* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Thyroid Hormone Synthesis, PDF
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
Neuroendocrine tumor wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (menopause) wikipedia , lookup
Signs and symptoms of Graves' disease wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamus wikipedia , lookup
Hypopituitarism wikipedia , lookup
Growth hormone therapy wikipedia , lookup
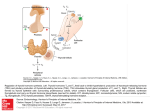
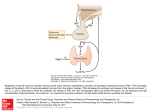
Thyroid Hormone Synthesis, Regulation and Diagnostics Howard J. Sachs, MD www.12daysinmarch.com Thyroid follicular lumen filled with colloid Colloid TGB Cuboidal Thyroglobin Tyrosine-rich protein Initial Step: Thyroglobulin (TGB) synthesized in ER of follicular cell Thyroid follicular lumen filled with colloid TGB The next slides will review the 3 critical steps in thyroid hormone synthesis: 1. Oxidation 2. Organification 3. Coupling Note: Each step is catalyzed by Thyroid Peroxidase Autoantibodies: Anti-TPO Meds: PTU, MTZ Oxidation (I- ® I2), Organification and Coupling I2 TGB I2 I2 I2 Thyroglobin Capillary 2Na-I Transporter Capillary Step One: Iodide (I -) is absorbed in inverse proportion to serum concentration. Oxidized to Iodine (I 2) Oxidation (I- ® I2), Organification and Coupling I2 TGB I2 I2 I2 Thyroglobin I- Capillary I- 2Na-I Transporter I- I- I- Stimulated by TSH Capillary Step One: Iodide (I -) is absorbed in inverse proportion to serum concentration. Oxidized to Iodine (I 2) Oxidation (I- ® I2), Organification and Coupling TGB I2 MIT TGB I2 TGB I2 DIT Thyroglobin Capillary Na-I Transporter Capillary Step Two: Organification. Iodine binds tyrosine residues on thyroglobulin (TGB) to form mono- and di-iodotyrosine Oxidation (I- ® I2), Organification and Coupling TGB I2 MIT TGB I2 TGB I2 MIT DIT T3 DIT DIT T4 DIT Thyroglobin Capillary Na-I Transporter Capillary Step Three: Coupling. Just as it sounds! MIT and DIT couple to form T4 >>> T3 Oxidation (I- ® I2), Organification and Coupling TGB I2 MIT TGB I2 TGB I2 MIT DIT T3 DIT DIT T4 DIT All Three Steps Catalyzed by ~ Thyroid Peroxidase ~ Thyroglobin Capillary Na-I Transporter Capillary Thyroid hormone release MIT DIT T3 DIT DIT T4 T3 T4 Na-I Transporter Capillary T4 T3 T4 Capillary Capillary I T4 T4 I T3 I Capillary I 5’-deiodinase I I I 1. T4 is released in higher concentration than T3. 2. T4 is less active than T3 (i.e. behaves as a ‘prohormone’). 3. T4 is converted in the periphery by 5’-deiodinase to T3, the biologically active form of thyroid hormone. Thyroid Hormone Infomercial Capillary I I T4 T4 I I T3 I Capillary I I I I rT3 is elevated in ‘sick euthyroid syndrome’ I 1. During times of ‘abundance’, T4 may also be converted to reverse T3 (rT3). 2. rT3 has a different iodine molecule removed. 3. It is biologically inactive. TBG = Thyroid Binding Globulin (do not confuse with thyroglobulin!) T4 T4 TBG T3 • • • T4 5’-deiodinase T3 T4 T4 TBG T3 TBG Trivia (synthesized in liver): Once released into the circulation. thyroid hormone circulates bound to TBG This serves as a ‘reservoir’ for hormone. High affinity for T4 Only free circulating hormone (~1%) is biologically active! TBG TBG Lots of bound T4 = TOTAL T4 TBG TBG TBG TBG TBG • • Free T4 Bioavailable Form Increased TBG (e.g. pregnancy, OCP) Decreased