* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Molecule: two or more atoms held together by
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
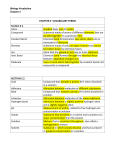
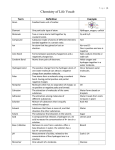
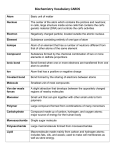
Chapter Two Vocabulary 2.1 Atom: smallest basic unit of matter Element: substance made up of only one type of atom that cannot be broken down by physical means Compound: substance made of atoms of different atoms that are bonded together in a particular ratio Ion: atom that has gained or lost one or more electrons Ionic bond: chemical bond formed through the electrical force between oppositely charged ions Covalent bond: chemical bond formed when two atoms share one or more pairs of electrons Molecule: two or more atoms held together by covalent bonds; not necessarily a compound 2.2 Hydrogen bond: attraction between a slightly positive hydrogen atom and a slightly negative atom Cohesion: attraction between molecules of the same the same substance Adhesion: attraction between molecules of different substances Solution: mixture that is consistent throughout; also called a homogeneous mixture Solvent: substance in which solutes dissolve and that is present in greatest concentration in a solution Solute: substance that dissolves in a solvent and is present at a lower concentration than the solvent Acid: compound that donates a proton (H+) when dissolved in a solution Base: compound that accepts a proton (H+) when dissolved in a solution pH: measurement of acidity; related to free hydrogen ion concentration in solution 2.3 Monomer: molecular subunit of a polymer Polymer: large, carbon-based molecule formed by monomers Carbohydrate: molecule composed of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen; includes sugars and starches Lipid: nonpolar molecule composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen; includes fats and oils. Fatty acid: hydrocarbon chain often bonded to glycerol in a lipid Protein: polymer composed of amino acids linked by peptide bonds; folds into a particular structure depending on bonds between amino acids. Amino acid: molecule that makes up proteins; composed of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and sometimes sulfur Nucleic acid: polymer of nucleotides; the genetic material of organisms 2.4 Chemical reaction: process by which substances change into different substances through the breaking and forming of chemical bonds Reactant: substance that is changed by a chemical reaction Product: substance formed by a chemical reaction Bond energy: amount of energy needed to break a bond between two particular atoms; or the amount of energy released when a bond forms between two particular atoms Equilibrium: condition in which reactants and products of a chemical reaction are formed at the same rate Activation energy: energy input necessary to initiate a chemical reaction Exothermic: chemical reaction that yields a net release of energy in the form of heat Endothermic: chemical reaction that requires a net input of energy 2.5 Catalyst: substance that decreases activation energy and increases reaction rate in a chemical reaction Enzyme: protein that catalyzes chemical reactions for organisms Substrate: reactant in a chemical reaction upon which an enzyme acts