* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Heart
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
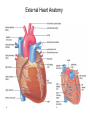
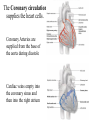
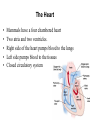
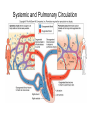
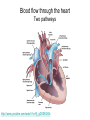
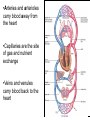
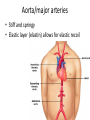
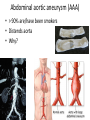
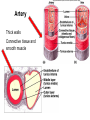
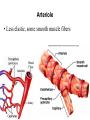
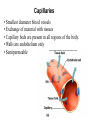
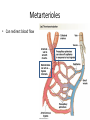
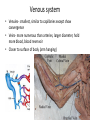
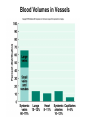
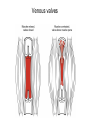
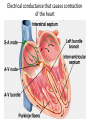
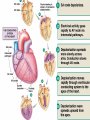
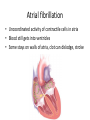
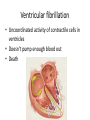
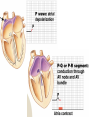
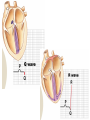
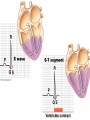
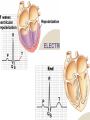
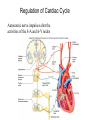
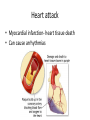
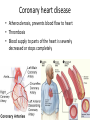
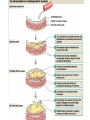
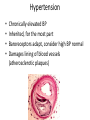
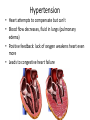
Cardiovascular Physiology Chapter 15 Cardiovascular System Functions: • Transports materials absorbed from the GIT • Circulates O2 / CO2 • Distributes hormones • Transports other compounds, cell products, wastes, nutrients.... • Important in the body’s defense • Essential in regulation of body temperature and homeostasis The Cardiovascular System is Composed of Blood Heart Blood Vessels arteries, arterioles, capillaries venules, and veins • Double pump • Primarily cardiac muscle • About the side of a fist Heart External Heart Anatomy The Coronary circulation supplies the heart cells. Coronary Arteries are supplied from the base of the aorta during diastole Cardiac veins empty into the coronary sinus and then into the right atrium The Heart • Major portion of the heart, myocardium, consists largely of cardiac muscle Wall of the Heart •Epicardium (visceral pericardium) •Myocardium (cardiac muscle) •Endocardium ( epithelial and connective tissue) The Heart • • • • • Mammals have a four chambered heart Two atria and two ventricles. Right side of the heart pumps blood to the lungs Left side pumps blood to the tissues Closed circulatory system Passage of Blood through the Heart • Deoxygenated blood does not mix with oxygen-rich blood. • Blood must go through the lungs to pass from right side to left side of the heart. • Right ventricle sends blood through lungs. Pulmonary circulation • Left ventricle sends blood throughout the body. Systemic circulation Systemic and Pulmonary Circulation Blood flow through the heart Two pathways http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Rj_qD0SEGGk Blood Vessels •Arteries and arterioles carry blood away from the heart •Capillaries are the site of gas and nutrient exchange •Veins and venules carry blood back to the heart Aorta/major arteries • Stiff and springy • Elastic layer (elastin) allows for elastic recoil Abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) • > 90% are/have been smokers • Distends aorta • Why? Artery Thick walls Connective tissue and smooth muscle Arteriole • Less elastic, some smooth muscle fibers Capillaries • Smallest diameter blood vessels • Exchange of material with tissues • Capillary beds are present in all regions of the body. • Walls are endothelium only • Semipermeable Exchange at the capillaries • Most cells within 0.1 mm of a capillary • 50,000 miles of capillaries • More metabolic, more capillaries Metarterioles • Can redirect blood flow Why? Exchange in the Capillaries Venous system • Venules- smallest, similar to capillaries except show convergence • Veins- more numerous than arteries, larger diameter, hold more blood, blood reservoir • Closer to surface of body (arm hanging) Blood Volumes in Vessels Venous valves The movement of blood through the veins is not dependent on cardiac contraction Excellent Summary Slide The Heartbeat Each heartbeat