cutout Boxes, and Meter Socket Enclosures Sections 312.1 & 312.5 PWIK – Neon Transformers and Power Supplies Article 600 “Electric Signs and Outline Lighting” WDGV – Swimming Pool and Spa Transformers XNWX – Transformers XOBA, XOKV, XOYT, XPFS, XPLH, XPTQ, XPZZ, XQNX, XRBV 69 69 The Transformer – Codes and Standards 70 70 • Specific Provisions Applicable to Different Types of Transformers • Dry types • indoors • Outdoors • Liquid-insulated • Indoors • Outdoors • Other types of insulated transformers 71 71 • Transformer Vaults • Location • Construction • Ventilation • Drainage • Storage 72 72