TBG Key Point: • • TBG levels can increase (e.g. pregnancy) or decrease (e.g. cirrhosis). The total amount of hormone (tT4) will increase or decrease with TBG levels BUT the amount of free (bioavailable) hormone will NOT change. Thyroid Hormone Regulation Pituitary and TSH are key players Hypothalamus: TRH Adenohypophysis: TSH Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Thyroid, TSH (Thyroid Stimulating Hormone) A trophic hormone that can cause hypertrophy and hyperplasia Hypothalamus: TRH Anterior Pituitary: TSH T3 T4 Hypothalamus: TRH (-) Anterior Pituitary: TSH (-) T3 T4 Thyroid Diagnostics Serology TSH Hormone Free T4 Total T4 (tT4) T3 rT3 Immune Markers TSIg Anti-TPO Anti-TGB Miscellaneous: ESR TGB Primary Thyroid Gland Dysfunction Imaging Pathology Ultrasound Nuclear Radioactive Iodide Uptake (RAIU) Technetium Cytopathology (FNA) (Excisional) Biopsy Thyroid Diagnostics Serology TSH Hormone Free T4 Total T4 (tT4) T3 rT3 Immune Markers TSIg Anti-TPO Anti-TGB Miscellaneous: ESR TGB Imaging Pathology Patient is treated with T3 for hypothyroidism. How do the Cytopathology (FNA) Ultrasound following respond? (Excisional) Biopsy Nuclear Radioactive Iodide Uptake (RAIU) Technetium ¯ TSH ¯ T4 ¯ rT3 Thyroid Diagnostics Serology TSH Hormone Free T4 Total T4 (tT4) T3 rT3 Immune Markers TSIg Anti-TPO Anti-TGB Miscellaneous: ESR TGB Imaging Pathology Patient is treated with T3 for hypothyroidism. How do the Cytopathology (FNA) Ultrasound following respond? (Excisional) Biopsy Nuclear Radioactive Iodide Uptake (RAIU) Technetium ¯ TSH ¯ T4 ¯ rT3 Question Hierarchy: Data >> Physical Exam >> Language Thyroid Diagnostics Serology TSH Hormone Free T4 Total T4 (tT4) T3 rT3 Immune Markers TSIg Anti-TPO Anti-TGB Miscellaneous: ESR TGB Imaging Pathology Ultrasound Cytopathology (FNA) (Excisional) Biopsy Nuclear Radioactive Iodide Graves Disease Uptake (RAIU) Technetium Hashimoto’s Lymphocytic Thyroid Diagnostics Serology TSH Hormone Free T4 Total T4 (tT4) T3 rT3 Immune Markers TSIg Anti-TPO Anti-TGB Miscellaneous: ESR TGB Imaging Pathology Ultrasound Cytopathology (FNA) (Excisional) Biopsy Nuclear Radioactive Iodide Uptake (RAIU) Technetium Granulomatous (Viral) Thyroiditis Serial monitoring, Neoplasm Hyperthyroidism, Inflammatory Thyroid Diagnostics Serology Imaging TSH Hormone Total T4 (tT4) Free T4 T3 rT3 Pathology Ultrasound Nuclear Radioactive Iodide Uptake (RAIU) Immune Markers TSIg Technetium Anti-TPO Anti-TGB Anatomic Miscellaneous: ESR TGB Functional Cystic v Solid Cytopathology (FNA) (Excisional) Biopsy Increased v Decreased Uptake Thyroid Diagnostics Serology Imaging Pathology Ultrasound FNA: Cytopathology Nuclear Radioactive Iodide Uptake (RAIU) (Excisional) Biopsy TSH Hormone Total T4 (tT4) Free T4 T3 rT3 Immune Markers TSIg Anti-TPO Anti-TGB Miscellaneous: ESR TGB Technetium Anatomic Functional Tumors, 4 Hashimoto Graves Granulomatous Riedel’s Thyroid Diagnostics Serology Imaging Pathology TSH FNA most useful for Ultrasound Hormone Total T4 (tT4)Papillary Carcinoma Free T4 T3 rT3 Immune Markers TSIg Anti-TPO Anti-TGB Miscellaneous: ESR TGB Nuclear Radioactive Iodide Uptake (RAIU) FNA: Cytopathology (Excisional) Biopsy Technetium Anatomic Functional Tumors, 4 Hashimoto Graves Granulomatous Riedel’s Thyroid Hormone Synthesis, Regulation and Diagnostics Key Derivatives