* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Exemplar Assignment Brief - An Introduction to Electronics at Level 3
Neutron magnetic moment wikipedia , lookup
Van Allen radiation belt wikipedia , lookup
Metamaterial wikipedia , lookup
Metamaterial cloaking wikipedia , lookup
Mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Magnetometer wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotactic bacteria wikipedia , lookup
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
Earth's magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic monopole wikipedia , lookup
Superconducting magnet wikipedia , lookup
Giant magnetoresistance wikipedia , lookup
Magnetoreception wikipedia , lookup
Negative-index metamaterial wikipedia , lookup
Electromotive force wikipedia , lookup
Magnetohydrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Multiferroics wikipedia , lookup
Force between magnets wikipedia , lookup
Magnetochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotellurics wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnet wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetic field wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Ferromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
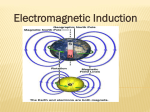
Assessment 4 Centre Canterbury College Course title: BTEC Extended Diploma in Engineering Level 3 Tutor name: Assignment title: Learner name Start date: Capacitors in DC Circuits Ref: Deadline: Unit 6 Electrical and Electronic Principles Scenario Knowledge of magnetism and electromagnetism is essential in order to underpin futher learning in electrical subjects. In this assessment you will discover how magnetism is used to produce and distribute electricity throughout the country and how the same underlying principles are used in various different types of machinery encountered throughout industry. Assessment evidence: Unit Assessment criteria The assessment criteria that this assignment relates to: P7 Describe the characteristics of a magnetic field P8 Describe the relationship between flux density (B) and field strength (H) 6 P9 Describe the principles and applications of electromagnetic induction D2 Evaluate the performance of a motor and a generator by reference to electronic theory Task Specific Feedback Learner declaration I certify that the work submitted for this assignment is my own and research sources fully acknowledged. Learner signature: Assessment Criteria P4 P5 P6 M2 Date: Achieved/Not Achieved Resubmit by Signed Lecturer Unit 6 P7 Describe the characteristics of a magnetic field Draw the magnetic field associated with a permanent bar magnet and use the diagram to carry out the following tasks. Give 5 general properties of a magnetic field. Define flux, flux density and magnetic field strength Describe the effects of reluctance and hysteresis with respect to magnetic circuits. Define the term ferromagnetic and give three examples of a ferromagnetic material Describe the process and advantages of magnetic screening Unit 6 P8 Describe the relationship between flux density (B) and field strength (H) Plot the B/H curve on a suitable graph for the materials shown on the table from the given data and determine the relative permeability (µr) of the material for each stage. Given that µo = 4 x 10-7 H/m find the range of relative permeability for each material. Use the data plotted on the graph to analyse and explain the relationship between the two given materials in terms of flux density (B) and magnetizing force (H) Remember relative permeability µr = B/(H x µo) Plot the graph that shows relative permeability against the magnetizing force Describe what happens to a material as the magnetizing force is increased in terms of flux density and relative permeability Magnetizing Force (H) At/m Mild steel Flux density (B) Tesla’s 1000 2000 3000 4000 5000 0.7 1.24 1.45 1.55 1.6 Cast Iron Flux density (B) Tesla’s 0.3 0.48 0.6 0.67 0.72 Unit 6 P9 Describe the principles and applications of electromagnetic induction Use the following tasks to describe the principles and applications of electromagnetic induction. Define Faraday’ laws in your own words using diagrams where appropriate. Define Lenz’s law in your own words using diagrams where appropriate. Draw a diagram of a simple AC generator and use Fleming’s right hand rule to demonstrate the direction of the current in the rotating conductor when it is perpendicular to the North Pole. Explain the principle of operation of a simple transformer with reference to Faradays law of electromagnetic induction Explain the principle operation of a 3 phase AC induction motor with reference to Faradays law of electromagnetic induction Unit 6 D2 Evaluate the performance of a motor and a generator by reference to electronic theory Describe the basic operation of a dc machine using diagrams as appropriate. Your description should include: The construction of the machine Types of field winding Types of armature winding A basic description of the action of the commutator How a dc machine can be used either as a motor or a generator Calculate the following a) The no-load terminal voltage of a d.c. generator is 300 volts when working at its rated speed and nominal flux density. If the speed is reduced by 15% and the flux per pole is increased by 20% calculate the new value of the no-load terminal voltage. b) d.c. motot develops a torque of 500 Nm when carrying an armature current of 25A. What torque is produced if the flux density is increased by 15 per cent and the armature current is increased to 35A?