* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download presentation source
Pain in animals wikipedia , lookup
History of zoology since 1859 wikipedia , lookup
History of zoology (through 1859) wikipedia , lookup
Zoopharmacognosy wikipedia , lookup
Emotion in animals wikipedia , lookup
Animal locomotion wikipedia , lookup
Animal culture wikipedia , lookup
Theory of mind in animals wikipedia , lookup
Deception in animals wikipedia , lookup
Animal communication wikipedia , lookup
Non-reproductive sexual behavior in animals wikipedia , lookup
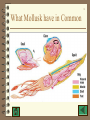
Insect physiology wikipedia , lookup
Chapter 30 and extras Extras: Mollusk Animal Segmented characteristics Classification of animal kingdom worms Dissection info Questions 1 2 Basic Animal Characteristics Embryo Development are similar Body plan : bilateral radial asymmetric Animals must digest food Animal Protection and support Dehydration problem 3 Embryo Development Stages of development – sex cells fuse = zygote – Blastula – Gastrula – ectoderm / mesoderm / endoderm 4 Frog development Movie 5 Chicken Development 6 Body plan : Bilateral = Can be divided down its length into similar right and left halves. Radial = Can be divided along any plane through a central axis Asymmetrical = Irregular in shape 7 Animals must digest food Digestive systems. – Food must be broken down after it is consume • Why???? – Digestive tract • one opening (Planaria) • two openings ( worm ) • organs that make digestive enzymes 8 Animal Protection and support The larger the animal the more support it needs – Skeletal system give something for muscles to attach to. – Help maintain body shape Two kinds of support Endoskeleton / exoskeleton Terrestial Animals : Water Problem 9 Living on land creates the problem of dehydration. Special organs, structures and behaviors are required: – Mucus – Thick skin or layers – Moist oxygen collectors (lungs) – Water recycling organs (intestine/rectum) – Special egg containers 10 Important Technical terms Dorsal Caudal Ventral Transverse Cephalic longitudinal Cranial Proximal Anterior Distal Posterior Sagittal 11 Classification of animals Invertebrates – Sponges – Jellyfish – Roundworm – Mollusk – Annelida – Arthropods Vertebrates – Agnatha (hagfish) – Sharks, Rays – Bony Fish – amphibians – Aves (birds) – Mammals 12 Mollusks and Segmented worm What is a mollusk? Where do Mollusks live? Classes of Mollusks What is a segmented worm? 13 What is a Mollusk Animals that are bilateral , have a coelom, two body openings, a muscular foot for movement and a mantle. Soft bodies composed of a foot, a mantle a shell, and a visceral mass that holds all the major organs 14 What Mollusk have in Common 15 Origin of Mollusk 16 Parts to Mollusk Digestive system Respiratory system Circulatory system Excretory system Reproductive system Nervous system Muscular/ Skeletal systems Protection 17 Digestive System. Mouth radula esophagus Stomach (1) Caecum (2) Intestine See Overhead for details 18 Digestive system - 21933 Beak 19 Respiratory system Oyster Morphology slide -21900 Squid Morphology Slide -21910 20 Circulatory system slide - Open system ( blood bathe the organs ) 21 Brain - slide 21915/ 21941 22 Reproductive system Male sex organs Female sex organs Copulation Lay Eggs 23 Excretory system Diffusion in the visceral cavity anus / Intestine 24 Protection Coloration water siphon Behaviors ( schooling) Ink Sac 25 Where do Mollusk live? These animals are aquatic, marine and terrestrial. 26 Classes of Mollusks Classes are : Gastropods - snails / slugs Bivalvia- clams / oysters/ scallop Cephalopoda- squid / octopus 27 Gastropods -Snails (14456) 28 Cephalopoda -Octopus 29 Squids and Octopus Octopus Squid 14447 30 Cephalopoda- Large Octopus 31 What is a segmented worm? 32 Parts to Worm Digestive system Respiratory system Circulatory system Excretory system Reproductive system Nervous system Muscular/ Skeletal systems 33 Digestive system slide- 21888 Protomium mouth pharynx esophagus crop gizzard Intestine 34 Respiratory System • Respiration = diffusion through the wet skin • This restrict the over all size of the animal. 35 Circulatory System slide 21892 Aortic Arches Closed system 36 Excretory System - worm Since this is a terrestial animal liquid waste is handled differently then solid waste. Solid waste is removed by the anus Liquid waste is removed by the NEPHREDIA 37 Reproductive system Worms are hermaphrodites Male pores Female pores copulation seminal vesicles clitellum egg sac 38 Nervous system Ventral Ganglia Ventral nerve cord pharyngeal ganglion (paired) See Overhead 39 Muscular system Circular muscle layer= causes the sections to swell making the animal push forward longitudinal muscle layers= pulls the other sections forward Seta = provide traction in the soil 40 Things to Know (100 words each) 1.How do each of the Dissected animals acquire food and how do they process it? 2.How is breathing accomplished for each? 3.How do terrestial animals adapt to living in a dry environment? 4.What special feature(s) makes each successful? Review material 41 What features allow these animals to become so large? Why is it important to have better senses if you are larger? How do land animals adjust to dry environments? Why is it important for these animals to develop behaviors? Explain how these animals are like us.