* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CHAPTER 2 VOCABULARY (Highlighted)
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
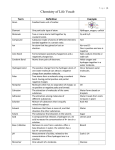
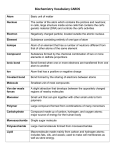
Biology Vocabulary Chapter 2 CHAPTER 2 VOCABULARY TERMS Section 2.1 Atom Compound Covalent Bond Element Ion Ionic Bond Molecule SECTION 2.2 Acid Adhesion Base Cohesion Hydrogen bond pH Solute Solution Solvent Smallest basic unit of matter Substance made of atoms of different elements that are bonded together in a particular ratio Chemical bond formed when two atoms share one or more pairs of electrons Substance made of only one type of atom that cannot be broken down by chemical means Atom that has gained or lost one or more electrons. Chemical bond formed through the electrical force between oppositely charged ions. Two or more atoms held together by covalent bonds not necessarily a compound Compound that donates a proton (H+) when dissolved in a solution Attraction between molecules of different substances. Compound that accepts a proton (H+) when dissolved in solution. Attraction between molecules of the same substance Attraction between a slightly positive hydrogen atom and a slightly negative atom. Measurement of acidity; related to free hydrogen ion concentration in solution Substance that dissolves in a solvent and is present at a lower concentration than the solvent Mixture that is consistent throughout; also called a homogeneous mixture Substance in which solutes dissolve and that is present in greatest concentration in a solution Section 2.3 Amino Acid Carbohydrate Fatty Acid Lipid Monomer Nucleic Acid Polymer Protein Section 2.4 Activation Energy Bond Energy Chemical Reaction Endothermic Equilibrium Exothermic Product Reactant Section 2.5 Catalyst Enzyme Substrate Molecule that makes up proteins; composed of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen and sometimes sulfur. Molecule composed of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen; includes sugars and starches. Hydrocarbon chain often bonded to glycerol in a lipid Nonpolar molecule composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen; includes fats and oils. Molecular subunit of a polymer Polymer of nucleotides; the genetic material of organisms. Large, carbon-based molecule formed by monomers. Polymer composed of amino acids linked by peptide bonds; folds into a particular structure depending on bonds between amino acids. Energy input necessary to initiate a chemical reaction Amount of energy needed to break a bond between two particular atoms; or the amount of energy released when a bond forms between two particular atoms. Process by which substances change into different substances through the breaking and forming of chemical bonds. Chemical reaction that requires a net input of energy Condition in which reactants and products of a chemical reaction are formed at the same rate. Chemical reaction that yields a net release of energy in the form of heat Substance formed by a chemical reaction Substance that is changed by a chemical reaction Substance that decreases activation energy and increases reaction rate in a chemical reaction Protein that catalyzes chemical reactions for organisms. Reactant in a chemical reaction upon which an enzyme acts.