* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Newton`s Laws of Motion Notes
Hunting oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Center of mass wikipedia , lookup
Coriolis force wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Length contraction wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Rigid body dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
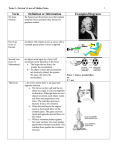
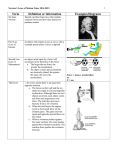
Newton’s Laws Notes Term Definition or Information Sir Isaac Newton He figured out three basic laws that explain common forces and how they interact to produce motion. First Law (Law of Inertia) an object will remain at rest or move with a constant speed unless a force is applied Second Law (Law of Momentum) an object acted upon by a force will accelerate in the direction of the force a. The larger the net force, the greater the acceleration. b. An object’s mass and acceleration are inversely related: the greater the mass, the lower the acceleration. Third Law ---for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction a. The forces on the wall and the ice skater are equal in size and opposite in direction. Although there are two objects involved, each object exerts one force and experiences one force. The wall does not move because it has a lot of inertia. b. When the fuel burns, the engine exerts a downward force on the exhaust gases. The gases exert an equal and opposite upward force on the rocket. c. When a swimmer pushes against the water (action), the water pushes against the swimmer (reaction). The reaction force pushes the swimmer forward. Examples/Diagrams Force = mass x acceleration or F = ma force push or pull; usually more than one force is acting on an object net force sum of all the forces acting on the object balanced forces forces that are equal in size and opposite in direction unbalanced forces two or more forces acting on an object that do not cancel, and cause the object to accelerate friction inertia force that opposes motion between two surfaces that are touching each other 1. natural tendency of an object to resist any changes in motion (depends on mass) 2. The greater the mass of an object, the more inertia it has. When inertia becomes greater, it becomes more difficult to slow down, speed up, or change the direction of a moving object. It is also harder to make an object with greater inertia start moving if it is at rest. velocity the rate of motion (speed/direction) terminal velocity It is reached when the force of gravity is balanced by air resistance. Air resistance depends on size and shape of the object. Air resistance is the force air exerts on a moving object. This force acts in the opposite direction to that of the object’s motion. In the case of a falling object, air resistance pushes up as gravity pulls down. speed rate of motion or rate of change in position S=d/t or Speed = distance/time distance how much ground is covered by an object, regardless of its starting or ending position The Indian Nation event was a 5-k race. The participants ran 5 kilometers. displacement --- an object's change in position considering its starting position and final position ---direction in straight line (not time) **travel time to the store is different than the actual distance to the store in a straight line (GPS) ---runner runs 400m around the track and back to the starting point—the displacement is zero ---people were displaced after Katrina ---water displacement distance= speed X time (d = vt) acceleration rate of change in velocity weight (gravitational force) measure of the force of gravity on an object, usually the force between Earth and an object at its surface momentum --a property a moving object has due to its mass and velocity --momentum of an object doesn’t change unless its mass, or velocity, or both, change --Momentum can be transferred from one object to another. momentum=mass x velocity ( p=m v )