* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Evidence for Evolution
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Molecular paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Precambrian body plans wikipedia , lookup
Transitional fossil wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Evolving digital ecological networks wikipedia , lookup
The eclipse of Darwinism wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Saltation (biology) wikipedia , lookup
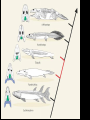
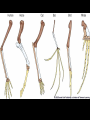
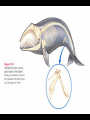
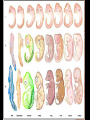
Recap on Evolution What is the Theory of Evolution? • Evolution is defined as change over time. • One of the earliest theories of evolution was put forward by Darwin. • He studied physical differences in finches on the Galapagos Islands. • From his studies he discovered the theory of Natural Selection which favors some adaptations. • Organisms not favored can become extinct. • Natural selection works off of competition for resources and adaptations that help animals survive in an environment. Evidence for Evolution Fossils (Palentology) • The study of fossils • Fossils show us what organisms looked like a long time ago • We know how old they are– Relative dating: what layer of rock the fossil is found in How are fossils evidence? • If modern species looked exactly the same as fossils, then it would show that nothing has changed but they do not look the same. • Extinctions: species were not “fit” for the environment any more Comparative anatomy • Anatomy is the study of the body parts of an organism • Homologous structures: structures in different species that are similar but have evolved to be different because they are used differently • Vestigial structures: structures that no longer serve a purpose in modern organisms • Divergent evolution: when one species evolves into two or more – Adaptive radiation: when one species evolves into many • Convergent evolution: when two unrelated organisms have similar structures because of their environment How is anatomy evidence? • If a group of organisms have similar structures, we know they had a common ancestor Embryology • Embryology is the study of embryos and how they are similar • During the first few hours and days of development, all animals start out looking the same because they all use the same genes to get started. How is embryology evidence? • If the organisms are using the same genes to create the same structures, it shows that they were at one time the same organism and that they share a common ancestor DNA and the universal code • DNA is the genetic molecule for every organism on earth • All organisms use A, T, G, and C which is called the universal code • DNA makes proteins out of 20 amino acids • Mutations cause changes to DNA sequences and amino acid sequences How is DNA evidence? • If all organisms use the same code (DNA), then they all started out as one organism (3.5 billion year ago) • Mutations have caused changes to some organisms and other changes to other organisms • The more similar the DNA (or protein) is between two species, the more recently they were related to each other Population genetics • Population genetics is a fusion of Darwin’s ideas with genetics • Speciation is the creation of a new species • Speciation can occur by: – Mutations – Gene flow – Genetic drift – Selective mating – Natural selection due to environmental changes How is population genetics evidence? • When speciation occurs, changes are made to the gene pool which cause different populations to be different • If there are enough differences, they become isolated from each other and they are considered different species • Types of isolation – Mechanical – Seasonal – Habitat - Geographic - Behavioral • Types of selection – Disruptive – Stabilizing – Directional