* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Quantum Mechanical Model
Symmetry in quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Particle in a box wikipedia , lookup
History of quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
Coupled cluster wikipedia , lookup
Hartree–Fock method wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization wikipedia , lookup
EPR paradox wikipedia , lookup
X-ray fluorescence wikipedia , lookup
Ferromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Wave–particle duality wikipedia , lookup
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Chemical bond wikipedia , lookup
Auger electron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen atom wikipedia , lookup
Quantum electrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
Electron scattering wikipedia , lookup
Tight binding wikipedia , lookup
Electron-beam lithography wikipedia , lookup
Molecular orbital wikipedia , lookup
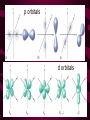
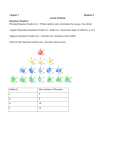
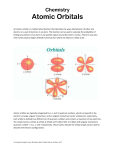
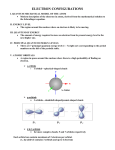
Quantum Mechanical Model • Or…”Electron Cloud Model” • Electrons move freely within “clouds” (called orbitals) not just restricted to orbits. [http://www.gly.fsu.edu/%7Esalters/GLY1000/6_Minerals/Slide9.jpg] Quantum Mechanical Model • Atoms have different numbers and shapes of orbitals depending on their number of electrons. “s orbital” p orbitals d orbitals Quantum Mechanical Model • As the energy of an electron increases, so does the quantum number (n) • Each principle energy level is also split up into one or more sublevels • Chart on Pg. 145 [http://www.chemistry.mcmaster.ca/esam/Chapter_4/fig4-2.jpg] Quantum Mechanical Model • In each orbital, only 2 electrons can exist because of electron spin Click here for an Atomic Orbital Applet Electron Orbital Diagrams • Show which orbitals in an atom electrons occupy. • Arrows are used to represent the electrons. Electron Orbital Diagrams • Aufbau Principle: • Electrons must “fill” lower energy orbitals before higher energy orbitals. • 1s before 2s, 2s before 2p … Electron Orbital Diagrams • Pauli Exclusion Principle: Electrons in a orbital always move in opposite directions (spin!) • Use up and down arrows. Electron Orbital Diagrams • Hund’s Rule: All orbitals of a certain shape must be occupied by one electron before they can be paired. Electron Orbital Diagrams • Example: Carbon Electron Orbital Diagrams • Example: Oxygen Orbital Diagrams provided by: [http://intro.chem.okstate.edu/1215/Lecture/Chapter11/Fri11216.gif]