* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Health Occupations
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
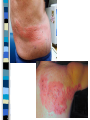
Health Occupations Nervous System Nervous System Complex & highly organized Coordinates all of the many activities of the body Allows body to respond and adapt to changes that occur both inside and outside of the body Neuron Also called nerve cell Basic structural unit of nervous system Parts of neuron – Cell body – Nucleus inside cell body – Nerve fibers • Dendrites – carry impulses to cell body • Axon – carry impulses away from cell body – Many covered with myelin sheath (fat covering) – Increases rate of transmission of impulses – Insulates & maintains the axon Neuron Axon lies close to dendrites of many other neurons – Synapse – space between neurons – Impulses coming from an axon jump synapse to get to the dendrite of a neuron that will carry the impulses in the right direction – Neurotransmitters – special chemicals located at end of axon to allow impulses to pass from neuron to another – Impulses may follow many different routes 1. Dendrites 3. Nucleus 4. Axon 5. Myelin Sheath 2. Cell body 6. Terminal branches Nerves Combination of many nerve fibers Located outside brain & spinal cord Afferent – sensory – Messages to brain & spinal cord Efferent – motor – Messages from brain & spinal cord Associative – both sensory & motor Divisions of nervous system Central nervous system – Brain – Spinal cord Peripheral nervous system – Nerves – Autonomic nervous system • Separate division of peripheral nervous system • Controls involuntary body functions Central nervous system Brain – Mass of nerve tissues – Protected by membranes & cranium – Cerebrum • Largest & highest section of brain • Convolutions – folds found on outer part • Lobes – Frontal, parietal, temporal, occipital – Named after bones that surround them • Responsible for reasoning, thought, memory, speech, sensation, sight, smell,hearing, & voluntary body movement Brain Cerebellum – Below back of cerebrum – Responsible for coordination of muscles, balance, posture, muscle tone Diencephalon – Between cerebrum & midbrain – Thalamus • Relay center to direct sensory impulses to cerebrum – Hypothalamus • Regulates & controls ANS, temperature, appetite, water balance, sleep, constriction & dilation of blood vessels, anger, fear, pleasure, pain, affection Brain Midbrain – Below cerebrum at top of brain stem – Responsible for conducting impulses between brain parts & eye reflexes Pons – Below midbrain in brain stem – Responsible for conducting messages to other parts of brain & reflexes like chewing, tasting, production of saliva, respiration Brain Medulla oblongata – Lowest part of brain stem – Connects with the spinal cord – Responsible for regulating heartbeat, respiration, swallowing, coughing, & blood pressure Ventricles Convolutions Cerebrum Cerebellum Midbrain Pons Medulla oblongata Spinal cord Spinal cord Continues down from the medulla oblongata Ends at L1 or L2 Surrounded & protected by vertebrae Responsible for many reflexes Carries sensory messages to brain (afferent) Carries motor messages away from brain (efferent) Meninges 3 membranes Cover & protect brain & spinal cord Dura mater – thick, tough outer layer Arachnoid membrane – middle layer, delicate & weblike Pia mater – innermost layer – Closely attached to brain & spinal cord – Contains blood vessels that nourish nerve tissue Ventricles 4 hollow spaces located in brain Connect with each other & with subarachnoid space Filled with CSF – Fluid circulates continually between ventricles & through subarachnoid space – Serves as shock absorber – Carries nutrients to brain & spinal cord – Helps remove metabolic products & wastes – Produced by choroid plexuses in ventricles – After circulating, absorbed into blood vessels of the dura mater & returned to bloodstream through arachnoid villi Peripheral Nervous System Made up of all the nerves Consists of cranial nerves & spinal nerves Cranial nerves – 12 pairs & branches – Responsible for special senses like sight, hearing, taste, smell – Receive general sensations like touch, pressure, pain, temperature – Send out impulses for voluntary & involuntary muscle control Peripheral Nervous System Spinal nerves – – – – 31 pairs & branches Carry messages to & from spinal cord Sensory & motor 8 cervical, 12 thoracic, 5 lumbar, 5 sacral, 1 pair of coccygeal spinal nerves – Each nerve goes directly to a particular part of the body or networks with other spinal nerves to form a plexus, supplying sensation to a larger segment of the body Autonomic Nervous System Part of PNS Helps maintain a balance in the involuntary functions of body, but allows body to react in emergency 2 divisions – sympathetic & parasympathetic – Usually 2 systems work together – Maintain homeostasis – Controls involuntary body functions at proper rates Autonomic Nervous System Sympathetic – – – – Acts in time of emergency – fight/flight Prepares body to act Increases heart rate, respirations, BP Slows activity in digestive tract Parasympathetic – Counteracts actions of sympathetic after emergency is over – Slows heart rate, respirations – Lowers BP – Increases digestive