* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Photosynthesis/Respiration Powerpoint
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
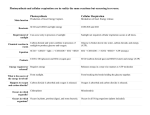
• Energy is all around you! • You can hear energy as sound. • You can see energy as light. • And you can feel it as wind. Nature of Energy You use energy when you: hit a softball. lift your backpack. compress a spring. Forms of Energy There are several forms energy can take: Heat Electromagnetic Nuclear Mechanical Chemical Light So…. What is Energy? Energy- the ability to do work. Can be converted from one type of energy to another. Ex. Gas in your car is burned to create mechanical energy(motion) Ex. Solar energy cells turn light energy into electrical energy Nature of Energy Living organisms need energy for growth and movement. Living organisms mainly use Light and Chemical Energy. Photosynthesis Photosynthesis- process in which plants convert light energy into chemical energy(food). Occurs in the leaves of plants in organelles called chloroplasts. Photosynthesis-starts all ecological food webs! Things needed for photosynthesis SUNLIGHT Gives the plant energy CHLOROPHYLL WATER Travels up from the roots CARBON DIOXIDE Enters the leaf through small holes on the underneath The green stuff in chloroplasts that convert light energy to chemical energy by combining water (H2O)and carbon dioxide (CO2) to create glucose (C6H12O6) How do we know that plants make food from just carbon dioxide, water and light energy? Experiments!! For example: Jan Baptist van Helmont (1648) planted a willow tree weighing 5 pounds into 200 pounds of soil and then after 5 years the tree weighed 169 pounds and the soil was still nearly 200 lbs. Photosynthesis Equation CO2 + H2O C6H12O6 + O2 6CO2 + 6H2O C6H12O6 + 6O2 Water(6 H2O) + carbon dioxide(6 CO2) glucose(C6H12O6) + oxygen(6 O2) Starch, Protein and Oil Synthesis Glucose is a short term energy molecule for plants when burned up by cellular respiration in mitochondria Plants convert glucose to starches, proteins and oils for storage by a process called dehydration synthesis. This process occurs in plastids in the cell. How do Cells get Energy? • Energy for living things comes from food. Originally, the energy in food comes from the sun. Whether you are an autotroph- make your own food or a heterotroph- eat your food … All organisms burn up food for daily energy needs. Types of Food(Macromolecules) Proteins- digested into amino acids Lipids- digested into fatty acids and glycerol Carbohydrates- digested into glucose All 3 types of food can be used for energy, but glucose is the main energy molecule used. Cells Use Energy Cells cannot use glucose directly for energy. Glucose must be converted into another energy molecule called ATP, Adenosine Triphosphate The conversion of glucose to ATP occurs in the mitochondria and is called cellular respiration. Cellular Respiration- burning up glucose to create ATP Burning something requires oxygen Organisms take in oxygen(O2) so they can burn up glucose during cellular respiration. Cellular Respiration Equation C6H12O6 + O2 CO2 + H2O C6H12O6 + 6O2 6 CO2 + 6H2O So…. Where’s the ATP ?? Glucose(C6H12O6) + oxygen (O2) water(H2O) + carbon dioxide(CO2) Cellular Respiration Equation C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O The ATP energy is produced by splitting the glucose molecule. It takes 2 ATP molecules to split the high energy bond of glucose, releasing 38 ATP molecules. 38 ATP – 2 ATP = a net of 36 ATP 2 ATP = 36 Net ATP Pause for a moment…?? C6H12O6 + 6O2 Cellular respiration 6CO2 + 6H2O Where have I seen these letters before??? They look so familiar??? … I know, I remember ….. 6CO2 + 6H20 Photosynthesis C6H12O6 + 6O2 The equation for cellular respiration is the exact opposite of the equation for photosynthesis. Isn’t life symmetrical!! Cellular Respiration Equation C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O This type of cellular respiration is called Aerobic Respiration- converting glucose to ATP in the presence of oxygen. Produces 36 molecules of ATP 2 ATP = 36 Net ATP • Aerobic Respiration mostly occurs in the mitochondria Electrons carried in NADH Mitochondria In Cytoplasm Glucose Krebs Cycle Glycolysis 2 2 Electrons carried in NADH and FADH2 Electron Transport Chain 32 Anaerobic Respiration: occurs when no oxygen is available to the cell (2 kinds: Alcoholic and Lactic Acid) • Also called fermentation • Much less ATP produced than in aerobic respiration •Alcoholic fermentation—occurs in bacteria and yeast Process used in the baking and brewing industry—yeast produces CO2 gas during fermentation to make dough rise and give bread its holes glucose ethyl alcohol + carbon dioxide + 2 ATP • Lactic acid fermentation—occurs in muscle cells Lactic acid is produced in the muscles during rapid exercise when the body cannot supply enough oxygen to the tissues—causes burning sensation in muscles glucose lactic acid + carbon dioxide + 2 ATP How do Cells Use ATP • All energy is stored in the bonds of compounds—breaking the bond releases the energy. Breaking the bond on the 3rd phosphate releases energy for the cell to use. • When the cell has food energy available it can “recharge” the molecule by adding a phosphate group back to ADP, producing ATP Energy from ATP is released for when a phosphate molecule is removed creating a lower energy molecule called ADP. Energy from glucose(cellular respiration) is used to push the loose phosphate molecule back to create high energy ATP. Overview of photosynthesis and respiration SUN Would anyone like to sing “The Circle of Life”?? RADIANT ENERGY PHOTOSYNTHESIS GLUCOSE RESPIRATION ATP(ENERGY) CELL ACTIVITIES