* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Solar system
Copernican heliocentrism wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Outer space wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Planets beyond Neptune wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
IAU definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Planets in astrology wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial skies wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Satellite system (astronomy) wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Late Heavy Bombardment wikipedia , lookup
Hebrew astronomy wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
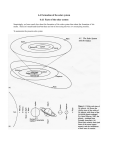
Put these events in the correct order 1) Creation of elements: At the core of the star, heavier “stuff” is created, including carbon and iron. 2) Gases are pulled together by gravity into clouds called Nebulas. 3) The singularity: All matter is crammed into a tiny point the size of a proton. 4) Protostars are formed: a dense cloud of gas surrounded by a spinning disk. 5) Supernova: As center of star gets heavier, it explodes dramatically. 6) Universe expands rapidly: Universe cools off, matter is created. THE SOLAR SYSTEM Essential Question: What orbits the Sun and why? The sun is a star in the center of our solar system Gravity is a force that holds the objects of our solar system in orbit Earth, its moon, and the sun form a system within our solar system The planets were created from a nebula that formed after a supernova A SYSTEM is a set of parts that come together to work as a whole Example: Solar System The SOLAR SYSTEM is the sun and all the objects that move around it *Other objects that orbit or move around the sun are planets, comets, meteors, and asteroids Formation of Planets http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DvN MBry5Nyg&safety_mode=true&persist_ safety_mode=1 Planets form from a nebula that is created from a Supernova. Unlike the nebula that created the original star, this planetary nebula contain heavy “stuff” that can turn into planet. Mars Mercury Venus Earth Uranus Jupiter Saturn Neptune 8 6 4 2 7 5 3 1 Creating Solar System Models Creating Mnemonic Devices Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune, Pluto (optional) My Very Elegant Mother Just Served Us Nine Pizzas Exit Slip • 1) What is a system? • 2) What is the major difference between the inner and outer planets? • 3) What is different between a nebula that creates stars and a nebula that creates planets and stars? Today’s objective •Earth, its moon, and the sun form a system within our solar system •Rotation causes day and night •Revolution causes seasons THE MOON A natural satellite that orbits around planets. The the is star, made up of gases, found in of the solar system ***The sun is the nearest star to earth The sun is the main source of light in the solar system The sun can be compared to a heat lamp We are able to see the moon at night because it reflects the sun’s light Sun Heat Lamp Sun Moon Earth Rotation and Revolution of the Earth ROTATION Rotation is the spinning of an object about its axis The earth rotates about its axis in a counter-clockwise direction The earth makes one complete rotation in 24 hours The earth is tilted at an angel of 24.5o Rotation of the earth on its axis causes day and night REVOLUTION OF THE EARTH The Revolution of the earth around the sun produces the seasons: summer, winter, spring and autumn/fall The earth complete one revolution in 365 days or 1 year Gravity from the sun helps to keep the planets in orbit or moving around it Rotation of the earth on its axis and the Revolution of the earth around the sun occur at the same time VIDEOS http://www.brainpopjr.com/science/space/earth/ Ignite Learning video http://www.classzone.com/books/earth_science/terc/content/visualizations/ es0408/es0408page01.cfm?chapter_no=04 Summer: •Warm to hot temperature •Less rainfall Fall: •Usually windy conditions •Relatively cooler temperatures Winter: •Colder temperatures •Snowy conditions •Sleet Spring: •Relatively cooler Temperature •Excessive rainfall sometimes humid TODAY’S VOCABULARY ORBIT- The path an object takes as it travels around another object REVOLUTION -The movement or orbit of an object around another object. ROTATION -The spinning of an object about its axis SOLAR SYSTEM -The sun and all the objects that move around it SYSTEM- A set of parts that come together to work as a whole INNER PLANETS- Mercury-Venus-Earth-Mars OUTER PLANETS- Jupiter-Saturn-Uranus-Neptune GRAVITY- The force that pulls objects towards each other SATELLITE- An object that moves or revolves around a planet SUNSPOT- A part of the sun that is very magnetic and is not as hot as other parts Asteroids are objects in the solar system that are smaller than planets but bigger than meteoroids. A comet is a relatively small objects in the solar system, made of dirty ice, that orbits or moves around the sun ***Usually in the outer solar system Meteoroids are small, particle-sized objects in the solar system that are usually seen as “shooting stars” or “falling stars”