* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cardiac Cycle - Uplift Education
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Aortic stenosis wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Ventricular fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
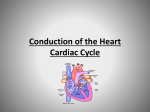
1. What are the different valves of the heart? 2. Where are they located? (use #s from diagram) 3. Why is the left ventricle larger than the right ventricle? Heart Actions •Cardiac Cycle: One complete heartbeat. The contraction of a heart chamber is called systole and the relaxation of a chamber is called diastole. The Cardiac Cycle There are two main parts of the cardiac cycle: 1. Contraction (systole) 2. Relaxation (diastole) Systole Term for the contraction phase The chambers pump blood out of the heart Systole 1. Atrial systole – atria contract, ventricles relax, tricuspid/bicuspid open, aortic/pulmonary closed 2. Early ventricular systole – atria relax, ventricles contract, ALL VALVES CLOSED 3. Late ventricular systole – atria relax, ventricles contract, tricuspid/bicuspid closed, aortic/pulmonary open Diastole The term for the relaxation phase This is the part of the cycle where the chambers of the heart fill with blood Diastole 4. Early Ventricular Diastole – Atria & ventricles relax, ALL VALVES CLOSED 5. Late Ventricular Diastole – Atria & ventricles relax, tricuspid/bicuspid open, aortic/pulmonary closed Diastole and Systole These terms refer more to the ventricles because they are the major pumps In a healthy heart, when the atria contract, the ventricles relax and vice versa. The Cardiac Cycle About 2/3 of the cycle is spent in diastole What does diastole mean? How many phases are in the cardiac cycle? What is the name of the contraction cycle? Systole What is the name of the relaxation cycle? Diastole