* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Function of the Heart
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
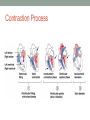
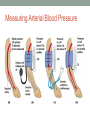
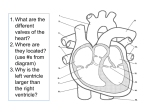
FUNCTION OF THE HEART Heart Sounds and Blood Pressure Terms: • Systole – Contraction of the myocardium • Diastole – Relaxation of the myocardium • Should already know: atria, ventricle, atrioventricular valve, aorta. Process/Sounds of the Heart 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Atrial systole (contraction) sends blood into the ventricles. The ventricles fill which causes the atrioventricular valves to start closing. Atrial diastole (relaxation). Ventricular systole injects blood into the aorta or pulmonary artery. AV-valves slam shut (“Lubb” sound) Process/Sounds of the Heart 6. Back pressure in the aorta or pulmonary trunk builds up. 7. The aortic valve and pulmonary valve slam shut (“Dupp” sound) 8. Ventricular diastole. Contraction Process Listen to Heart Sounds • Listen to your partner’s heart sounds. • Should hear lubb-dubb, lubb-dubb. • If a valve does not close all the way, it is called a murmur. Regulation of Cardiac Output BLOOD PRESSURE Section 13.5 Brainpop Blood Pressure Facts • The human heart creates enough pressure to squirt blood 30 ft. Blood Pressure Measurements by health professionals are made on the pressure in large arteries Systolic – pressure at the peak of ventricular contraction Diastolic – pressure when ventricles relax Pressure in blood vessels decreases as the distance away from the heart increases Measuring Arterial Blood Pressure Blood Pressure: Effects of Factors Neural factors Autonomic nervous system adjustments (sympathetic division) Renal factors Regulation by altering blood volume Renin – hormonal control Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings Slide 11.39a Blood Pressure: Effects of Factors Temperature Heat has a vasodilation effect Cold has a vasoconstricting effect Chemicals Various substances can cause increases or decreases Diet Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings Slide 11.39b Variations in Blood Pressure Human normal range is variable Normal 140–110 mm Hg systolic 80–75 mm Hg diastolic Hypotension Low systolic (below 110 mm HG) Often associated with illness Hypertension High systolic (above 140 mm HG) Can be dangerous if it is chronic Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings Slide 11.41