* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Earth - Indiana University Astronomy
Geomorphology wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Future of Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geodesy wikipedia , lookup
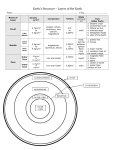
A100 Oct. 6 The Earth READ Chapter 5 – The Earth Homework 4 Due Friday Quiz on Friday Today’s APOD The Sun Today Looking outward to the blackness of space, sprinkled with the glory of a universe of lights, I saw majesty – but no welcome. Below was a welcoming planet. There, contained in the thin, moving, incredibly fragile shell of the biosphere is everything that is dear to you, all the human drama and comedy. That’s where life is; that’s where all the good stuff is. Loren Acton (1936 – ) U.S. astronaut The Earth from Space Understanding Earth helps us understand other planets Understanding other planets helps us understand the Earth How has Earth has changed over time Why does it change? How does it differ from other planets? Size and Shape of the Earth The Earth is a huge, rocky sphere spinning in space and moving around the Sun at a speed of about 100 miles every few seconds Earth also has a blanket of air and a magnetic field that protects the surface from the hazards of interplanetary space Earth Data Distance from Sun 1 AU = 1.5 x 108 km Orbital velocity 30 km / second Orbital period 365.256 days Rotation period 23.9345 hours Inclination of equator to orbit: 23.26 degrees Diameter: 12,756 km Mass 6 x 1024 kg Mean density 5.5 gm/cm3 Surface temperature -130 F to +140 F (avg. 70F) An Average Planet Our Earth is about average Earth is the largest and most massive of the four terrestrial planets, but smaller and less massive than the four giant, or Jovian, planets. Earth is third in distance from the Sun among the four terrestrial planets. Earth has a moderately dense atmosphere; 90 times less dense than that of Venus but 100 times denser than that of Mars. Unique Features of Earth Plate Tectonics – the only planet with a surface shaped by this type of tectonics Atmospheric Oxygen – the only planet with significant Oxygen in its atmosphere Surface Liquid Water – the only planet where temperature & pressure allow surface water to be stable as a liquid Climate Stability - differs from Venus & Mars in having a relatively stable climate Life – The only world known to have life; it certainly has abundant & diverse life forms Magnetic Field Large moon Size and Shape of the Earth The Earth is large enough for gravity to have shaped it into a sphere More precisely, Earth’s spin makes its equator bulge into a shape referred to as an oblate spheroid – a result of inertia Composition of the Earth The most common elements of the Earth’s surface rocks are: oxygen (45.5% by mass), silicon (27.2%), aluminum (8.3%), iron (6.2%), calcium (4.66%), and magnesium (2.76%) Silicon and oxygen usually occur together as silicates Ordinary sand is the silicate mineral quartz and is nearly pure silicon dioxide Density of the Earth Density is a measure of how much material (mass) is packed into a given volume Typical unit of density is grams per cubic centimeter Water has a density of 1 g/cm3, ordinary surface rocks are 3 g/cm3, while iron is 8 g/cm3 For a spherical object of mass M and radius R, its average density is given by M 3 4 R 3 For Earth, this density is found to be 5.5 g/cm3 Consequently, the Earth’s interior (core) probably is iron (which is abundant in nature and high in density) What’s Inside? Crust Asthenosphere Mantle Outer Core Inner Core How do we know this? A sonogram of the Earth Earthquakes generate seismic waves that move through the Earth with speeds depending on the properties of the material through which they travel These speeds are determined by timing the arrival of the waves at remote points on the Earth’s surface A seismic “picture” is then generated of the Earth’s interior along the path of the wave Interior Structure of the Earth A solid, low-density and A liquid, outer core with thin crust made mainly of a mixture of iron, nickel silicates and perhaps sulfur A hot, thick, not-quite A solid, inner core of liquid mantle with silicates iron and nickel Differentiation The densest materials are at the center of the Earth and the least dense materials are at the surface – differentiation Differentiation occurs in a mixture of heavy and light materials if these materials are liquid for a long enough time The Earth must have been almost entirely liquid in the past Earth’s Interior Earth’s interior gets hotter towards the center (6500K, as hot as the Sun’s surface) The Earth’s inner nickel/iron core is solid because the high pressure (from overlying materials) forces it into a solid state – even at that high temperature The outer core is liquid nickel/iron Why so hot??? The high temperature in the Earth’s core (6500K) is probably due to two causes Left-over heat from the impact of small bodies that eventually formed the Earth The radioactive decay of radioactive elements that occur naturally in the mix of materials that made up the Earth The Earth cools very slowly Pseudo-color infrared image of the Earth from space. The red areas are warm water during an El Nino event Heat is trapped inside the Earth’s interior due to the long time it takes to move to the surface and escape Age of the Earth • Radioactive decay used to determine the Earth’s age – Radioactive atoms decay into daughter atoms – The more daughter atoms there are relative to the original radioactive atoms, the older the rock is Age of the Earth Radioactive potassium has a half-life of 1.28 billion years and decays into argon, which is a gas that is trapped in the rock unless it melts Assume rock has no argon when originally formed Measuring the ratio of argon atoms to potassium atoms gives the age of the rock This method gives a minimum age of the Earth as 4 billion years Other considerations put the age at 4.5 billion years Early History of Earth Four main stages of evolution: Differentiation Bombardment Cooling Surface evolution Earth formed 4.6 billion years ago from the inner solar nebula Most traces of ancient bombardment (impact craters) have been destroyed by later geological activity Meteorite Impacts Still Occur Famous example: Barringer Crater near Flagstaff, AZ: Over 150 impact craters found on Earth. 1.2 km diameter 200 m deep Formed ~ 50,000 years ago by a meteorite of ~ 80 – 100 m diameter The Chicxulub Crater Comet nucleus impact producing the Chicxulub crater ~ 65 million years ago may have caused major climate change, leading to the extinction of many species, including dinosaurs. The impact of a large body formed a crater ~ 180 – 300 km in diameter in the Yucatán peninsula, ~ 65 million years ago Evidence of the event is seen in rock layers around the world Dates to ASSIGNMENTS Remember this week READ Chapter 5 – The Earth Homework 4 Due Friday Quiz on Friday