* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Prologue and Chapter 1
Cursus honorum wikipedia , lookup
Roman army of the late Republic wikipedia , lookup
Constitutional reforms of Sulla wikipedia , lookup
Travel in Classical antiquity wikipedia , lookup
Promagistrate wikipedia , lookup
Food and dining in the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Roman economy wikipedia , lookup
Education in ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Roman temple wikipedia , lookup
The Last Legion wikipedia , lookup
Roman historiography wikipedia , lookup
Rome (TV series) wikipedia , lookup
Culture of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Roman agriculture wikipedia , lookup
History of the Roman Constitution wikipedia , lookup
Leges regiae wikipedia , lookup
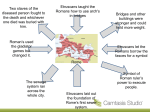
Prologue and Chapter 1 The Pre-Roman World A Bit of Perspective Prologue Roman civilization – lasted over 1,000 years. Why? Efficient network of government officials and a system of laws that protects each citizen Separation of powers System of checks and balances Greatly influenced the framework for the U.S. Also, the Romans were masters of diplomacy! By incorporating the people they conquered into their culture, they established unity and loyalty. The citizens lived in peace and harmony for a long time. Prologue, continued Romans Serious-minded Industrious Disciplined Flexible, compromising Allowed conquered people to keep their traditions Made allies with former enemies Respected cultural achievements of other societies Adopted and adapted customs they liked Prologue, continued Technology Bridges Roads Aqueducts Amphitheaters Temples Innovation First hospitals Licensing of physicians Food inspection Invention Glass windowpanes Milestones Chemical fertilizer Theater curtains Scissors Ice cream Scales with weights Plane, brace, and bit And many more! Prologue, continued Language Latin Many languages today have evolved from Latin (French, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, and Romanian) Almost half of the words in English are derived from Latin Also inspired our alphabet, months of the year History We know about Ancient Rome through writings, like plays, as well as art and ruins The Geography of Italy Not much of Italy is flat Land that isn’t mountainous is covered with hills People built cities on hills to aid in defense Many ancient cities of Italy, including Rome, sat atop hills Rome was built on seven hills (Septimonium) Also built cities near rivers (gave people a source of fresh water) Rome is on the Tiber River Climate – similar to southern California The Geography of Italy Places to know! Italy Rome Corsica Sardinia Adriatic Sea Ionian Sea Mediterranean Sea Tyrrhenian Sea Po River Arno River Tiber River Apennine Mountains Etruria, Latium, (regions) From Village to Empire Indo-Europeans migrated to Italy around 1000 B.C.E. Farmers and herdsmen Rome grew and eventually controlled the entire peninsula, and then the land around the Mediterranean Sea Included land on Asia, Europe, and Africa Roman civilization lasted for more than 1,000 years Roman History – 3 Eras Monarchy Ruled by kings Republic Rule by the people Empire Age of emperors Height of Roman civilization The Age of Kings Key Terms Palatine Hill Pontifex maximus Paterfamilias Pales Virgil Livy (Titus Livius) Romulus and Remus Senate Pontifex Maximus Ostia Etruscans Augury Haruspicy Servian Wall century The Age of Kings Palatine Hill First of the seven hills to be settled Hills offered protection How did they build their homes? Advantages to Rome’s Location Rome is 16 miles away from the coast, which allows people to fish and transport goods. Rome is far enough inland to be safe from pirates. City was built on a hill so they could see enemies. The city looked over the place where the Tiber was most easily crossed. The Hilltop Villages Families Divided into clans, or gens Head of the family (oldest male) paterfamilias Religion Believed in spirits related to nature Pales = goddess of shepherds and sheep Jupiter = sky god, most important Legends of the Founding of Rome Myths and legends give a more interesting take on the founding of Rome The Aeneid by Virgil An epic about the final days of the Trojan War and the travels of Aeneas, a prince of Troy who fled to seek a new home after the war. Romulus and Remus Story passed down over generations Livy (Titus Livius) Roman historian who recorded the story Twins born to Rhea Silva and, supposedly, Mars Her father is King Numitor of Alba Longa (descendent of Aeneas) Uncle, Amulius, overthrows her father and tries to have the twins killed…why? Servant sends them downstream in a basket, found by a shewolf, who nurses them. Later found by a shepherd who raises them. Romulus and Remus They return to Alba Longa, kill Amulius, and return power to Numitor Return to the place of their discovery, but can’t decide where to build their city. Remus choses Aventine Hill – why? Romulus choses Palatine Hill – why? Romulus marks his city…what does Remus do? Romulus After killing his brother, Romulus continues to build his city Names it after himself – Rome Significance of April 21st ? Romulus builds an army and expands the territory Sabines Neighboring tribe Women don’t want to see fighting and end the battle Sabines become allies of Rome Rome’s Legendary Origins What epic poem tells the story of Aeneas? Who was its author? The Aeneid; Virgil What was remarkable about the childhood of the legendary Romulus and Remus? The twins were thrown into a river in a basket, rescued and raised by a wolf, and adopted by a shepherd. How might a legendary beginning make a country or empire more stable? The First Roman Kings Most of what we know comes from the writings of Livy. How are Livy and Herodotus similar? Seven kings ruled Rome (Romulus was the 1st) King advised by the Senate (older men, “senex”) Comitia Curiata Assembly of ordinary townsmen Kings duties to: 1. 