* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1 - Peoria Public Schools
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Electrostatics wikipedia , lookup
Field (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
Condensed matter physics wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Neutron magnetic moment wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Aharonov–Bohm effect wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic monopole wikipedia , lookup
Superconductivity wikipedia , lookup
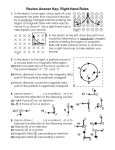
Physics 1 Section Review19-2 Name pp 670-672 1. Describe the magnetic field produced by an electric current in a long straight wire: 2. What happens to the magnetic field near a long straight wire if the current in the wire is reversed? 3. As you get further away from a straight wire carrying an electric current, what happens to the strength of the magnetic field? 4. What happens to the strength of the magnetic field created by a current in a long straight wire as the current increases? 5. How do you predict the direction of the magnetic field of a current-carrying straight wire? 6. How would you make a solenoid? 7. How is an electromagnet related to a solenoid? 8. Where is the magnetic field created by a current in a solenoid the strongest? 9. How does domain theory explain why putting an iron rod in a solenoid increase the magnetic field? Physics 1 Section Review 19-3 Name pp 673-679 10. What factors determine the magnitude of the magnetic force on a charge? 11. How does the direction of the magnetic force on a moving charge related to the direction of the velocity of the charge and the direction of the magnetic field? 12. What is the magnetic force on a charge moving parallel (or anti-parallel) to a magnetic field? 13. What is the symbol for a magnetic field? 14. What is the SI unit for magnetic field strength? 15. How can you find the direction of the magnetic force on a moving charge? 16. Why can a magnetic force make a charge move in a circular path? 17. What causes the force on a (current-carrying) wire in a magnetic field? 18. Why would having more (current-carrying) wire in a magnetic field make the magnetic force on the wire 19. What would be the force on a current-carrying wire that is parallel to the magnetic field? 20. Why do two parallel conducting wires exert a magnetic force on each other? 21. Why does changing the current through a loudspeaker make the “cone” of a speaker move?