activity Diseases & Abnormal Conditions Cerebral Palsy – Disturbance in voluntary muscle action – Caused by brain damage • Lack of oxygen to brain &/or birth injury • Prenatal rubella (German measles) & infections – Spastic, athetoid, & atactic (most common) – Symptoms • • • • • Exaggerated reflexes & seizures Tense muscles & contractures Speech impairment Muscle spasms & tremors Mental retardation in some cases Cerebral palsy Treatment but no cure – PT, OT, & speech tx – Muscle relaxants & anticonvulsive druges – Casts & braces – Orthopedic surgery for severe contractures Cerebrovascular Accident (CVA) Stroke, apoplexy Blood flow to brain is impaired resulting in lack of oxygen & destruction of brain tissue Causes – Cerebral hemorrhage • HTN • Aneurysm • Weak blood vessel – Occlusion or blockage • Atherosclerosis • Thrombosis (blood clot) CVA Symptoms – vary depending on area & amount of brain tissue damaged – – – – – – – Loss of consciousness Weakness & vertigo Hemiplegia (paralysis on 1 side) Dysphagia (difficulty swallowing) Visual disturbances & difficulty swallowing Aphasia (speech impairment) Incontinence CVA Immediate treatment – 1st THREE hours – Thrombolytic (clot busting) drugs – Angioplasty of cerebral arteries – CT scans needed to determine cause – Neuroprotective agents can be used to prevent permanent brain damage to neurons CVA Treatment – Depends on symptoms present – Directed toward helping person recover from OR adapt to symptoms present – PT, OT, speech therapy ESSENTIAL Encephalitis Inflammation of brain caused by virus, bacteria, or chemical agent Mosquitoes are common vector Symptoms vary – fever, extreme weakness, lethargy, visual changes, HA, N & V, stiff neck & back, seizures, coma Treatment – supportive – Antiviral & antiseizure meds – Maintenance of fluids & electrolytes – Monitoring of respiratory & kidney function Epilepsy Brain disorder associated with abnormal electrical impulses in neurons of brain Causes – brain injury, birth trauma, tumors, toxins (lead & carbon monoxide) Many cases are idiopathic Absence (Petit mal) seizures – Milder, characterized by loss of consciousness lasting several seconds – Common in children – Usually disappears by late adolesence Epilepsy Tonic-clonic (grand mal) seizures – Most severe – Loss of consciousness lasting at least several minutes – Convulsions with violent thrashing movements & shaking – Hypersalivation, foaming at mouth – Loss of body functions Treatment – antiseizure medications Hydrocephalus Excessive accumulation of CSF in ventricles & subarachnoid space Usually caused by congenital defect, infection, or tumor that obstructs the flow of CSF Symptoms – – Abnormally large head & prominent forehead with bulging eyes – Irritability – Distended scalp veins – Retardation when pressure prevents proper development of brain Hydrocephalus Treatment – surgical implantation of a shunt between ventricles & veins, heart, or abdominal peritoneal cavity to drain excess CSF Meningitis Inflammation of meninges of brain &/or spinal cord caused by bacteria, fungus, virus, or toxins (lead, arsenic) Symptoms – – – – – High fever HA, back & neck pain, stiffness N&V Delirium & confusion Coma & death if untreated Treatment – antibiotics, anticonvulsants, meds for pain & cerebral edema Multiple Sclerosis Chronic, progressive, disabling condition resulting from degeneration of the myelin sheath in the CNS Usually occurs between 20 – 40 Unknown cause Progresses at different rates Early symptoms – – – – Visual disturbances Weakness, fatigue Poor coordination Tingling & numbness Multiple sclerosis Later symptoms – – – – – Tremor, spasticity of muscles Paralysis Speech impairment Emotional swings incontinence Treatment – PT, muscle relaxants, steroids, psychological counseling Goal is to maintain functional ability Neuralgia Nerve pain Caused by inflammation, pressure, toxins, & other diseases Treatment directed towards eliminating cause Paralysis Brain or spinal cord injury destroys neurons & results in loss of function & sensation below level of injury Hemiplegia – paralysis on 1 side of body Paraplegia – paralysis in lower extremities Quadriplegia – paralysis of arms, legs, & body No cure, research being done towards repair Treatment – supportive, PT, OT Parkinson’s Disease Chronic progressive condition involving degeneration of brain cells Usually occurs in people over 50 Symptoms – – – – – – Tremors, stiffness, muscle rigidity Forward leaning position & shuffling gait Difficulty stopping when walking Loss of facial expression & drooling Mood swings with frequent depression Behavior changes Parkinson’s Disease Treatment but no cure – Levodopa used to relieve symptoms – In selected cases, surgery to selectively destroy a small area of brain to control involuntary movements or implant a device – PT to treat rigidity Shingles or herpes zoster Acute inflammation of nerve cells Caused by herpes virus, similar to chicken pox Characteristically, occurs in thoracic area on 1 side of body & follows path of the affected nerves Symptoms – fluid filled vesicles, severe pain, redness, itching, fever, abnormal skin sensations Treatment – relief of pain & itching until inflammation subsides, usually 1-4 weeks