* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Tricyclic Antidepressants
Pharmaceutical industry wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinic agonist wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of cyclooxygenase 2 inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Toxicodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Prescription costs wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacognosy wikipedia , lookup
Drug design wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of proton pump inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Oral rehydration therapy wikipedia , lookup
Drug interaction wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacokinetics wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
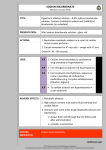
Tricyclic Antidepressants PHARMACOLOGY — TCAs have several important cellular effects, including: Inhibition of presynaptic neurotransmitter reuptake (norepinephrine and serotonin) Blockade of cardiac fast sodium channels Antagonism of central and peripheral muscarinic acetylcholine receptors Antagonism of peripheral alpha-1 adrenergic receptors Antagonism of histamine (H1) receptors Antagonism of CNS gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) A receptors Therapeutic doses of TCAs are rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, reaching maximal plasma concentrations within two to eight hours. Following overdose, antimuscarinic effects may delay gastric emptying and absorption, significantly prolonging the time to peak plasma concentration. TCAs are lipophilic and have a large volume of distribution (Vd). The plasma fraction of drug is usually highly bound to alpha-1 acid glycoprotein. The combination of a large Vd and protein binding means that forced diuresis, dialysis, and hemoperfusion have no role in the management of TCA overdose. TCAs are primarily metabolized by the liver. Some drugs of this class have active metabolites, which may persist for 12 to 24 hours. Half-life varies according to drug and ranges from 7 to 58 hours, but can be prolonged in overdose. Seventy percent of the total dose is excreted via the kidney as inactive metabolites; the remainder is excreted via the biliary system. Enterohepatic recirculation can delay final elimination of a large fraction of the drug, prolonging absorption and potentially increasing toxicity following overdose CLINICAL FEATURES Presenting signs of TCA overdose typically include CNS sedation (from antihistaminic effects), but may also include confusion, delirium, or hallucinations. Arrhythmias, cardiac conduction delays, hypotension, and anticholinergic toxicity (hyperthermia, flushing, dilated pupils, intestinal ileus, urinary retention, and sinus tachycardia) Cardiac toxicity Cardiac conduction abnormalities occur because TCAs inhibit the fast sodium channels in the His-Purkinje system as well as the atrial and ventricular myocardium. This decreases conduction velocity, increases the duration of repolarization, and prolongs absolute refractory periods. Sinus tachycardia is common in overdose, likely as a result of anticholinergic (vagolytic) effects of the drug and a reflex tachycardia due to hemodynamic decompensation. ECG changes in TCA overdose Prolongation of the QRS >100 msec Abnormal morphology of the QRS (eg, deep, slurred S wave in leads I and AVL) Abnormal size and ratio of the R and S waves in lead AVR: R wave in AVR >3 mm; R to S ratio in AVR >0.7. Management Isotonic saline to address hypotension. Sodium bicarbonate to address other cardiovascular toxicities - The benefit of sodium bicarbonate is probably due to both an increase in serum pH and the increase in extracellular sodium. The increase in serum pH favors the neutral form of the drug, making it less available to bind to sodium channels. Increasing the extracellular sodium concentration increases the electrochemical gradient across cardiac cell membranes, potentially attenuating the TCA-induced blockade of rapid sodium channel Alpha adrenergic vasopressors to address hypotension refractory to aggressive fluid resuscitation and bicarbonate infusion. Antiepileptic therapy — Benzodiazepines remain the treatment of choice for TCA-induced seizures