* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cellular Biology
History of catecholamine research wikipedia , lookup
Mammary gland wikipedia , lookup
Neuroendocrine tumor wikipedia , lookup
Hyperthyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Hyperandrogenism wikipedia , lookup
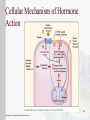
Endocrine disruptor wikipedia , lookup
Growth hormone therapy wikipedia , lookup
Mechanisms of Hormonal Regulation Chapter 20 1 Hormones General characteristics Specific rates and rhythms of secretion Diurnal, pulsatile and cyclic, and patterns depending on circulating substances Operate within feedback systems Affect only cells with appropriate receptors The liver inactivates hormones, rendering the hormones more water soluble for renal excretion 2 Mosby items and derived items © 2006 by Mosby, Inc. The Endocrine System 3 Mosby items and derived items © 2006 by Mosby, Inc. Regulation of Hormone Release Hormones are released: In response to an alteration in the cellular environment To maintain a regulated level of certain substances or other hormones Hormones are regulated by chemical, hormonal, or neural factors Negative feedback Positive feedback 4 Mosby items and derived items © 2006 by Mosby, Inc. Feedback 5 Mosby items and derived items © 2006 by Mosby, Inc. Hormone Transport Hormones are released into the circulatory system by endocrine glands Water-soluble hormones circulate in free, unbound forms Lipid soluble hormones are primarily circulating bound to a carrier 6 Mosby items and derived items © 2006 by Mosby, Inc. Cellular Mechanism of Hormone Action Target cell Up-regulation Down-regulation Hormone effects Direct effects Permissive effects 7 Mosby items and derived items © 2006 by Mosby, Inc. Cellular Mechanism of Hormone Action Hormone receptors Water-soluble hormones Located in or on the plasma membrane or in the intracellular compartment of the target cell High molecular weight Cannot diffuse across the plasma membrane Lipid-soluble hormones Easily diffuse across the plasma membrane and bind to cytosolic or nuclear receptors 8 Mosby items and derived items © 2006 by Mosby, Inc. Cellular Mechanism of Hormone Action Water-soluble hormones First messenger Signal transduction Second-messenger molecules Calcium Cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) Cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) 9 Mosby items and derived items © 2006 by Mosby, Inc. Cellular Mechanism of Hormone Action 10 Mosby items and derived items © 2006 by Mosby, Inc. Cellular Mechanism of Hormone Action Lipid-soluble hormones Steroid hormones Diffuse across the plasma membrane Androgens, estrogens, progestins, glucocorticoids, mineralocorticoids, and thyroid hormones Bind to cytoplasmic or nuclear receptors Activate RNA polymerase DNA transcription and translation 11 Mosby items and derived items © 2006 by Mosby, Inc. Lipid-Soluble Hormones 12 Mosby items and derived items © 2006 by Mosby, Inc. Structure and Function of the Endocrine Glands Hypothalamic-pituitary axis Hypothalamus Pituitary gland Anterior pituitary (adenohypophysis) Posterior pituitary (neurohypophysis) 13 Mosby items and derived items © 2006 by Mosby, Inc. The Pituitary Gland 14 Mosby items and derived items © 2006 by Mosby, Inc. Posterior Pituitary Hormones Synthesized with their binding proteins in the supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei of the hypothalamus Secreted by the posterior pituitary Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) Controls plasma osmolality Oxytocin Uterine contractions and milk ejection in lactating women 15 Mosby items and derived items © 2006 by Mosby, Inc. Posterior Pituitary Hormones 16 Mosby items and derived items © 2006 by Mosby, Inc. Anterior Pituitary Hormones Adrenocorticotropic hormone Melanocyte-stimulating hormone Growth hormone Prolactin Thyroid-stimulating hormone Luteinizing hormone Follicle-stimulating hormone β-lipotropin β-endorphins 17 Mosby items and derived items © 2006 by Mosby, Inc. Anterior Pituitary Hormones 18 Mosby items and derived items © 2006 by Mosby, Inc. Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands Thyroid gland Two lobes lateral to the trachea Isthmus Follicles (follicle cells surrounding colloid) Parafollicular cells (C cells) Secrete calcitonin Regulation of thyroid hormone secretion Thyrotropin-releasing hormone and thyroid stimulating hormone 19 Mosby items and derived items © 2006 by Mosby, Inc. Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands Thyroid hormones 90% T4 and 10% T3 Bound to thyroxine-binding globulin, thyroxinebinding prealbumin, or albumin Affect growth and maturation of tissues, cell metabolism, heat production, and oxygen consumption 20 Mosby items and derived items © 2006 by Mosby, Inc. Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands 21 Mosby items and derived items © 2006 by Mosby, Inc. Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands Parathyroid glands Small glands located behind the upper and lower poles of the thyroid gland Produce parathyroid hormone Regulator of serum calcium Antagonist of calcitonin 22 Mosby items and derived items © 2006 by Mosby, Inc. Parathyroid Glands 23 Mosby items and derived items © 2006 by Mosby, Inc. Parathyroid Glands 24 Mosby items and derived items © 2006 by Mosby, Inc. Endocrine Pancreas The pancreas is both an endocrine and an exocrine gland Houses the islets of Langerhans Secretion of glucagon and insulin Cells Alpha—glucagon Beta—insulin Delta—somatostatin and gastrin F cells—pancreatic polypeptide 25 Mosby items and derived items © 2006 by Mosby, Inc. Endocrine Pancreas 26 Mosby items and derived items © 2006 by Mosby, Inc. Endocrine Pancreas Insulin Synthesized from proinsulin Secretion is promoted by increased blood glucose levels Facilitates the rate of glucose uptake into the cells of the body Anabolic hormone Synthesis of proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids 27 Mosby items and derived items © 2006 by Mosby, Inc. Endocrine Pancreas Glucagon Secretion is promoted by decreased blood glucose levels Stimulates glycogenolysis, gluconeogenesis, and lipolysis Somatostatin Possible involvement in regulating alpha and beta cell secretions 28 Mosby items and derived items © 2006 by Mosby, Inc. Endocrine Pancreas 29 Mosby items and derived items © 2006 by Mosby, Inc. Adrenal Glands Adrenal cortex 80% of an adrenal gland’s total weight Zona glomerulosa Zona fasciculata Zona reticularis Adrenal medulla Innervated by the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems 30 Mosby items and derived items © 2006 by Mosby, Inc. Endocrine Pancreas 31 Mosby items and derived items © 2006 by Mosby, Inc. Adrenal Glands Adrenal cortex Stimulated by adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) Glucocorticoid hormones Direct effects on carbohydrate metabolism Anti-inflammatory and growth-suppressing effects Influence awareness and sleep habits Most potent naturally occurring glucocorticoid is cortisol 32 Mosby items and derived items © 2006 by Mosby, Inc. Adrenal Glands Adrenal cortex Mineralocorticoid hormones Affect ion transport by epithelial cells Increase the activity of the sodium pump of the epithelial cells Cause sodium retention and potassium and hydrogen loss Most potent naturally occurring mineralocorticoid is aldosterone Regulated by the renin-angiotensin system 33 Mosby items and derived items © 2006 by Mosby, Inc. Aldosterone 34 Mosby items and derived items © 2006 by Mosby, Inc. Adrenal Glands Adrenal cortex Adrenal estrogens and androgens Estrogen secretion by the adrenal cortex is minimal The adrenal cortex secretes weak androgens Androgens are converted by peripheral tissues to stronger androgens such as testosterone 35 Mosby items and derived items © 2006 by Mosby, Inc. Adrenal Glands Adrenal medulla Chromaffin cells (pheochromocytes) Chromaffin cells secrete the catecholamines epinephrine (majority) and norepinephrine Release of catecholamines has been characterized as a “fight or flight” response Catecholamines promote hyperglycemia 36 Mosby items and derived items © 2006 by Mosby, Inc. Catecholamines 37 Mosby items and derived items © 2006 by Mosby, Inc. Neuroendocrine Response to Stress The endocrine system reacts with the nervous system to respond to stressors The stress response also involves the immune system Influenced by corticotropin-releasing hormone from the hypothalamus 38 Mosby items and derived items © 2006 by Mosby, Inc. Tests of Endocrine Function Radioimmunoassay Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) Bioassay 39 Mosby items and derived items © 2006 by Mosby, Inc. Aging and the Endocrine System Thyroid gland Glandular atrophy, fibrosis, nodularity, and increased inflammatory infiltrates Parathyroid glands Related to alterations in calcium balance Inadequate intake, malabsorption, or renal changes Adrenal glands Decreased clearance of cortisol 40 Mosby items and derived items © 2006 by Mosby, Inc.