* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Geosphere PP
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Future of Earth wikipedia , lookup
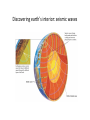
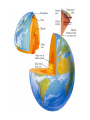
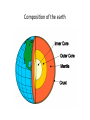
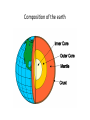
Dynamic earth: geosphere objec4ve Students will be able to describe the composi4on and structure of the Earth. Earth as a system Scien4sts divided this system into four parts: • The Geosphere (rock) • The Atmosphere (air) • The Hydrosphere (water) • The Biosphere (living things) GEOSPHERE: mostly solid, rocky part of the Earth; extends from the center of the core to the surface of the crust Discovering earth’s interior • Scien4sts use seismic waves to learn about Earth’s interior (waves altered by the material it travels through) • Measure changes in the speed and direc4on of seismic waves that penetrate the interior of the planet • Learned that Earth is made up of different layers and have INFERRED what substances make up each layer Discovering earth’s interior: seismic waves Composi4on of the earth • Scien4sts divide the Earth into layers: • The crust • The mantle • The core (inner and outer) • These layers are made up of progressively DENSER material toward the center of the Earth Composi4on of the earth CRUST = solid, outermost layer of the Earth • thinnest layer • makes up less than 1 percent of the planet’s mass • 5 km to 8 km thick beneath the oceans (thin) • 20 km to 70 km thick beneath the con4nents (thick) Composi4on of the earth Composi4on of the earth MANTLE = layer of rock between the Earth’s crust and core • rocks of medium density • 64 percent of the mass of the Earth Composi4on of the earth CORE = central part of the Earth below the mantle; composed of the densest elements OUTER CORE = dense liquid layer INNER CORE= solid, dense; made up mostly of iron and nickel between 4,000°C to 5,000°C solid because it is under enormous pressure • The inner and outer core make up about one-‐third of Earth’s mass. Composi4on of the earth Composi4on of the earth The Earth can be divided into five layers based on the physical proper4es of each – Lithosphere – Asthenosphere – Mesosphere – Outer Core – Inner Core Layers of the earth Lithosphere (litho = rock, sphere = layer) Solid, outer layer of the Earth that consists of the crust and the rigid upper part of the mantle. • cool, rigid layer that is 15 km to 300 km thick • divided into huge pieces called tectonic plates Layers of the Earth Asthenosphere (a = without, stheno = strength) Layer of the mantle beneath the lithosphere • Weak and easily deformed • made of mantle rock that flows slowly (allows tectonic plates to move on top of it) Layers of the earth Mesosphere (meso = middle) middle layer between outer core and asthenosphere – Solid and strong • Outer Core – dense liquid • Inner Core – solid; dense, made up of mostly iron and nickel between 4,000°C to 5,000°C; solid because it is under enormous pressure