* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Maps and Globes are Models of Earth
Iberian cartography, 1400–1600 wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of cartography wikipedia , lookup
Major explorations after the Age of Discovery wikipedia , lookup
Counter-mapping wikipedia , lookup
Cartography wikipedia , lookup
Early world maps wikipedia , lookup
Scale (map) wikipedia , lookup
History of navigation wikipedia , lookup
Map database management wikipedia , lookup
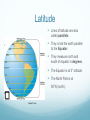
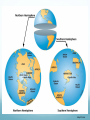
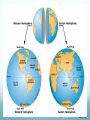
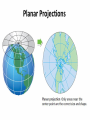
Maps and Globes are Models of Earth Section 1.2 Maps and Globes A map is a flat model of the surface of the Earth It is the “Bird’s eye view” of an area Show natural AND human-made features A globe represents Earth as if you were looking at it from Outer Space Shows relative sizes and shapes of Earth’s land and water features Land Features on Maps A Relief Map is a map that shows how high or low each feature is on Earth A mapmaker uses pictures or satellite images to build the Three Dimensional view of the surface Relief Maps show three main features: Mountains Plateaus Plains Mountains Mountains stand taller than the land around them A group of mountains is called a mountain range The base of a mountain may cover several square kilometers Name some well known mountain ranges: Plateaus Have fairly level surfaces but stand high above sea level Often found near mountain ranges Colorado Plateau spans from Arizona, Colorado, New Mexico and Utah Plains Gently rolling or flat features The United States has two types of plains: Coastal Plains near the eastern and southeastern shores Interior plains in the center of the nation The interior Great Plains covers the middle third of the country Map Symbols and Scale To read a map, you need to know who to read the scale and key! The Map Scale relates distances on a map to actual distances on Earth’s Surface The scale can be in a ratio, a bar, or equivalent units of distance For example, a ratio of 1:25,000 means that 1 cm on the map represents 25,000 cm (0.25 km) on Earth Map Legend A map legend (also called a key) is a chart that explains the meanings of each symbol on the map Symbols can stand for highways, buildings, parks, etc. Compass A map usually includes a compass rose to show which directions are North, East, South and West In general, north on a map points to the top of the page Understanding Latitude and Longitude Lines of latitude and lines longitude cross one another. They form a grid system around the earth. http://www.navfltsm.addr.com/globe.jpg Latitude Lines of latitude are also called parallels. They circle the earth parallel to the Equator. They measure north and south of equator in degrees. The Equator is at 0° latitude. The North Pole is at 90°N (north). Maps101.com Longitude Lines of longitude are also called meridians. They circle the earth from Pole to Pole. They measure east and west of the starting line, at 0° longitude or the Prime Meridian. Maps101.com Absolute Location Only one place can be found at the point where lines cross one another. Use degrees (°) and minutes (’) to give an exact spot where one line of latitude crosses one line of longitude – an absolute location. http://www.navfltsm.addr.com/globe.jpg Hemispheres The equator circles the middle of the Earth. It divides the earth into hemispheres or “half-spheres.” North of the equator is the Northern Hemisphere. South of the equator is the Southern Hemisphere. Maps101.com Hemispheres The Prime Meridian runs from north to south. It divides the earth into half spheres in the other direction. East of the Prime Meridian for 180 degrees is the Eastern Hemisphere. West of the Prime Meridian for 180 degrees is the Western Hemisphere. Maps101.com Using Latitude and Longitude Review your answers is 15°N latitude and 150°W longitude. is 45°N latitude and 90°W longitude. is 15°S latitude and 60°W longitude. is 0° latitude and 150°E longitude. is 30°N latitude and 60°E longitude. is 60°N latitude and 0° longitude. is 45°S latitude and 90°E longitude. Map Projections A Projection is a way of representing Earth’s curved surface on a flat map Mapmakers use different projections, but all distort Earth’s surface in different ways Cylindrical Projections Conic Projections Planar Projections Cylindrical Projections Also called the Mercator projection Useful for navigating at sea or in the air Allows you to plot a course easily Problem: Areas really far away from the equator appear much bigger than they actually are Conic Projections Based on the shape of a cone The latitude lines are curved slightly, this allows for a more accurate size and shape of some landmasses Good for mapping large areas in the middle latitudes However, landmasses near the equator or near the north or south pole will be distorted Planar Projections Developed to help people find the shortest distance between two points Good for plotting ocean or air voyages and showing the polar regions (both north and south) However, landmasses further away from center point are distorted