* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Organs of the Immune System
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
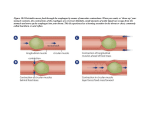
Cells Tissues ◦ Epithelial, connective, muscular, nervous Organs ◦ Examples include stomach, liver, heart Organ Systems ◦ Examples include digestive and circulatory systems Epithelial ◦ Covering or lining tissue Connective ◦ Joins, stores and supports Blood Muscle ◦ Internal and external movement Nerve Muscle ◦ Conducts electrical signals Nerve Functions ◦ Framework and support ◦ Protection ◦ Storage Axial and appendicular skeleton Bone structure Joints and ligaments Functions Movement Warmth Posture Muscle Properties Ability to contract Ability to be stretched Ability to respond to a stimulus Muscle Types Skeletal Smooth Cardiac Actin Myosin Human Circulatory Functions Protein hemoglobin in RBC’s transport oxygen and carbon dioxide gas Transport food molecules (lipids, carbs, amino acids) Transport hormones Maintain body temp Works with immune system to help fight disease Blood In 1628, William Harvey demonstrated that blood travels in one direction and in a “closed circuit” Blood is a liquid tissue Blood Vessels Arteries=Oxygenated exception is pulmonary artery) Veins=Deoxygenated (exception is pulmonary ve Oxygen gas leaves the blood here in the capillaries ARTERY from the heartCAPILLARYVEIN to the heart Double Loop System Loop 1: To/from the lu to pick up oxygen and drop off carbon dioxid Loop 2: To/from the body to drop off oxygen and pick up carbon dioxide Human Heart Right half: accepts oxygen poor blood from body and pumps this blood to the lungs to pick up oxygen. Left half: accepts oxygen rich blood from lungs and pumps this blood to the body. Respiration is gas exchange between an organism and the environment Respiratory structures include the nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles and alveoli Mechanics of Breathing Exhalation Inhalation Respiratory Overview Picture Nasal Cavity Throat Nose (pharynx) Mouth Bronchus Bronchiole Alveolus Diaphragm Windpipe (Trachea) Left lung Ribs Alveoli and Bronchi Picture Trachea Bronchi Tubes Bronchiole Alveoli Alveoli and Gas Exchange The protein hemoglobin in red blood cells carries O2 to body cells and brings back CO2 waste from them NUTRITION • Nutrition-study of how food affects the function of living organisms. • If cells don’t get nutrients, they don’t function correctly. • Poor diet = poor cells. • There are six general categories of nutrition: carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, minerals, water 3 FACTORS LEADING TO NUTRITIONAL PROBLEMS • • • 1) Too little physical activity (sedentary lifestyle) 2) Over consumption of food 3) Malnutrition/undernutrition THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM •Responsible for breaking down food so that it can be absorbed by the bloodstream. •Digestion = breakdown • Mechanical-large chunks into small chunks by grinding, ripping and crushing by teeth • Chemical-larger molecules broken into smaller molecules by enzymes and acid. •The “ALIMENTARY CANAL” is the pathway which food travels through the digestive system. THE ALIMENTARY CANAL ORDER OF TRAVEL THROUGH THE CANAL: Mouth Esophagus Stomach 36 feet long!!! Small intestine Large intestine Rectum Anus * The liver, pancreas, and gallbladder are parts of the digestive system but are not parts of the alimentary canal. THE MOUTH • Mechanical (chewing) and chemical (saliva) digestion occur in the mouth • Salivary glands produce saliva, which lubricates food • Saliva contains enzyme amylase • ***Starch digestion starts here AMYLASE STARCH SUGARS • • • • ESOPHAGUS Muscular tube leads from back of throat (pharynx) to stomach Opening to trachea and esophagus are right next to each other Epiglottis prevents food from going down the trachea Muscular contractions (peristalsis) pushes food down the esophagus, not gravity 9.8 IN STOMACH 4 HOURS •Responsible for protein digestion •Mechanical digestion—stomach churns •Chemical digestion with stomach •Sphincter muscles control what enters and leaves the stomach •Stomach lining contains mucus that protects stomach from acid •Ulcers SMALL INTESTINE •20 ft. long •Remaining carbs and proteins are broken down •***ALL lipids are digested in S.I. •Gall bladder is attached (stores bile from the liver & delivers to the S.I.) SMALL INTESTINE (CONT.) •**After nutrients are digested from food, they are absorbed into the blood here •S.I. contains lots of capillaries for this •Mesentery—weblike group of capillaries LARGE INTESTINE •All proteins, carbs, and lipids have been removed from food by the time it gets here •Water and vitamins in food is absorbed into the blood •Whatever undigested food is left is feces and passes out of the anus LIVER AND PANCREAS SECRETE DIGESTIVE ENZYMES LIVER FUNCTIONS Detoxifies drugs and alcohol Makes and secretes bile, which breaks down lipids. Bile is stored in the gall bladder. PANCREAS FUNCTIONS Regulates blood sugar. Releases digestive enzymes into the S.I and neutralizes stomach acid before it enters S.I. EXCRETORY SYSTEM •Kidney • Filters the blood, removing waste • Vital role in maintaining homeostasis • Regulate amount of water in blood • ~1 Liter of urine produced each day. KIDNEY DISORDERS & TREATMENT 13 million people suffer from kidney disorders in the US. •~ • Kidney stones-uric or oxalic acid, calcium salts, etc. collect outside of kidneys • Hemodialysisfiltering of blood • Receive 2x’s a week HUMAN NERVOUS SYSTEM Controls and coordinates functions throughout the body Neurons are specialized cells that transmit impulses throughout the body. Nervous System Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Somatic Autonomic HUMAN NEURON DIAGRAM Dendrite Cell body Myelin sheath Axon Node of Ranvier Axon terminals HUMAN ENDOCRINE SYSTEM The endocrine system consists of ductless glands that produce hormones. Hypothalamus, pituitary, pineal, thyroid, parathyroid, thymus, adrenal, pancreas, ovary, testes Hormones are chemical messengers that travel through the blood stream and affect activities throughout the body. Steroid hormones Nonsteroid hormones Nonspecific defense responses ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Skin and mucous membranes Inflammatory response Temperature Proteins White blood cells Specific immune responses ◦ Humoral immunity ◦ Cell-mediated immunity Body’s attack against a pathogen that made it past the “front lines.” Results in “immunity” because your immune response creates memory cells SPECIFIC for each pathogen. White blood cells are called leukocytes Made in the thymus (T cells) and bone marrow (B cells) Stored in tonsils, spleen, and lymph nodes. Main function: produce and deliver sperm A sexually mature human male, produces millions each day. Sperm are produced in the testes by meiosis (spermatogenesis). Tail- used for locomotion Midsection- contains mitochondria. Why? Head- holds chromosomes and digestive enzymes which allow sperm to penetrate into the egg The females’ reproductive role is to: 1.) Make and release eggs 2.) Nourish the developing fetus Ovulation: egg bursts out of the follicle and is released, moving through fallopian tube, where it may be fertilized The uterus must be ready to accept a fertilized egg. Different hormones help to control the cycle Zygote- Newly fertilized egg. Once it begins to divide, it is called an embryo. Embryo must “implant” itself into the uterine wall. Transports materials back and forth to the embryo ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Oxygen – Carbon dioxide Nutrients (carb’s, protein, fat) Urea (liquid, cellular waste) Antibodies