is referred to as a cardiac cycle. – Systole - Contraction of heart muscle – Diastole - Relaxation of heart muscle Electrical conductance that causes contraction of the heart Atrial fibrillation • Uncoordinated activity of contractile cells in atria • Blood still gets into ventricles • Some stays on walls of atria, clot can dislodge, stroke Ventricular fibrillation • Uncoordinated activity of contractile cells in ventricles • Doesn’t pump enough blood out • Death Electrocardiogram (ECG) • • • • • Reflects electrical activity in the heart Sum of all action potentials occurring in the heart Waves- deflections from baseline Segments- between two waves Interval- waves and segments Major components of an ECG Regulation of Cardiac Cycle • Physical exercise • Body temperature • Concentration of various ions potassium calcium • Parasympathetic impulses decrease heart action • Sympathetic impulses increase heart action • Cardiac center regulates autonomic impulses to the heart Regulation of Cardiac Cycle Autonomic nerve impulses alter the activities of the S-A and A-V nodes Extrinsic Control of Heartbeat • Cardiac control center in the medulla oblongata can alter the beat of the heart by way of the autonomic system – Parasympathetic system – Sympathetic system • Hormones epinephrine and norepinephrine are released by the adrenal medulla and also stimulate the heart Blood pressure • Heart pumping causes blood pressure • Pressure without volume change Arterial Blood Pressure Blood Pressure – force the blood exerts against the inner walls of the blood vessels Arterial Blood Pressure rises when ventricles contract falls when ventricles relax systolic pressure – maximum pressure diastolic pressure – minimum pressure Freq. written as a fraction 120/60 systolic 120 mm Hg, diastolic 60 mm Hg Measuring Blood Pressure with a Sphygmomanometer Factors That Influence Arterial Blood Pressure Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Blood volume increases Heart rate increases Stroke volume increases Blood pressure increases Blood viscosity increases Peripheral resistance increases 46 Cardiac output • Regulated by mechanical, neural and chemical factors • Equal to heart rate X stroke volume • Example pt with a pulse of 72 72 beats/min X 70 ml= 5,040 ml Control of Blood Pressure • Blood pressure (BP) is determined by cardiac output (CO) and peripheral resistance (PR) BP = CO x PR • Homeostasis requires regulation of CO and PR https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=X9ZZ6t cxArI&index=25&list=PL8dPuuaLjXtOAKed _MxxWBNaPno5h3Zs8 Dysfunction/disorders/disease of the cardiovascular system • Disorders of the heart and blood vessels account for more than half of all deaths in the US • Coronary heart disease is involved in majority of deaths A few terms, just for fun! • Tachycardia- increased heart rate (adults >100 bpm) • Bradycardia- slow heart rate (adults <60 bpm) • Atherosclerosis- hardening of the arteries • Arrhythmia- irregular heart rhythm • Angina- chest pain • Aneurysm- localized bulge in the wall of a blood vessel • Thrombosis- blood clot Heart attack • Myocardial infarction- heart tissue death • Can cause arrhythmias Orthostatic Hypotension • Decrease in blood pressure upon standing • Blood evenly distributed, pools upon standing • Decrease in venous return and bp, compensate with increased cardiac output, peripheral resistance, MAP Moon face Syncope (fainting) • Vasovagal- body overreacts to certain stimuli (blood, needles, emotional stress), drop in heart rate and blood pressure • Ground parade- standing too long, blood in legs doesn’t return to heart Coronary heart disease • Atherosclerosis, prevents blood flow to heart • Thrombosis • Blood supply to parts of the heart is severely decreased or stops completely Hypertension • • • • Chronically elevated BP Inherited, for the most part Baroreceptors adapt, consider high BP normal Damages lining of blood vessels (atherosclerotic plaques) Hypertension • Heart attempts to compensate but can’t • Blood flow decreases, fluid in lungs (pulmonary edema) • Positive feedback: lack of oxygen weakens heart even more • Leads to congestive heart failure