2. 3. Lead the army Judge major disputes Offer sacrifices to the gods The First Roman Kings Numa Pompilius (King #2) Created special priesthoods for religious ceremonies Pontifices Pontifex maximus (highest priest) Flamens (sacred priests) Vestal Virgins (guarded the sacred flames of the hearth in Rome) Numa Pompilius Numa built a Temple to Janus – god of beginnings and transitions Revised the lunar calendar Organized the workers of Rome into guilds Distributed land to the poor Numa ruled peacefully for many years. Tullus Hostilius (#3) Total opposite of Numa Warlike, wanted to expand Tullus attacked Alba Longa Rather then go to war, they each selected a family brothers to fight it out. Ancus Marcius (#4) Built Rome’s first: Prison Bridge – Pons Sublicious (“bridge on pilings”) Took control of the mouth of the Tiber and founded Ostia – a port city and salt collection center. The Etruscans Trade, as we have seen, leads the Romans to the Etruscans Arrived from Asia Minor around 800 B.C.E. Settled in Etruria (north of the Tiber) Created farmland Mined for iron, copper, and tin Traded their tools and weapons Expanded their territory Women held high place in culture; heredity traced through females Etruscans and Greeks Greeks settled on the SE coast of Italy and Sicily Etruscans and Greeks traded Trade spreads culture Etruscans adapted many Greek religious beliefs Augury Haruspicy Etruscans and Greeks Also , the written alphabet – basis for ours! Etruscan Way of Life Believed in an afterlife Wealthy class buried in stone tombs dug into large mounds of earth Had multiple rooms, decorated with frescoes The Etruscans Rule Rome Etruscan civilization grew to include land between the Tiber and Arno Rivers Wealthy Etruscans lured by the seven hills of Rome Lucius Tarquinius Priscus (#5) Wealthy Etruscan nobleman Moved to Rome with his wife, Tanaquil She was a prophetess Saw the eagle taking his cap, flying away, then returning the cap, as an omen that he would be king He got to know Ancus Marcius (King #4) When Ancus died, Tarquinius sent his sons away and took over the throne Tarquinius Raised the number of Senators to 300 Increased the size of the army Defeated the Sabines and others Expanded the empire into Latium Built the: Cloaca Maxima (main sewer of the city) Circus Maximus (“great circle”) A racetrack where chariot races were held He started the temple of Jupiter (King #7 finished it) Etruscans brought new ideas in farming: Drained the marshes to aid in farming Crop rotation and fertilization Crops – olives and grapes The Later Kings Tarquinius was killed by the sons of Ancus (What happened when Ancus died?) Servius Tullius becomes King #6 Was not elected by the Senate He was popular Built first fortification around the seven hills – the Servian Wall Five miles around 19 gates Servius Tullius (#6) Also built: Temple of Diana on Aventine Hill Continued work on temple of Jupiter on Capitoline Hill Implemented the world’s first census Counted all landowners Conducted every 5 years Divided the people into 5 classes based on wealth Each class had to contribute to the army He had a daughter named Tullia The Death of Servius Tullia was married to Lucius Tarquinius He was the son of Tarquinius Priscus (King #5) Tullia wanted her husband to be king He went to the Senate , in royal robes, and proclaimed himself king. Servius hears of this, but is stabbed by assassins hired by Tarquinius. When Tullia was on her way home, her carriage ran over the body of her father, Servius Street renamed “Vicus Sceleratus” – the street of shame (Lucius) Tarquinius Superbus (#7) “Tarquin the Proud” Tyrant, haughty and cruel Expanded army and territory Completed the temple of Jupiter Optimus Maximus and other projects to show his power The Etruscans Are Defeated Romans did not like the Etruscans They resented their rule – Etruscan leaders (Kings 5, 6, and 7) Things go from bad to worse… A son of Tarquinius attacks Lucretia, the wife of a well-known Roman She was known for her beauty and honor She was so upset by the attack that she took her own life The Etruscans Are Defeated A rebellion by Brutus and Collatinus (Lucretia’s husband) drove the Etruscans out Senate declared they wanted no more kings Leads to the founding of the republic The Death of Lucretia, Jerome Preudhomme, 1784 Tarquinius Superbus 1. True or False? According to legend, Remus named the city of Rome after his brother Romulus. FALSE! Romulus named the city after himself. 2. Roman records show that Rome’s last three kings were not Romans, but Etruscans. TRUE! 3. The Roman Republic is said to have been founded by Rome’s last king, who was known for his visionary leadership and kindness. FALSE! The last Roman king was said to have been cruel, and a group of nobles rose up against him to create a new government.