* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Heart
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
History of invasive and interventional cardiology wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Pericardial heart valves wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Aortic stenosis wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
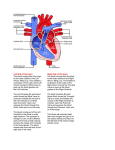
The Heart YC Wong, PhD 王雲川 The University of Hong Kong [email protected] Scope • Overview of anatomy of the heart • Surface markings and gross anatomical structure • Vascular system of the heart • Impulse conducting system • Histology of the heart Location and surface markings Sternal angle • Located in middle mediastinum 纵隔 • Locate the sternal angle • Point one: right 3rd costal cartilage 1 cm from sternum border • Point 2: 6th costal cartilage, 1 cm from sternum • Point 3: 5th left intercostal space just medial to mid clavicular line • Point 4: 2nd left intercostal space at the border of sternum • Join the 4 points to mark the outer shape of the heart The Pericardium 心包膜 • • • • • • Fibrous capsule enclosing the heart Separated by pericardial cavity filled with fluid To reduce the friction of heart during pumping Lined by serous pericardium 浆膜心包 Subdivided into parietal and visceral layers The parietal layer closely adheres to fibrous pericardium 纤维 心包; the visceral layer reflected on the outer surface of heart, the external limit of epicardium 心外膜, lined by mesothelium 间皮 • Perforated only at the roots of major vessels • Reflections of serous pericardium forms transverse sinus 横窦 and oblique sinus 斜窦 The Pericardium 心包膜 Trans Sinus R. Pulmonary V L pulmonary V Oblique Sinus Anatomy of the Heart Right atrium Left auricle Left ventricle Right ventricle Apex • Located in middle mediastinum • Surrounded by pericardium • Apart from attachment to major vessels, the rest is basically free within pericardial cavity • Three surfaces: sternocostal surface, diaphramatic surface and base, i.e. the posterior surface • The apex 心尖 of the heart is directed forward, downward and to the left Four Chambers • • • Right Atrium Left atrium • • Pulmonary v Aortic v Mitral v • Tricuspid v • Right ventricle Left ventricle • Divided by vertical septa to form 4 chambers Right atrium and left atrium, separated by interatrial septum Right ventricle and left ventricle, separated by interventricular septum Right atrium and right ventricle is guarded by a valve, the tricuspid valve, 三尖瓣 Left atrium and left ventricle is guarded by mitral valve 二尖瓣 Deoxygenated blood returns to right atrium then to right ventricle which is pumped to the lungs via pulmonary trunk, guarded by pulmonary valve 肺动脉瓣 Oxygenated blood from the lungs enters the left atrium, then to left ventricle This blood is pumped through aorta guarded by aortic valve 主动脉瓣 Right atrium 右心房 Right auricle Superior vena cava Musculi pectinati Fossa ovale Inferior vena cava with valve • Receive blood from superior vena cava 上腔靜脈 • Inferior vena cava 下腔靜脈 • Venous blood from the heart, the coronary sinus 冠状窦 • Interior surface, musculi pectinati 梳状肌 • Fossa ovale 卵圆窝, on interatrial septum • Crista terminalis 界嵴 • Right auricle 心耳, an extension from atrium, irregular surface • Location of sinoatrial node 竇 房結at junction with superior vena cava Patent foramen ovale • • • • Fairly common Hidden condition No obvious symptoms Left atrium pressure higher than right, the potent opening is physiologically closed • Reason for the opening to stay patent, and not fused afterbirth remains unclear. • No treatment is needed in most cases Atrial Septal Defect (ASD) • Hole in interatrial septum • Allow left atrial blood (oxygenated) to enter right atrium (lower pressure) • Increased work load of right ventricle • Small hole, no significant effect • Medium or large hole may require surgical repair Ventricular Septal Defect • Hole in interventricular septum • Can be in different location along the septum • Blood flow from left ventricle through hole to right venricle • Increased right ventricle work load • Increase pulmonary pressure, pulmonary hypertension • Require surgical intervention Right ventricle 右心室 Anterior cusp Septal cusp Chordae tendinease Posterior cusp of tricuspid valve Papillary muscle Moderator band • Wall much thicker than atrium • Separated from atrium by tricuspid valve • With anterior, posterior and septal cusps • Papillary muscle for the attachment of heart valve tendons, chordae tendineae 腱索 • Moderator band 节制带 • Pumps blood into pulmonary trunk • Guarded by semilunar valves 半月瓣 Left atrium 左心房 • The wall is thin, like right atrium, • Located mainly at the posterior surface • A large portion is formed by absorption of major blood vascular wall during development • Extension of left auricle to the stenocostal surface • Smooth interior surface receive 4 pulmonary veins from the lungs Left ventricle 左心室 Mitral valve Chordae tendinease Papillary muscle • Wall very thick, twice as thick as right ventricle • Separated from left atrium by mitral valve, with only two leaflets • Responsible for systemic circulation • Interior surface is rough with trabeculae carneae心肉柱, papillary muscles, but no moderator band • Chordae tendineae 腱索, to strengthen the leaflets of the valve • Pumps blood out through aorta • Guarded by aortic valve, semilunar valve • The part of heart immediately below the aortic orifice is known as aortic vestibule Cardiac skeleton 心骨架 Fibrous ring of pulm trunk Mitral valve ring • Not a true skeleton • Fibrous connective tissues located