* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Carbon Compounds
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
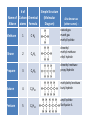
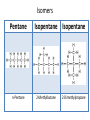
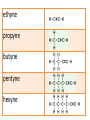
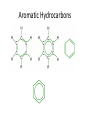
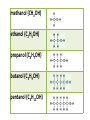
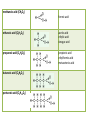
Carbon • Over 90% of the compounds in nature are based on carbon. • Different pure forms are found in nature. – Diamond – Graphite – Buckminsterfullerene – Amorphous Diamond • Network solid – All atoms have 4 covalent bonds • Hardest substance known • Conducts heat but not electricity Graphite • Soft – Strong bonds only in 2d (carbon fiber materials) Slippery – Layers glide over one another easily – Semimetal conducts electricity – Used in batteries, steel making, brake linings lubricant, pencil, electric motors Buckminsterfullerene • C60 – Medical research • Carbon Nanotubes – Strong – Electronics Amorphous • No crystalline shape – Coal: carbon and other compounds • Peat, lignite, bituminous, anthracite – Charcoal – Activated carbon Carbon Compounds Organic • Do not dissolve in water • Decompose easily with heat • Chemical reactions slow • Reactions rate affected by environment conditions • Covalent bonding • Isomers Inorganic • Dissolve in water • Difficult to decompose • Reactions very quick • Reaction rate not affected by conditions • Many have ionic bonds • No isomers Hydrocarbons • Composed of carbon and hydrogen only Alkanes • All single bonds between the carbons – Saturated – Low chemical reactivity – The general formula is CnH2n+2 – Names end with “ane” – Natural gas (mostly methane) # of Name of Carbon Chemical Alkane atoms Formula Methane Ethane Propane Butane Pentane 1 2 3 4 5 Simple Structure (Molecular Diagram) Also known as (other names) : C H4 natural gas marsh gas methyl hydride C2H6 dimethyl methyl methane ethyl hydride C3H8 C4H10 C5H12 dimethyl methane propyl hydride methylethyl methane butyl hydride amyl hydride Skellysolve A # of Carbon atoms Chemical Formula Hexane 6 C6H14 Heptane 7 C7H16 Octane 8 C8H18 Nonane 9 C9H20 Decane 10 C10H22 Name of Alkane Simple Structure (Molecular Diagram) Isomers • Same chemical formula but different structural formula Isomers Pentane n-Pentane Isopentane Isopentane 2-Methylbutane 2-Dimethylpropane Cycloalkanes • Ring structure of single carbon bonds • Add the prefix cyclo to the alkane name • Similar properties to alkanes Cycloalkanes cyclopropane cyclobutane cyclopentane cyclohexane Alkenes • Hydrocarbons which have at least one double bond between two carbons. We will always use one double bond only. • Unsaturated • The naming prefixes are the same as for alkanes with an ene ending • The general formula is CnH2n • Plastics ripen fruit Alkynes • Hydrocarbons which have at least one triple bond between two carbons. We will always use one triple bond only. • Unsaturated • The naming prefixes are the same as for alkanes with an yne ending • The general formula is CnH2n-2 • pharmaceuticals ethyne propyne butyne pentyne hexyne Aromatic Hydrocarbons • Ring structure with alternating single and double bonds. (resonance) • Many have pleasant aroma • Benzene is very important because it is found as part of many complex organic molecules Aromatic Hydrocarbons Aromatic Hydrocarbons Substituted Hydrocarbons • One or more hydrogen or carbon atoms are replaced by another element or group of elements. • The replacement atoms are called a functional group. • The functional group determines the new properties of the molecule. Halocarbons • One or more halogen atoms are substituted for hydrogen atoms in an alkane • Add the halogen prefix to the alkane name – Chloropropane – Draw: difloromonochloropentane Alcohol • A hydroxyl group replaces a hydrogen • The suffix ol is added to the name of the molecule • Common and official names (use official) • Some widely used alcohols are – Methanol: mixed with gasoline, very poisonous – Ethanol: mixed with gasoline, Ingested – Glycerol: cosmetics, foods methanol (CH3OH) ethanol (C2H5OH) propanol (C3H7OH) butanol (C4H9OH) pentanol (C5H11OH) Organic Acid • A carboxyl group (COOH) replaces three hydrogen atoms. The group has to stay together. • Common and official names • Some common organic acid – Acetic: good solvent of organic compounds – Formic: used by certain plants and animals (ants) – Oxalic: dyeing fabrics, stain removal methanoic acid (CH2O2) formic acid ethanoic acid (C2H4O2) acetic acid ethylic acid vinegar acid propanoic acid (C3H6O2) propionic acid ethylformic acid metacetonic acid butanoic acid (C4H8O2) pentanoic acid (C5H10O2) Organic Base • An amine group (NH2) replaces a carbon atom – Paints, dyes, disinfectants Dehydration Synthesis • A process by which small molecules can be hooked together to form large ones • A hydroxide from one molecule reacts with a hydroxide in another. Water is released and the two molecules are joined by the remaining oxygen Esters • A molecule made from the dehydration synthesis of an organic acid and an alcohol • Excellent solvents for organic compounds • Odors and flavors of fruits and flowers • Perfumes and artificial flavorings methyl methanoate ethyl methanoate methyl ethanoate ethyl ethanoate methyl propanoate ethyl propanoate Carbohydrates • Contain only the elements Carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. Monosaccharides • All have formula (CH2O)n where n is between 3 and 7 • Glucose is the main transport sugar in animals • Main source of energy in animals Disaccharides Polysaccharides • Long chains of monosaccharides Starch • Plant energy storage Glycogen • Animal energy storage Cellulose • Main component of cell walls. • Sometimes referred to as fiber. • Cannot be broken down by animals. No enzyme – Need mutualistic bacteria Lipids • A type of ester. “fatty acid” + alcohol • High energy storage molecules – Contain more than twice as much energy per gram as carbohydrates • Insoluble in water Lipids • Wax: solid, high melting point – Waterproof coating on leaves, feathers, hair, skin • Fats: solid, low melting point, glycerol – Saturated, unsaturated • Oils: liquid, glycerol – Saturated, unsaturated • Triglycerides Lipids • Phospholipids: 1 or 2 fatty acids are replaced by phosphate groups – Chief lipid in Biological membranes • Steroids: ring structures – Cholesterol: used in cell membranes, nerves – Some types of hormones: cortisone, estrogen, epinephrine (adrenalin) • Terpins Amino Acids • An amine (NH2) functional group and a carboxyl (COOH) functional group are attached to a central carbon. • We use 21 (20 + 1)but can only manufacture 12 • Monomers used to make proteins Protein • Made up of amino acids that have been joined together by a peptide bond DNA • Natural Polymers Enzymes / Vitamins • Enzymes – Proteins that speed up chemical reactions • Lock and key: read your bio book • Vitamins – Organic compounds that you need but cannot manufacture Photosynthesis / Respiration • Photosynthesis – Plants – 6H2O + 6CO2 + energy → C6H12O6 + 6O2 • Respiration – Plants and Animals – C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6H2O + 6CO2 + energy Nylon • http://prezi.com/7o64juvf5jua/copy-of-apbio-chemistry-2-macromolecules/