* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1 - tamta
Magnetosphere of Saturn wikipedia , lookup
Geomagnetic storm wikipedia , lookup
Skin effect wikipedia , lookup
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
Van Allen radiation belt wikipedia , lookup
Edward Sabine wikipedia , lookup
Electromotive force wikipedia , lookup
Mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic stripe card wikipedia , lookup
Giant magnetoresistance wikipedia , lookup
Neutron magnetic moment wikipedia , lookup
Superconducting magnet wikipedia , lookup
Earth's magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Magnetometer wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic monopole wikipedia , lookup
Induction heater wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotactic bacteria wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Multiferroics wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Magnetohydrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Magnetoreception wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotellurics wikipedia , lookup
Force between magnets wikipedia , lookup
Magnetochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Friction-plate electromagnetic couplings wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnet wikipedia , lookup
Ferromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
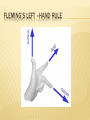
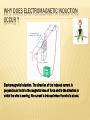
Electromagnetic Induction THE MAGNETIC FORCE ON MOVING CHARGE THE NORTHEN LIGHTS QS. 1- Where does the northern lights happen ? 2-Where does the magnetic field of Erath very strong ? 3- How does the northern lights occur ? 4- F = B Q v , what does the equation mean ? 5- In which direction does the force act ? Look pg :224-226 FLEMING’S LEFT –HAND RULE WHAT IS ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION ? When does the pointer of ammeter move ? WHY DOES ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION OCCUR ? Electromagnetic induction. The direction of the induced current is perpendicular both to the magnetic lines of force and to the direction in which the wire is moving. No current is induced when the wire is at rest. USEFUL WEBSITE http://nuweb.neu.edu/bmaheswaran/phyu121 /data/ch05/fig05.htm FARADAY’S MODEL ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION : 1- what happens when you move the magnet into coil ? What happens if you move the coil instead of the magnet ? http://www.bbc.co.uk/scotland/learning/bitesi ze/standard/physics/energy_matters/source_t o_consumer_rev1.shtml What is the relation between the turns of wire in coil and E.M.F.? The more turns on the coil , the greater the e.m.f. this is because N turns will cut N times more lines of flux than just one turn . How can you increase the size of the e.m.f. induced across a coil ? Useful information Magnetic flux is the amount of magnetic field threading or “flowing through” a certain area A, such as the area inside a flat coil of wire. This is represented diagrammatically by the total number of magnetic flux lines that pass through area A. The stronger the magnetic field at a point, the higher the magnetic flux density B is at that point and the more magnetic flux lines there are cutting or threading a given area. B is a measure of magnetic flux per unit area perpendicular to the direction of the field at a point in the field. To find the total amount of flux passing through area A, we need to multiply the magnetic flux density B by the number of square meters in area A. This can be expressed mathematically as flux = flux density × area, or In SI units, magnetic flux is measured in Webers (Wb) and magnetic flux density is measured in Webers per square meter (Wb m-2)