* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Motion - Gulfport School District
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Jerk (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Coriolis force wikipedia , lookup
Faster-than-light wikipedia , lookup
Velocity-addition formula wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Rigid body dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Seismometer wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Hunting oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Length contraction wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Mass versus weight wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
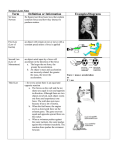
Science Vocabulary Terms: Force and Motion The Force and Motion vocabulary quiz will be Thursday, January 12, 2017. 1. Position: an object’s place or location 2. Reference point: the nonmoving point from which motion is compared 3. Speed: a measure of the distance an object moves in a given amount of time 4. Velocity: an object’s speed in a particular direction 5. Acceleration: a change in motion caused by a change in velocity 6. Momentum: a measure of how hard it is to slow down or stop an object 7. Inertia: the property of matter that keeps it moving in a straight line or keeps it at rest 8. Force: any push or pull from one object to another 9. Balanced force: a force acting on an object WITHOUT changing the object’s motion 10. Unbalanced force: a force acting on an object that causes a change to its motion Lyrics for “Speed and Velocity” by They Might Be Giants When I'm on an airplane And we're on a runway Ready to take off And then we're in the air Motion, direction, acceleration Motion, direction, acceleration I've got speed That's how fast I am moving I've got velocity That's my speed and direction When I'm on my Big Wheel Skateboard, roller coaster Race car, motorcycle Rocket ship into outer space Motion (Keep movin', keep movin', keep movin') Direction (Which way, anyway, uptown, all around) Acceleration (Let's go faster) Acceleration (Let's go faster) I've got speed (That's how fast I am moving) I've got velocity (That's my speed and direction) I've got speed (That's how fast I am moving) I've got velocity (That's my speed and direction) Source: http://www.metrolyrics.com/speed-and-velocity-lyrics-they-might-be-giants.html Science Notes: Motion and Forces Position and Motion: To observe motion, you must first determine an object’s position. Position is an object’s place or location. If an object’s position changes, the object is in motion. Motion is a change in an object’s position over time. Your frame of reference determines if an object is actually in motion. Frame of reference of motion is observed when comparing the motion of an object to a background that is not moving. It is the perspective, or point-of-view, from which motion is observed. THE MOTION OF ANY OBJECT DEPENDS ON YOUR MOTION WHEN YOU OBSERVE THE OBJECT. Speed and Velocity: Speed is a measure of the distance an object moves in a given amount of time. Speed is calculated by dividing the distance an object travels in a certain amount of time: o Speed (S) = Distance (D) / Time (T) Velocity is a measure of an object’s speed in a particular direction. Acceleration: ANY change in velocity (speed or direction) is considered a change in acceleration. When an object starts, stops, speeds up, slows down, turns left, or turns right, the velocity of that object changes to cause a change in the object’s acceleration. THE ONLY TIME AN OBJECT IS NOT ACCELERATING IS WHEN IT IS MOVING IN A STRAIGHT LINE AT A CONSTANT SPEED. Momentum: Momentum is a measure of how hard it is to slow down or to stop an object. If two objects have the same velocity, the one with the greater mass has more momentum. If two objects have the same mass, the one with the greater velocity has more momentum. THE GREATER THE VELOCITY OF AN OBJECT, THE GREATER ITS MOMENTUM. Summary: Motion is a change in an object’s position. Speed is a measure of the distance an object moves in a given amount of time. Velocity is speed in a particular direction. Acceleration is any change in velocity, either in direction or in speed. Momentum is a measure of how hard it is to slow down or stop an object; it is the product of an object’s velocity and its mass. The Laws of Motion Newton’s Ideas: Newton’s laws were the first to describe the movement of objects in terms of forces. His laws of motion describe the movement of objects on Earth, but they also describe the movement of planets and moons. Forces: A force is a push, pull, or lift from one object to another. Forces are measured in newtons (N) or pounds (lb). Spring scales are used to measure force. Forces always occur in pairs. Magnetism, thrust, lift, drag, gravity, and friction are all forces. When forces act on an object without changing its motion, a balanced force is present. A force that causes an object to change its motion is an unbalanced force. The First Law of Motion (aka Law of Inertia): An object at rest will remain at rest, and an object in motion will continue moving in a straight line at a constant speed, until acted upon by an outside force. Inertia is the property of matter that keeps it moving in a straight line or keeps it at rest. The greater an object’s mass, the greater the object’s inertia. The Second Law of Motion: An object’s acceleration depends on the size and direction of the force acting on it and on the mass of the object. F (force) = M (mass) x A (acceleration) The size of the force: A large force acting on an object will cause more acceleration than a small force. The direction of the force: A force that acts on an object may cause it to speed up, slow down, stop, or change direction. The mass of the object: A force has more effect on an object with less mass than it has on an object with more mass. The Third Law of Motion: For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. The first force is the action force. This is the push of the first object on the second object. The force that pushes or pulls back is the reaction force. This is the push of the second object on the first object. Forces always occur in pairs. Action and reaction forces are not balanced forces.