between atria and ventricles • One ring between right atrium and right ventricle • The other between left atrium and left ventricle Fibrous ring • Forms an 8 shape figure at aortic valve • For the attachment of atrial fibres and ventricular fibres as well as attachment of tricuspid and mitral valves • Extensions of fibrous connective tissues to the roots of pulmonary trunk and aorta for Tricuspid valve ring attachment of semilunar valve leaflets • No direct connection/contact between atrial and ventricular muscle fibres Heart valves 心瓣 • Atrio-ventricular valves 房室瓣 – Tricuspid valve: between right atrium and right ventricle • Three leaflets anchor through tenon-like structure, chordae tendineae – Mitral valve: between left atrium and left ventricle • Two leaflets • Pulmonary valve: at the junction of pulmonary trunk with right ventricle – Semilunar valve: three leaflets of half moon shape • Aortic valve: junction of aorta with left ventricle – Semilunar valve with three leaflets of half moon shape – Origin of coronary arteries from aortic sinus The coronary arteries 冠狀動脈 • Left coronary artery: larger, from left posterior aortic sinus. It enters atrioventricular groove and gives rise to: L coronary a L circumflex b R coronary a Anterior interventricul ar branch Marginal b Posterior interventric ular branch – Anterior interventricular branch, anastomoses with posterior interventricular branch from right coronary artery – Left circumflex branch, anastomosing with right coronary artery • Right coronary artery: from anterior aortic sinus runs between pulmonary trunk and right auricle, and atrioventricular groove – Marginal branch – Posterior interventricular branch Variations of coronary arteries A. Left coronary artery dominant B. Only one coronary artery, the right one is missing C. Circumflex artery is arising from right coronary artery Coronary arteries and heart diseases • Crucial for heart health • Anastomoses between artery branches though occur, but most branches supply a secluded area • Blockage of vessels or branches of vessels often results in death of cardiac muscle fibres in the affected, myocardiac infarction 心肌梗 塞 • Serious cases result in death Venous drainage of the heart Coronary sinus Great cardiac vein Small cardiac vein Middle cardiac vein Coronary sinus Middle cardiac vein • Venous blood returns to right atrium via coronary sinus • It is a continuation of great cardiac vein running parallel to anterior interventricular artery • Small and middle cardiac veins are tributories of coronary sinus • Anterior cardiac vein empties directly into right atrium Impulse conducting system of heart Impulse conducting system 心臟之傳導系統 • Specialized cardiac muscle to regulate the rhythm of heart • Sinoatrial node , 窦房结 pace-maker of the heart, to set the pace of heart beat • Initiates atrial heart muscle contraction as well as spreading the signals to AV node 旁室結 • Atrioventricular node passes the singals to Purkinje fibres • Two branches extended out from here, known as bundle of HIS • Bundles of His run down along the sides of interventricular septum and give off Purkinje fibres • Purkinje fibres spread contraction signals to ventricular cardiac fibres, to start ventricular contraction • Cardiac arrththmia 心律失常 PA X-ray of the Heart Auscultation points of heart sounds Aortic valve Right atrium Tricuspid valve Right ventricle • A for aortic valve • P for pulmonary valve • T for tricuspid valve • M for mitral valve Histology of the heart With three basic layers Endocardium 心內膜 Myocardium 心肌膜 Epicardium 心外膜 Endocardium • Inner most • Endothelium • Sub-endothelial connective tissue • Sub-endocardial layer which may contain conducting system of heart, Purkinje fibres Myocardium • Substantially thicker • Contains cardiac muscle • With intervening collagen tissue and smaller vessels • Atrial walls are much thinner than myocardium in ventricles • Muscles are attached to cardiac skeleton between atria and ventricles • Typical cardiac fibre morphology with striations and intercalated disks Epicardium • Rich in fat (A; adipose tissue) • Free surface covered by mesothelial (M) cells • Connective tissue • Blood vessels, coronary vessels M Heart valves 心瓣 • Aortic valve: semilunar valve with three leaflets, each is shaped as half-moon • Pulmonary valve: same as aortic valve with three leaflets • Left atrioventricular valve or mitral valve: two leaflets reinforced with tendinous cords known as chordae tendineae, to prevent eversion • Right atrioventricular valve or tricuspid valve: three leaflets, also reinforced with chordae tendineae Structure of heart valves • • • • Attached to fibrous cardiac skeleton Formed as a flap extending from tunica intima Normally avascular in nature Supported by a core of irregular dense connective tissue continuous with cardiac skeleton • Covered on both side by endothelial cells Impulse conducting system (structure) • Sinuatrial (SA) node, pacemaker, specialized group of cardiac fibres located at junction between superior vena cava and right atrium – Smaller than ordinary fibres • Atrioventricular (AV) node • AV bundle of His, further divide to left and right bundles and then into subendocardial fibres • Purkinje fibres – Larger in diameter, paler staining and carry impulses to ordinary cardiac muscle in ventricles – Rich in sarcoplasm, scarce myofibrils Purkinje fibres (P) Myocardium Summary • • • • • • Surface anatomy of the heart Structure of the heart Common septal defects The coronary vessels Impulse conducting system Histological organization of the heart End